This is the coding implementations of the DSA.js book and the repo for the NPM package.
In this repository, you can find the implementation of algorithms and data structures in JavaScript. This material can be used as a reference manual for developers, or you can refresh specific topics before an interview. Also, you can find ideas to solve problems more efficiently.
You can clone the repo or install the code from NPM:
npm install dsa.jsand then you can import it into your programs or CLI
const { LinkedList, Queue, Stack } = require('dsa.js');For a list of all available data structures and algorithms, see index.js.
Algorithms are an essential toolbox for every programmer.
You will need to mind algorithms runtime when you have to sort data, search for a value in a big dataset, transform data, scale your code to many users, to name a few. Algorithms are just the step you follow to solve a problem, while data structures are where you store the data for later manipulation. Both combined create programs.
Algorithms + Data Structures = Programs.
Most programming languages and libraries indeed provide implementations for basic data structures and algorithms. However, to make use of data structures properly, you have to know the tradeoffs to choose the best tool for the job.
This material is going to teach you to:
- 🛠 Apply strategies to tackle algorithm questions. Never to get stuck again. Ace those interviews!
- ✂️ Construct efficient algorithms. Learn how to break down problems into manageable pieces.
- 🧠 Improve your problem-solving skills and become a well-rounded developer by understanding fundamental computer science concepts.
- 🤓 Cover essential topics, such as big O time, data structures, and must-know algorithms. Implement 10+ data structures from scratch.
All the code and explanations are available on this repo. You can dig through the links and code examples from the (src folder). However, the inline code examples are not expanded (because of Github's asciidoc limitations), but you can follow the path and see the implementation.
Note: If you prefer to consume the information more linearly, then the book format would be more appropriate for you.
The topics are divided into four main categories, as you can see below:
Computer Science nuggets without all the mumbo-jumbo. (Click to expand)
Learn how to compare algorithms using Big O notation. (Click to expand)
Let's say you want to find the duplicates on an array. Using Big O notation, we can compare different solutions that solve the same problem but has a massive difference in how long it takes to do it.
8 examples to explain with code how to calculate time complexity. (Click to expand)
8 examples to explain with code how to calculate time complexity
Understand the ins and outs of the most common data structures. (Click to expand)
Arrays: Built-in in most languages so not implemented here. Array Time complexity
Linked List: each data node has a link to the next (and previous). Code | Linked List Time Complexity
Queue: data flows in a "first-in, first-out" (FIFO) manner. Code | Queue Time Complexity
Stack: data flows in a "last-in, first-out" (LIFO) manner. Code | Stack Time Complexity
When to use an Array or Linked List. Know the tradeoffs. (Click to expand)
Use Arrays when…
- You need to access data in random order fast (using an index).
- Your data is multi-dimensional (e.g., matrix, tensor).
Use Linked Lists when:
- You will access your data sequentially.
- You want to save memory and only allocate memory as you need it.
- You want constant time to remove/add from extremes of the list.
- when size requirement is unknown - dynamic size advantage
Build a List, Stack, and a Queue. (Click to expand)
Build any of these data structures from scratch:
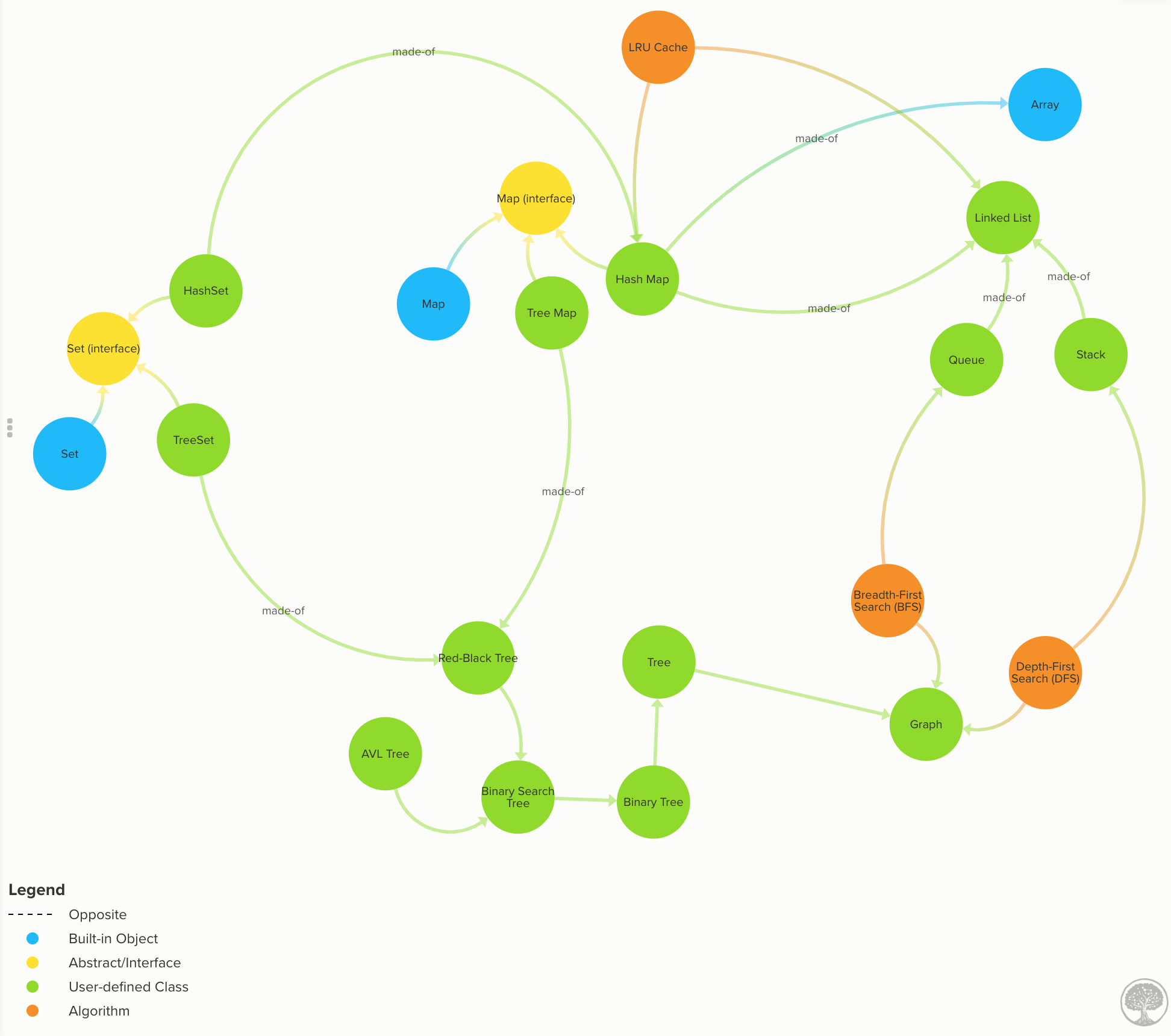
Understand one of the most versatile data structure of all: Hash Maps. (Click to expand)
Learn how to implement different types of Maps such as:
Also, learn the difference between the different Maps implementations:
HashMapis more time-efficient. ATreeMapis more space-efficient.TreeMapsearch complexity is O(log n), while an optimizedHashMapis O(1) on average.HashMap’s keys are in insertion order (or random depending on the implementation).TreeMap’s keys are always sorted.TreeMapoffers some statistical data for free such as: get minimum, get maximum, median, find ranges of keys.HashMapdoesn’t.TreeMaphas a guarantee always an O(log n), whileHashMaps has an amortized time of O(1) but in the rare case of a rehash, it would take an O(n).
Know the properties of Graphs and Trees. (Click to expand)
Know all the graphs properties with many images and illustrations.
Graphs: data nodes that can have a connection or edge to zero or more adjacent nodes. Unlike trees, nodes can have multiple parents, loops. Code | Graph Time Complexity
Learn all the different kinds of trees and their properties.
Trees: data nodes has zero or more adjacent nodes a.k.a. children. Each node can only have one parent node otherwise is a graph, not a tree. Code | Docs
Binary Trees: same as a tree but only can have two children at most. Code | Docs
Binary Search Trees (BST): same as a binary tree, but the nodes value keep this order
left < parent < right. Code | BST Time complexityAVL Trees: Self-balanced BST to maximize lookup time. Code | AVL Tree docs | Self-balancing & tree rotations docs
Red-Black Trees: Self-balanced BST looser than AVL to maximize insertion speed. Code
Implement a binary search tree for fast lookups.
From unbalanced BST to balanced BST
1 2 \ / \ 2 => 1 3 \ 3
Never get stuck solving a problem with 7 simple steps. (Click to expand)
- Understand the problem
- Build a simple example (no edge cases yet)
- Brainstorm solutions (greedy algorithm, Divide and Conquer, Backtracking, brute force)
- Test your answer on the simple example (mentally)
- Optimize the solution
- Write code. Yes, now you can code.
- Test your written code
- Analyse the complexity, both space and time, and make sure to optimize further.
Full details here
Master the most popular sorting algorithms (merge sort, quicksort, etc.) (Click to expand)
We are going to explore three essential sorting algorithms O(n^2), which have low overhead:
and then discuss efficient sorting algorithms O(n log n) such as:
Learn different approaches to solve problems such as divide and conquer, dynamic programming, greedy algorithms, and backtracking. (Click to expand)
We are going to discuss the following techniques for solving algorithms problems:
- Greedy Algorithms: makes greedy choices using heuristics to find the best solution without looking back.
- Dynamic Programming: a technique for speeding up recursive algorithms when there are many overlapping subproblems. It uses memoization to avoid duplicating work.
- Divide and Conquer: divide problems into smaller pieces, conquer each subproblem, and then join the results.
- Backtracking: search all (or some) possible paths. However, it stops, and go back as soon as notice the current solution is not working.
- Brute Force: generate all possible solutions and tries all of them. (Use it as a last resort or as the starting point).
How would I apply these to my day-to-day work? (Click to expand)
As a programmer, we have to solve problems every day. If you want to solve problems well, it's good to know about a broad range of solutions. Often, it's more efficient to learn existing resources than stumble upon the answer yourself. The more tools and practice you have, the better. This book helps you understand the tradeoffs among data structures and reason about algorithms performance.
Why you created this repo/book?
There are not many books about Algorithms in JavaScript. This material fills the gap. Also, it's good practice :)
Is there anyone I can contact if I have questions about something in particular?
Yes, open an issue or ask questions on the [slack channel](https://dsajs-slackin.herokuapp.com).
This project is also available in a book. You will get a nicely formatted PDF with 180+ pages + ePub and Mobi version.
Reach out to me at one of the following places!
- Twitter at
@iAmAdrianMejia - Chat on
dsajs.slack.com