dl-time-series
Deep-learning applied to time series classification of remote sensing data, according to this workflow:
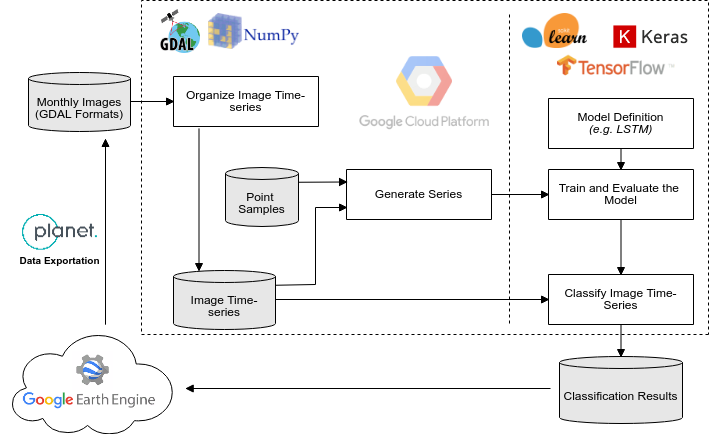
Workflow Execution (Deforestation toy data)
Download the Deforestation toy data in https://storage.googleapis.com/nextgenmap-dataset/dl-time-series/deforestation_toy.zip and follow the instructions below:
- Stack all the images inside deforestation_toy/images to produce a image time-series, organized per band.
$ ./generate_img_series.py -i deforestation_toy/images -b 1 2 3 4 -o deforestation_toy/image_series- Generate the time-series data (e.i. numpy arrays) considering the samples:
$ ./generate_series.py -i deforestation_toy/image_series/ -s deforestation_toy/samples/toy_samples.shp -o deforestation_toy/data_series/ -n 2- Train a LSTM model, for 100 epochs, using default hyperparameter (see usages):
$ ./train_model.py -i deforestation_toy/data_series/ -e 100 -o deforestation_toy/model- Follow the trainning process using tensorboard:
$ tensorboard --logdir=deforestation_toy/model/log- Classify the image time-series using the last epoch model:
$ ../classify_img_series.py -i deforestation_toy/image_series/ -m deforestation_toy/model/last_model.H5 -o deforestation_toy/classification/result.img- Check the classification result, deforestation_toy/classification/result.img, in QGIS:
Usages
generate_img_series.py
usage: generate_img_series.py [-h] -i INPUT_DIR [-b BANDS [BANDS ...]] -o OUTPUT_DIR
STEP 01/04 - Stack all images of input directory, producing one Virtual
Dataset-VRT per band in output directory
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i INPUT_DIR, --input-dir INPUT_DIR
<Required> Input image directory.
-b BANDS [BANDS ...], --bands BANDS [BANDS ...]
The bands that should be considered. [DEFAULT=All]
-o OUTPUT_DIR, --output-dir OUTPUT_DIR
<Required> Output VRTs directory
generate_series.py
usage: generate_series.py [-h] -i INPUT_DIR -s SAMPLES -n NUM_CLASSES
[-c COLUMN_LABEL] -o SERIES_DIR
STEP 02/04 - Generate the time-series considering the vector file informed as
samples.
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i INPUT_DIR, --input-dir INPUT_DIR
<Required> Input directory that contains the VRTs
images.
-s SAMPLES, --samples SAMPLES
<Required> Vector file with the point geometries and
class labels.
-n NUM_CLASSES, --num-classes NUM_CLASSES
<Required> Number of possible class labels.
-c COLUMN_LABEL, --column-label COLUMN_LABEL
Name of column that contains the class label values.
[DEFAULT=class]
-o SERIES_DIR, --series-dir SERIES_DIR
<Required> The name of output directory
train_model.py
usage: train_model.py [-h] -i SERIES_DIR [-s SEED] [-n] [-v VALIDATION_SPLIT]
[-t TEST_SPLIT] [-e EPOCHS] [-b BATCH_SIZE]
[-l LEARNING_RATE] -o OUTPUT_DIR
STEP 03/04 - LSTM training approach using several time-series
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i SERIES_DIR, --series-dir SERIES_DIR
<Required> Input directory that contains the VRT
images.
-s SEED, --seed SEED Seed that will be used to split the time-series in
train, validation, test groups. [DEFAULT=2]
-n, --only-evaluate Execute only the evaluation, using the test group.
[DEFAULT=False]
-v VALIDATION_SPLIT, --validation-split VALIDATION_SPLIT
Percentage size of the validation group.
[DEFAULT=0.15]
-t TEST_SPLIT, --test-split TEST_SPLIT
Percentage size of the test group. [DEFAULT=0.15]
-e EPOCHS, --epochs EPOCHS
Number of epochs of the training process.
[DEFAULT=100]
-b BATCH_SIZE, --batch-size BATCH_SIZE
Batch size of training process.
-l LEARNING_RATE, --learning-rate LEARNING_RATE
Learning rate of training process. [DEFAULT=0.00005]
-o OUTPUT_DIR, --output-dir OUTPUT_DIR
<Required> The output directory that will have the
trained model and the tensorboard logs
classify_img_series.py
usage: classify_img_series.py [-h] -i INPUT_DIR -m MODEL -o OUTPUT
04/04 - Classify image series using a trained model.
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-i INPUT_DIR, --input-dir INPUT_DIR
<Required> Input directory that contains the VRTs
images.
-m MODEL, --model MODEL
<Required> The model filepath that should be used in
the classification approach.
-o OUTPUT, --output OUTPUT
<Required> The output filepath. The file will be
generated in ERDAS_IMG format.
