leetcode's People
leetcode's Issues
53. Maximum Subarray
Given an integer array nums, find the contiguous subarray (containing at least one number) which has the largest sum and return its sum.
A subarray is a contiguous part of an array.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4]
Output: 6
Explanation: [4,-1,2,1] has the largest sum = 6.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1]
Output: 1
Example 3:
Input: nums = [5,4,-1,7,8]
Output: 23
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 105
-104 <= nums[i] <= 104
Follow up: If you have figured out the O(n) solution, try coding another solution using the divide and conquer approach, which is more subtle.
1704. Determine if String Halves Are Alike
You are given a string s of even length. Split this string into two halves of equal lengths, and let a be the first half and b be the second half.
Two strings are alike if they have the same number of vowels ('a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u', 'A', 'E', 'I', 'O', 'U'). Notice that s contains uppercase and lowercase letters.
Return true if a and b are alike. Otherwise, return false.
Example 1:
Input: s = "book"
Output: true
Explanation: a = "bo" and b = "ok". a has 1 vowel and b has 1 vowel. Therefore, they are alike.
Example 2:
Input: s = "textbook"
Output: false
Explanation: a = "text" and b = "book". a has 1 vowel whereas b has 2. Therefore, they are not alike.
Notice that the vowel o is counted twice.
Example 3:
Input: s = "MerryChristmas"
Output: false
Example 4:
Input: s = "AbCdEfGh"
Output: true
Constraints:
2 <= s.length <= 1000
s.length is even.
s consists of uppercase and lowercase letters.
Problem 1673
Given an integer array nums and a positive integer k, return the most competitive subsequence of nums of size k.
An array's subsequence is a resulting sequence obtained by erasing some (possibly zero) elements from the array.
We define that a subsequence a is more competitive than a subsequence b (of the same length) if in the first position where a and b differ, subsequence a has a number less than the corresponding number in b. For example, [1,3,4] is more competitive than [1,3,5] because the first position they differ is at the final number, and 4 is less than 5.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [3,5,2,6], k = 2
Output: [2,6]
Explanation: Among the set of every possible subsequence: {[3,5], [3,2], [3,6], [5,2], [5,6], [2,6]}, [2,6] is the most competitive.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [2,4,3,3,5,4,9,6], k = 4
Output: [2,3,3,4]
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 1050 <= nums[i] <= 1091 <= k <= nums.length
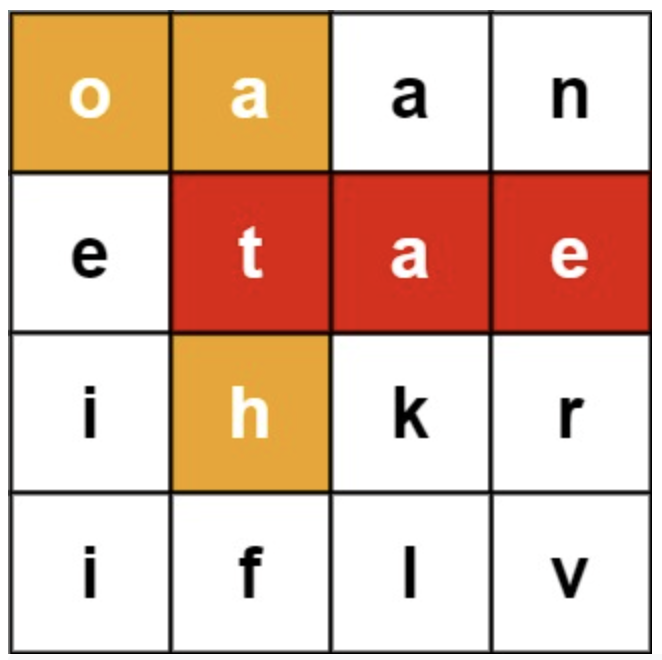
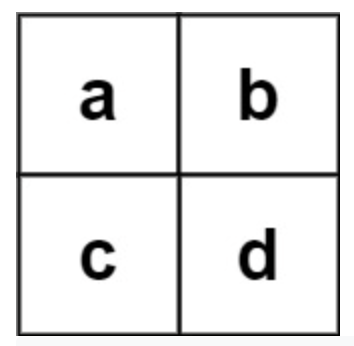
212. Word Search II
Given an m x n board of characters and a list of strings words, return all words on the board.
Each word must be constructed from letters of sequentially adjacent cells, where adjacent cells are horizontally or vertically neighboring. The same letter cell may not be used more than once in a word.
Input: board = [["o","a","a","n"],["e","t","a","e"],["i","h","k","r"],["i","f","l","v"]], words = ["oath","pea","eat","rain"]
Output: ["eat","oath"]
Example 2:
Input: board = [["a","b"],["c","d"]], words = ["abcb"]
Output: []
Constraints:
m == board.length
n == board[i].length
1 <= m, n <= 12
board[i][j] is a lowercase English letter.
1 <= words.length <= 3 * 104
1 <= words[i].length <= 10
words[i] consists of lowercase English letters.
All the strings of words are unique.
1768. Merge Strings Alternately
You are given two strings word1 and word2. Merge the strings by adding letters in alternating order, starting with word1. If a string is longer than the other, append the additional letters onto the end of the merged string.
Return the merged string.
Example 1:
Input: word1 = "abc", word2 = "pqr"
Output: "apbqcr"
Explanation: The merged string will be merged as so:
word1: a b c
word2: p q r
merged: a p b q c r
Example 2:
Input: word1 = "ab", word2 = "pqrs"
Output: "apbqrs"
Explanation: Notice that as word2 is longer, "rs" is appended to the end.
word1: a b
word2: p q r s
merged: a p b q r s
Example 3:
Input: word1 = "abcd", word2 = "pq"
Output: "apbqcd"
Explanation: Notice that as word1 is longer, "cd" is appended to the end.
word1: a b c d
word2: p q
merged: a p b q c d
Constraints:
1 <= word1.length, word2.length <= 100
word1 and word2 consist of lowercase English letters.
977. Squares of a Sorted Array
Given an integer array nums sorted in non-decreasing order, return an array of the squares of each number sorted in non-decreasing order.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [-4,-1,0,3,10]
Output: [0,1,9,16,100]
Explanation: After squaring, the array becomes [16,1,0,9,100].
After sorting, it becomes [0,1,9,16,100].
Example 2:
Input: nums = [-7,-3,2,3,11]
Output: [4,9,9,49,121]
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 104
-104 <= nums[i] <= 104
nums is sorted in non-decreasing order.
Follow up: Squaring each element and sorting the new array is very trivial, could you find an O(n) solution using a different approach?
1920. Build Array from Permutation
Given a zero-based permutation nums (0-indexed), build an array ans of the same length where ans[i] = nums[nums[i]] for each 0 <= i < nums.length and return it.
A zero-based permutation nums is an array of distinct integers from 0 to nums.length - 1 (inclusive).
Example 1:
Input: nums = [0,2,1,5,3,4]
Output: [0,1,2,4,5,3]
Explanation: The array ans is built as follows:
ans = [nums[nums[0]], nums[nums[1]], nums[nums[2]], nums[nums[3]], nums[nums[4]], nums[nums[5]]]
= [nums[0], nums[2], nums[1], nums[5], nums[3], nums[4]]
= [0,1,2,4,5,3]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [5,0,1,2,3,4]
Output: [4,5,0,1,2,3]
Explanation: The array ans is built as follows:
ans = [nums[nums[0]], nums[nums[1]], nums[nums[2]], nums[nums[3]], nums[nums[4]], nums[nums[5]]]
= [nums[5], nums[0], nums[1], nums[2], nums[3], nums[4]]
= [4,5,0,1,2,3]
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 1000
0 <= nums[i] < nums.length
The elements in nums are distinct.
Follow-up: Can you solve it without using an extra space (i.e., O(1) memory)?
199. Binary Tree Right Side View
Given a binary tree, imagine yourself standing on the right side of it, return the values of the nodes you can see ordered from top to bottom.
Example:
Input: [1,2,3,null,5,null,4]
Output: [1, 3, 4]
Explanation:
1 <---
/ \
2 3 <---
\ \
5 4 <---
1290. Convert Binary Number in a Linked List to Integer
Given head which is a reference node to a singly-linked list. The value of each node in the linked list is either 0 or 1. The linked list holds the binary representation of a number.
Return the decimal value of the number in the linked list.
Example 1:
Input: head = [1,0,1]
Output: 5
Explanation: (101) in base 2 = (5) in base 10
Example 2:
Input: head = [0]
Output: 0
Example 3:
Input: head = [1]
Output: 1
Example 4:
Input: head = [1,0,0,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0,0,0,0]
Output: 18880
Example 5:
Input: head = [0,0]
Output: 0
Constraints:
The Linked List is not empty.
Number of nodes will not exceed 30.
Each node's value is either 0 or 1.
242. Valid Anagram
Given two strings s and t , write a function to determine if t is an anagram of s.
Example 1:
Input: s = "anagram", t = "nagaram"
Output: true
Example 2:
Input: s = "rat", t = "car"
Output: false
Note:
You may assume the string contains only lowercase alphabets.
Follow up:
What if the inputs contain unicode characters? How would you adapt your solution to such case?
1332. Remove Palindromic Subsequences
Given a string s consisting only of letters 'a' and 'b'. In a single step you can remove one palindromic subsequence from s.
Return the minimum number of steps to make the given string empty.
A string is a subsequence of a given string, if it is generated by deleting some characters of a given string without changing its order.
A string is called palindrome if is one that reads the same backward as well as forward.
Example 1:
Input: s = "ababa"
Output: 1
Explanation: String is already palindrome
Example 2:
Input: s = "abb"
Output: 2
Explanation: "abb" -> "bb" -> "".
Remove palindromic subsequence "a" then "bb".
Example 3:
Input: s = "baabb"
Output: 2
Explanation: "baabb" -> "b" -> "".
Remove palindromic subsequence "baab" then "b".
Example 4:
Input: s = ""
Output: 0
Constraints:
0 <= s.length <= 1000
s only consists of letters 'a' and 'b'
709. To Lower Case
Implement function ToLowerCase() that has a string parameter str, and returns the same string in lowercase.
Example 1:
Input: "Hello"
Output: "hello"
Example 2:
Input: "here"
Output: "here"
Example 3:
Input: "LOVELY"
Output: "lovely"
1614. Maximum Nesting Depth of the Parentheses
A string is a valid parentheses string (denoted VPS) if it meets one of the following:
It is an empty string "", or a single character not equal to "(" or ")",
It can be written as AB (A concatenated with B), where A and B are VPS's, or
It can be written as (A), where A is a VPS.
We can similarly define the nesting depth depth(S) of any VPS S as follows:
depth("") = 0
depth(C) = 0, where C is a string with a single character not equal to "(" or ")".
depth(A + B) = max(depth(A), depth(B)), where A and B are VPS's.
depth("(" + A + ")") = 1 + depth(A), where A is a VPS.
For example, "", "()()", and "()(()())" are VPS's (with nesting depths 0, 1, and 2), and ")(" and "(()" are not VPS's.
Given a VPS represented as string s, return the nesting depth of s.
Example 1:
Input: s = "(1+(2*3)+((8)/4))+1"
Output: 3
Explanation: Digit 8 is inside of 3 nested parentheses in the string.
Example 2:
Input: s = "(1)+((2))+(((3)))"
Output: 3
Example 3:
Input: s = "1+(2*3)/(2-1)"
Output: 1
Example 4:
Input: s = "1"
Output: 0
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 100
s consists of digits 0-9 and characters '+', '-', '*', '/', '(', and ')'.
It is guaranteed that parentheses expression s is a VPS.
1732. Find the Highest Altitude
There is a biker going on a road trip. The road trip consists of n + 1 points at different altitudes. The biker starts his trip on point 0 with altitude equal 0.
You are given an integer array gain of length n where gain[i] is the net gain in altitude between points i and i + 1 for all (0 <= i < n). Return the highest altitude of a point.
Example 1:
Input: gain = [-5,1,5,0,-7]
Output: 1
Explanation: The altitudes are [0,-5,-4,1,1,-6]. The highest is 1.
Example 2:
Input: gain = [-4,-3,-2,-1,4,3,2]
Output: 0
Explanation: The altitudes are [0,-4,-7,-9,-10,-6,-3,-1]. The highest is 0.
Constraints:
n == gain.length
1 <= n <= 100
-100 <= gain[i] <= 100
785. Is Graph Bipartite?
Given an undirected graph, return true if and only if it is bipartite.
Recall that a graph is bipartite if we can split its set of nodes into two independent subsets A and B, such that every edge in the graph has one node in A and another node in B.
The graph is given in the following form: graph[i] is a list of indexes j for which the edge between nodes i and j exists. Each node is an integer between 0 and graph.length - 1. There are no self edges or parallel edges: graph[i] does not contain i, and it doesn't contain any element twice.
Example 1:
Input: graph = [[1,3],[0,2],[1,3],[0,2]]
Output: true
Explanation: We can divide the vertices into two groups: {0, 2} and {1, 3}.
Example 2:
Input: graph = [[1,2,3],[0,2],[0,1,3],[0,2]]
Output: false
Explanation: We cannot find a way to divide the set of nodes into two independent subsets.
Constraints:
1 <= graph.length <= 100
0 <= graph[i].length < 100
0 <= graph[i][j] <= graph.length - 1
graph[i][j] != i
All the values of graph[i] are unique.
The graph is guaranteed to be undirected.
322. Coin Change
You are given coins of different denominations and a total amount of money amount. Write a function to compute the fewest number of coins that you need to make up that amount. If that amount of money cannot be made up by any combination of the coins, return -1.
You may assume that you have an infinite number of each kind of coin.
Example 1:
Input: coins = [1,2,5], amount = 11
Output: 3
Explanation: 11 = 5 + 5 + 1
Example 2:
Input: coins = [2], amount = 3
Output: -1
Example 3:
Input: coins = [1], amount = 0
Output: 0
Example 4:
Input: coins = [1], amount = 1
Output: 1
Example 5:
Input: coins = [1], amount = 2
Output: 2
Constraints:
1 <= coins.length <= 12
1 <= coins[i] <= 231 - 1
0 <= amount <= 104
856. Score of Parentheses
Given a balanced parentheses string S, compute the score of the string based on the following rule:
() has score 1
AB has score A + B, where A and B are balanced parentheses strings.
(A) has score 2 * A, where A is a balanced parentheses string.
Example 1:
Input: "()"
Output: 1
Example 2:
Input: "(())"
Output: 2
Example 3:
Input: "()()"
Output: 2
Example 4:
Input: "(()(()))"
Output: 6
Note:
S is a balanced parentheses string, containing only ( and ).
2 <= S.length <= 50
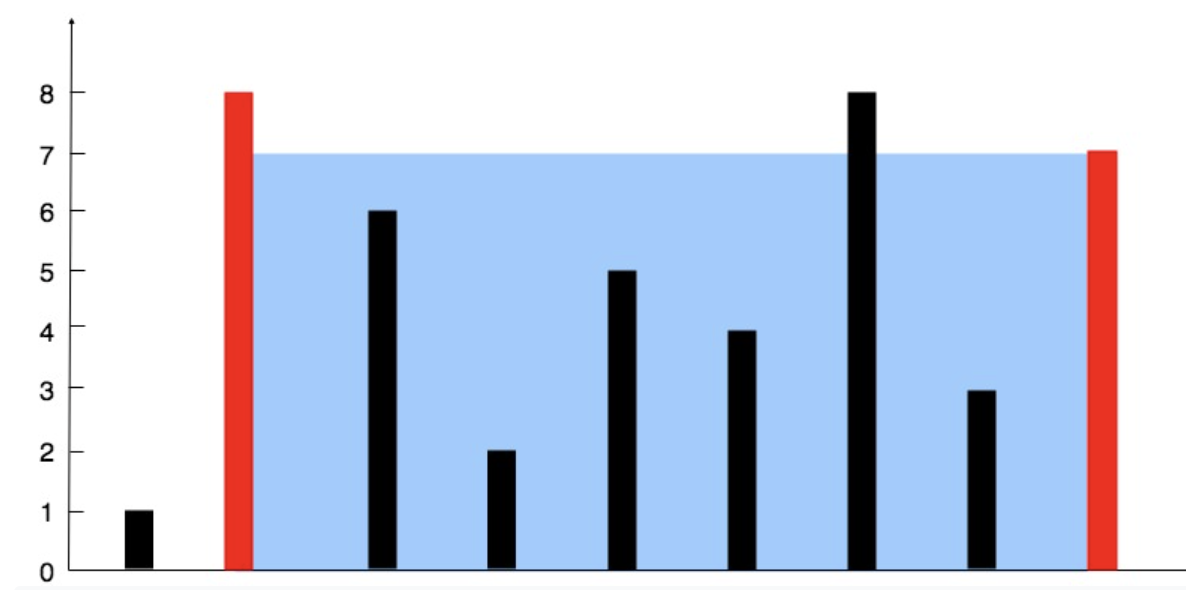
11. Container With Most Water
Given n non-negative integers a1, a2, ..., an , where each represents a point at coordinate (i, ai). n vertical lines are drawn such that the two endpoints of the line i is at (i, ai) and (i, 0). Find two lines, which, together with the x-axis forms a container, such that the container contains the most water.
Notice that you may not slant the container.
Input: height = [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]
Output: 49
Explanation: The above vertical lines are represented by array [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]. In this case, the max area of water (blue section) the container can contain is 49.
Example 2:
Input: height = [1,1]
Output: 1
Example 3:
Input: height = [4,3,2,1,4]
Output: 16
Example 4:
Input: height = [1,2,1]
Output: 2
Constraints:
n == height.length
2 <= n <= 3 * 104
0 <= height[i] <= 3 * 104
581. Shortest Unsorted Continuous Subarray
Given an integer array nums, you need to find one continuous subarray that if you only sort this subarray in ascending order, then the whole array will be sorted in ascending order.
Return the shortest such subarray and output its length.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [2,6,4,8,10,9,15]
Output: 5
Explanation: You need to sort [6, 4, 8, 10, 9] in ascending order to make the whole array sorted in ascending order.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,4]
Output: 0
Example 3:
Input: nums = [1]
Output: 0
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 104
-105 <= nums[i] <= 105
637. Average of Levels in Binary Tree
Given a non-empty binary tree, return the average value of the nodes on each level in the form of an array.
Example 1:
Input:
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
Output: [3, 14.5, 11]
Explanation:
The average value of nodes on level 0 is 3, on level 1 is 14.5, and on level 2 is 11. Hence return [3, 14.5, 11].
Note:
The range of node's value is in the range of 32-bit signed integer.
5658. Maximum Absolute Sum of Any Subarray
You are given an integer array nums. The absolute sum of a subarray [numsl, numsl+1, ..., numsr-1, numsr] is abs(numsl + numsl+1 + ... + numsr-1 + numsr).
Return the maximum absolute sum of any (possibly empty) subarray of nums.
Note that abs(x) is defined as follows:
If x is a negative integer, then abs(x) = -x.
If x is a non-negative integer, then abs(x) = x.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,-3,2,3,-4]
Output: 5
Explanation: The subarray [2,3] has absolute sum = abs(2+3) = abs(5) = 5.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [2,-5,1,-4,3,-2]
Output: 8
Explanation: The subarray [-5,1,-4] has absolute sum = abs(-5+1-4) = abs(-8) = 8.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 105
-104 <= nums[i] <= 104
1089. Duplicate Zeros
Given a fixed length array arr of integers, duplicate each occurrence of zero, shifting the remaining elements to the right.
Note that elements beyond the length of the original array are not written.
Do the above modifications to the input array in place, do not return anything from your function.
Example 1:
Input: [1,0,2,3,0,4,5,0]
Output: null
Explanation: After calling your function, the input array is modified to: [1,0,0,2,3,0,0,4]
Example 2:
Input: [1,2,3]
Output: null
Explanation: After calling your function, the input array is modified to: [1,2,3]
Note:
1 <= arr.length <= 10000
0 <= arr[i] <= 9
821. Shortest Distance to a Character
Given a string s and a character c that occurs in s, return an array of integers answer where answer.length == s.length and answer[i] is the shortest distance from s[i] to the character c in s.
Example 1:
Input: s = "loveleetcode", c = "e"
Output: [3,2,1,0,1,0,0,1,2,2,1,0]
Example 2:
Input: s = "aaab", c = "b"
Output: [3,2,1,0]
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 104
s[i] and c are lowercase English letters.
c occurs at least once in s.
485. Max Consecutive Ones
Given a binary array nums, return the maximum number of consecutive 1's in the array.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,1,0,1,1,1]
Output: 3
Explanation: The first two digits or the last three digits are consecutive 1s. The maximum number of consecutive 1s is 3.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,0,1,1,0,1]
Output: 2
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 105
nums[i] is either 0 or 1.
5657. Sum of Unique Elements
You are given an integer array nums. The unique elements of an array are the elements that appear exactly once in the array.
Return the sum of all the unique elements of nums.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,2]
Output: 4
Explanation: The unique elements are [1,3], and the sum is 4.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,1,1,1,1]
Output: 0
Explanation: There are no unique elements, and the sum is 0.
Example 3:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: 15
Explanation: The unique elements are [1,2,3,4,5], and the sum is 15.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 100
1 <= nums[i] <= 100
594. Longest Harmonious Subsequence
We define a harmonious array as an array where the difference between its maximum value and its minimum value is exactly 1.
Given an integer array nums, return the length of its longest harmonious subsequence among all its possible subsequences.
A subsequence of array is a sequence that can be derived from the array by deleting some or no elements without changing the order of the remaining elements.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,3,2,2,5,2,3,7]
Output: 5
Explanation: The longest harmonious subsequence is [3,2,2,2,3].
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,4]
Output: 2
Example 3:
Input: nums = [1,1,1,1]
Output: 0
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 2 * 104
-109 <= nums[i] <= 109
1313. Decompress Run-Length Encoded List
We are given a list nums of integers representing a list compressed with run-length encoding.
Consider each adjacent pair of elements [freq, val] = [nums[2i], nums[2i+1]] (with i >= 0). For each such pair, there are freq elements with value val concatenated in a sublist. Concatenate all the sublists from left to right to generate the decompressed list.
Return the decompressed list.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,4]
Output: [2,4,4,4]
Explanation: The first pair [1,2] means we have freq = 1 and val = 2 so we generate the array [2].
The second pair [3,4] means we have freq = 3 and val = 4 so we generate [4,4,4].
At the end the concatenation [2] + [4,4,4] is [2,4,4,4].
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,1,2,3]
Output: [1,3,3]
Constraints:
2 <= nums.length <= 100
nums.length % 2 == 0
1 <= nums[i] <= 100
1249. Minimum Remove to Make Valid Parentheses
Given a string s of '(' , ')' and lowercase English characters.
Your task is to remove the minimum number of parentheses ( '(' or ')', in any positions ) so that the resulting parentheses string is valid and return any valid string.
Formally, a parentheses string is valid if and only if:
It is the empty string, contains only lowercase characters, or
It can be written as AB (A concatenated with B), where A and B are valid strings, or
It can be written as (A), where A is a valid string.
Example 1:
Input: s = "lee(t(c)o)de)"
Output: "lee(t(c)o)de"
Explanation: "lee(t(co)de)" , "lee(t(c)ode)" would also be accepted.
Example 2:
Input: s = "a)b(c)d"
Output: "ab(c)d"
Example 3:
Input: s = "))(("
Output: ""
Explanation: An empty string is also valid.
Example 4:
Input: s = "(a(b(c)d)"
Output: "a(b(c)d)"
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 10^5
s[i] is one of '(' , ')' and lowercase English letters.
1309. Decrypt String from Alphabet to Integer Mapping
Given a string s formed by digits ('0' - '9') and '#' . We want to map s to English lowercase characters as follows:
Characters ('a' to 'i') are represented by ('1' to '9') respectively.
Characters ('j' to 'z') are represented by ('10#' to '26#') respectively.
Return the string formed after mapping.
It's guaranteed that a unique mapping will always exist.
Example 1:
Input: s = "10#11#12"
Output: "jkab"
Explanation: "j" -> "10#" , "k" -> "11#" , "a" -> "1" , "b" -> "2".
Example 2:
Input: s = "1326#"
Output: "acz"
Example 3:
Input: s = "25#"
Output: "y"
Example 4:
Input: s = "12345678910#11#12#13#14#15#16#17#18#19#20#21#22#23#24#25#26#"
Output: "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 1000
s[i] only contains digits letters ('0'-'9') and '#' letter.
s will be valid string such that mapping is always possible.
524. Longest Word in Dictionary through Deleting
Given a string and a string dictionary, find the longest string in the dictionary that can be formed by deleting some characters of the given string. If there are more than one possible results, return the longest word with the smallest lexicographical order. If there is no possible result, return the empty string.
Example 1:
Input: s = "abpcplea", d = ["ale","apple","monkey","plea"]
Output: "apple"
Example 2:
Input: s = "abpcplea", d = ["a","b","c"]
Output: "a"
Note:
All the strings in the input will only contain lower-case letters.
The size of the dictionary won't exceed 1,000.
The length of all the strings in the input won't exceed 1,000.
191. Number of 1 Bits
Write a function that takes an unsigned integer and returns the number of '1' bits it has (also known as the Hamming weight).
Note:
Note that in some languages such as Java, there is no unsigned integer type. In this case, the input will be given as a signed integer type. It should not affect your implementation, as the integer's internal binary representation is the same, whether it is signed or unsigned.
In Java, the compiler represents the signed integers using 2's complement notation. Therefore, in Example 3 above, the input represents the signed integer. -3.
Follow up: If this function is called many times, how would you optimize it?
Example 1:
Input: n = 00000000000000000000000000001011
Output: 3
Explanation: The input binary string 00000000000000000000000000001011 has a total of three '1' bits.
Example 2:
Input: n = 00000000000000000000000010000000
Output: 1
Explanation: The input binary string 00000000000000000000000010000000 has a total of one '1' bit.
Example 3:
Input: n = 11111111111111111111111111111101
Output: 31
Explanation: The input binary string 11111111111111111111111111111101 has a total of thirty-one '1' bits.
Constraints:
The input must be a binary string of length 32
841. Keys and Rooms
There are N rooms and you start in room 0. Each room has a distinct number in 0, 1, 2, ..., N-1, and each room may have some keys to access the next room.
Formally, each room i has a list of keys rooms[i], and each key rooms[i][j] is an integer in [0, 1, ..., N-1] where N = rooms.length. A key rooms[i][j] = v opens the room with number v.
Initially, all the rooms start locked (except for room 0).
You can walk back and forth between rooms freely.
Return true if and only if you can enter every room.
Example 1:
Input: [[1],[2],[3],[]]
Output: true
Explanation:
We start in room 0, and pick up key 1.
We then go to room 1, and pick up key 2.
We then go to room 2, and pick up key 3.
We then go to room 3. Since we were able to go to every room, we return true.
Example 2:
Input: [[1,3],[3,0,1],[2],[0]]
Output: false
Explanation: We can't enter the room with number 2.
Note:
1 <= rooms.length <= 1000
0 <= rooms[i].length <= 1000
The number of keys in all rooms combined is at most 3000.
1342. Number of Steps to Reduce a Number to Zero
Given a non-negative integer num, return the number of steps to reduce it to zero. If the current number is even, you have to divide it by 2, otherwise, you have to subtract 1 from it.
Example 1:
Input: num = 14
Output: 6
Explanation:
- Step 1) 14 is even; divide by 2 and obtain 7.
- Step 2) 7 is odd; subtract 1 and obtain 6.
- Step 3) 6 is even; divide by 2 and obtain 3.
- Step 4) 3 is odd; subtract 1 and obtain 2.
- Step 5) 2 is even; divide by 2 and obtain 1.
- Step 6) 1 is odd; subtract 1 and obtain 0.
Example 2:
Input: num = 8
Output: 4
Explanation:
- Step 1) 8 is even; divide by 2 and obtain 4.
- Step 2) 4 is even; divide by 2 and obtain 2.
- Step 3) 2 is even; divide by 2 and obtain 1.
- Step 4) 1 is odd; subtract 1 and obtain 0.
Example 3:
Input: num = 123
Output: 12
Constraints:
0 <= num <= 10^6
677. Map Sum Pairs
Implement the MapSum class:
MapSum() Initializes the MapSum object.
void insert(String key, int val) Inserts the key-val pair into the map. If the key already existed, the original key-value pair will be overridden to the new one.
int sum(string prefix) Returns the sum of all the pairs' value whose key starts with the prefix.
Example 1:
Input
["MapSum", "insert", "sum", "insert", "sum"]
[[], ["apple", 3], ["ap"], ["app", 2], ["ap"]]
Output
[null, null, 3, null, 5]
Explanation
MapSum mapSum = new MapSum();
mapSum.insert("apple", 3);
mapSum.sum("ap"); // return 3 (apple = 3)
mapSum.insert("app", 2);
mapSum.sum("ap"); // return 5 (apple + app = 3 + 2 = 5)
Constraints:
1 <= key.length, prefix.length <= 50
key and prefix consist of only lowercase English letters.
1 <= val <= 1000
At most 50 calls will be made to insert and sum.
5659. Minimum Length of String After Deleting Similar Ends
Given a string s consisting only of characters 'a', 'b', and 'c'. You are asked to apply the following algorithm on the string any number of times:
- Pick a non-empty prefix from the string s where all the characters in the prefix are equal.
- Pick a non-empty suffix from the string s where all the characters in this suffix are equal.
- The prefix and the suffix should not intersect at any index.
- The characters from the prefix and suffix must be the same.
- Delete both the prefix and the suffix.
Return the minimum length of s after performing the above operation any number of times (possibly zero times).
Example 1:
Input: s = "ca"
Output: 2
Explanation: You can't remove any characters, so the string stays as is.
Example 2:
Input: s = "cabaabac"
Output: 0
Explanation: An optimal sequence of operations is:
- Take prefix = "c" and suffix = "c" and remove them, s = "abaaba".
- Take prefix = "a" and suffix = "a" and remove them, s = "baab".
- Take prefix = "b" and suffix = "b" and remove them, s = "aa".
- Take prefix = "a" and suffix = "a" and remove them, s = "".
Example 3:
Input: s = "aabccabba"
Output: 3
Explanation: An optimal sequence of operations is:
- Take prefix = "aa" and suffix = "a" and remove them, s = "bccabb".
- Take prefix = "b" and suffix = "bb" and remove them, s = "cca".
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 105
s only consists of characters 'a', 'b', and 'c'.
4. Median of Two Sorted Arrays
Given two sorted arrays nums1 and nums2 of size m and n respectively, return the median of the two sorted arrays.
The overall run time complexity should be O(log (m+n)).
Example 1:
Input: nums1 = [1,3], nums2 = [2]
Output: 2.00000
Explanation: merged array = [1,2,3] and median is 2.
Example 2:
Input: nums1 = [1,2], nums2 = [3,4]
Output: 2.50000
Explanation: merged array = [1,2,3,4] and median is (2 + 3) / 2 = 2.5.
Example 3:
Input: nums1 = [0,0], nums2 = [0,0]
Output: 0.00000
Example 4:
Input: nums1 = [], nums2 = [1]
Output: 1.00000
Example 5:
Input: nums1 = [2], nums2 = []
Output: 2.00000
Constraints:
nums1.length == m
nums2.length == n
0 <= m <= 1000
0 <= n <= 1000
1 <= m + n <= 2000
-106 <= nums1[i], nums2[i] <= 106
13. Roman to Integer
Roman numerals are represented by seven different symbols: I, V, X, L, C, D and M.
| Symbol | Value |
|---|---|
| I | 1 |
| V | 5 |
| X | 10 |
| L | 50 |
| C | 100 |
| D | 500 |
| M | 1000 |
For example, 2 is written as II in Roman numeral, just two one's added together. 12 is written as XII, which is simply X + II. The number 27 is written as XXVII, which is XX + V + II.
Roman numerals are usually written largest to smallest from left to right. However, the numeral for four is not IIII. Instead, the number four is written as IV. Because the one is before the five we subtract it making four. The same principle applies to the number nine, which is written as IX. There are six instances where subtraction is used:
I can be placed before V (5) and X (10) to make 4 and 9.
X can be placed before L (50) and C (100) to make 40 and 90.
C can be placed before D (500) and M (1000) to make 400 and 900.
Given a roman numeral, convert it to an integer.
Example 1:
Input: s = "III"
Output: 3
Example 2:
Input: s = "IV"
Output: 4
Example 3:
Input: s = "IX"
Output: 9
Example 4:
Input: s = "LVIII"
Output: 58
Explanation: L = 50, V= 5, III = 3.
Example 5:
Input: s = "MCMXCIV"
Output: 1994
Explanation: M = 1000, CM = 900, XC = 90 and IV = 4.
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 15
s contains only the characters ('I', 'V', 'X', 'L', 'C', 'D', 'M').
It is guaranteed that s is a valid roman numeral in the range [1, 3999].
1663. Smallest String With A Given Numeric Value
The numeric value of a lowercase character is defined as its position (1-indexed) in the alphabet, so the numeric value of a is 1, the numeric value of b is 2, the numeric value of c is 3, and so on.
The numeric value of a string consisting of lowercase characters is defined as the sum of its characters' numeric values. For example, the numeric value of the string "abe" is equal to 1 + 2 + 5 = 8.
You are given two integers n and k. Return the lexicographically smallest string with length equal to n and numeric value equal to k.
Note that a string x is lexicographically smaller than string y if x comes before y in dictionary order, that is, either x is a prefix of y, or if i is the first position such that x[i] != y[i], then x[i] comes before y[i] in alphabetic order.
Example 1:
Input: n = 3, k = 27
Output: "aay"
Explanation: The numeric value of the string is 1 + 1 + 25 = 27, and it is the smallest string with such a value and length equal to 3.
Example 2:
Input: n = 5, k = 73
Output: "aaszz"
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 105
n <= k <= 26 * n
575. Distribute Candies
Alice has n candies, where the ith candy is of type candyType[i]. Alice noticed that she started to gain weight, so she visited a doctor.
The doctor advised Alice to only eat n / 2 of the candies she has (n is always even). Alice likes her candies very much, and she wants to eat the maximum number of different types of candies while still following the doctor's advice.
Given the integer array candyType of length n, return the maximum number of different types of candies she can eat if she only eats n / 2 of them.
Example 1:
Input: candyType = [1,1,2,2,3,3]
Output: 3
Explanation: Alice can only eat 6 / 2 = 3 candies. Since there are only 3 types, she can eat one of each type.
Example 2:
Input: candyType = [1,1,2,3]
Output: 2
Explanation: Alice can only eat 4 / 2 = 2 candies. Whether she eats types [1,2], [1,3], or [2,3], she still can only eat 2 different types.
Example 3:
Input: candyType = [6,6,6,6]
Output: 1
Explanation: Alice can only eat 4 / 2 = 2 candies. Even though she can eat 2 candies, she only has 1 type.
Constraints:
n == candyType.length
2 <= n <= 104
n is even.
-105 <= candyType[i] <= 105
234. Palindrome Linked List
Given a singly linked list, determine if it is a palindrome.
Example 1:
Input: 1->2
Output: false
Example 2:
Input: 1->2->2->1
Output: true
Follow up:
Could you do it in O(n) time and O(1) space?
31. Next Permutation
Implement next permutation, which rearranges numbers into the lexicographically next greater permutation of numbers.
If such an arrangement is not possible, it must rearrange it as the lowest possible order (i.e., sorted in ascending order).
The replacement must be in place and use only constant extra memory.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3]
Output: [1,3,2]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [3,2,1]
Output: [1,2,3]
Example 3:
Input: nums = [1,1,5]
Output: [1,5,1]
Example 4:
Input: nums = [1]
Output: [1]
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 100
0 <= nums[i] <= 100
645. Set Mismatch
You have a set of integers s, which originally contains all the numbers from 1 to n. Unfortunately, due to some error, one of the numbers in s got duplicated to another number in the set, which results in repetition of one number and loss of another number.
You are given an integer array nums representing the data status of this set after the error.
Find the number that occurs twice and the number that is missing and return them in the form of an array.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,2,4]
Output: [2,3]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,1]
Output: [1,2]
Constraints:
2 <= nums.length <= 104
1 <= nums[i] <= 104
1657. Determine if Two Strings Are Close
Two strings are considered close if you can attain one from the other using the following operations:
- Operation 1: Swap any two existing characters.
- For example, abcde -> aecdb
- Operation 2: Transform every occurrence of one existing character into another existing character, and do the same with the other character.
- For example, aacabb -> bbcbaa (all a's turn into b's, and all b's turn into a's)
You can use the operations on either string as many times as necessary.
- For example, aacabb -> bbcbaa (all a's turn into b's, and all b's turn into a's)
Given two strings, word1 and word2, return true if word1 and word2 are close, and false otherwise.
Example 1:
Input: word1 = "abc", word2 = "bca"
Output: true
Explanation: You can attain word2 from word1 in 2 operations.
Apply Operation 1: "abc" -> "acb"
Apply Operation 1: "acb" -> "bca"
Example 2:
Input: word1 = "a", word2 = "aa"
Output: false
Explanation: It is impossible to attain word2 from word1, or vice versa, in any number of operations.
Example 3:
Input: word1 = "cabbba", word2 = "abbccc"
Output: true
Explanation: You can attain word2 from word1 in 3 operations.
Apply Operation 1: "cabbba" -> "caabbb"
Apply Operation 2: "caabbb" -> "baaccc"
Apply Operation 2: "baaccc" -> "abbccc"
Example 4:
Input: word1 = "cabbba", word2 = "aabbss"
Output: false
Explanation: It is impossible to attain word2 from word1, or vice versa, in any amount of operations.
Constraints:
1 <= word1.length, word2.length <= 105
word1 and word2 contain only lowercase English letters.
160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists
Write a program to find the node at which the intersection of two singly linked lists begins.
For example, the following two linked lists:
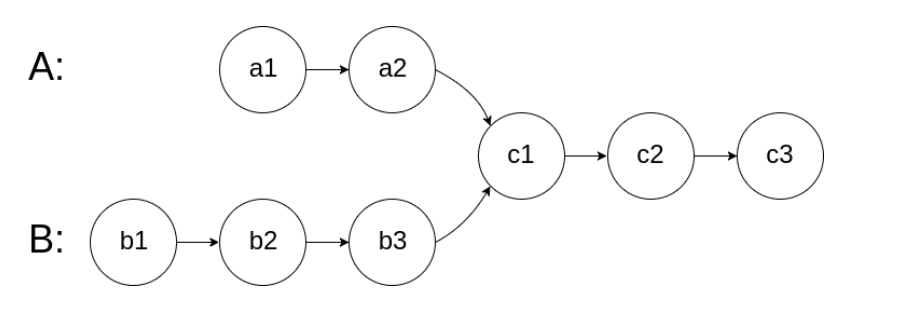
begin to intersect at node c1.
Example 1:
Input: intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,6,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
Output: Reference of the node with value = 8
Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 8 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [4,1,8,4,5]. From the head of B, it reads as [5,6,1,8,4,5]. There are 2 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in B.
Example 2:
Input: intersectVal = 2, listA = [1,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
Output: Reference of the node with value = 2
Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 2 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [1,9,1,2,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [3,2,4]. There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 1 node before the intersected node in B.
Example 3:
Input: intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
Output: null
Input Explanation: From the head of A, it reads as [2,6,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [1,5]. Since the two lists do not intersect, intersectVal must be 0, while skipA and skipB can be arbitrary values.
Explanation: The two lists do not intersect, so return null.
Notes:
- If the two linked lists have no intersection at all, return null.
- The linked lists must retain their original structure after the function returns.
- You may assume there are no cycles anywhere in the entire linked structure.
- Each value on each linked list is in the range [1, 10^9].
- Your code should preferably run in O(n) time and use only O(1) memory.
268. Missing Number
Given an array nums containing n distinct numbers in the range [0, n], return the only number in the range that is missing from the array.
Follow up: Could you implement a solution using only O(1) extra space complexity and O(n) runtime complexity?
Example 1:
Input: nums = [3,0,1]
Output: 2
Explanation: n = 3 since there are 3 numbers, so all numbers are in the range [0,3]. 2 is the missing number in the range since it does not appear in nums.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [0,1]
Output: 2
Explanation: n = 2 since there are 2 numbers, so all numbers are in the range [0,2]. 2 is the missing number in the range since it does not appear in nums.
Example 3:
Input: nums = [9,6,4,2,3,5,7,0,1]
Output: 8
Explanation: n = 9 since there are 9 numbers, so all numbers are in the range [0,9]. 8 is the missing number in the range since it does not appear in nums.
Example 4:
Input: nums = [0]
Output: 1
Explanation: n = 1 since there is 1 number, so all numbers are in the range [0,1]. 1 is the missing number in the range since it does not appear in nums.
Constraints:
n == nums.length
1 <= n <= 104
0 <= nums[i] <= n
All the numbers of nums are unique.
946. Validate Stack Sequences
Given two sequences pushed and popped with distinct values, return true if and only if this could have been the result of a sequence of push and pop operations on an initially empty stack.
Example 1:
Input: pushed = [1,2,3,4,5], popped = [4,5,3,2,1]
Output: true
Explanation: We might do the following sequence:
push(1), push(2), push(3), push(4), pop() -> 4,
push(5), pop() -> 5, pop() -> 3, pop() -> 2, pop() -> 1
Example 2:
Input: pushed = [1,2,3,4,5], popped = [4,3,5,1,2]
Output: false
Explanation: 1 cannot be popped before 2.
Constraints:
0 <= pushed.length == popped.length <= 1000
0 <= pushed[i], popped[i] < 1000
pushed is a permutation of popped.
pushed and popped have distinct values.
623. Add One Row to Tree
Given the root of a binary tree, then value v and depth d, you need to add a row of nodes with value v at the given depth d. The root node is at depth 1.
The adding rule is: given a positive integer depth d, for each NOT null tree nodes N in depth d-1, create two tree nodes with value v as N's left subtree root and right subtree root. And N's original left subtree should be the left subtree of the new left subtree root, its original right subtree should be the right subtree of the new right subtree root. If depth d is 1 that means there is no depth d-1 at all, then create a tree node with value v as the new root of the whole original tree, and the original tree is the new root's left subtree.
Example 1:
Input:
A binary tree as following:
4
/ \
2 6
/ \ /
3 1 5
v = 1
d = 2
Output:
4
/ \
1 1
/ \
2 6
/ \ /
3 1 5
Example 2:
Input:
A binary tree as following:
4
/
2
/ \
3 1
v = 1
d = 3
Output:
4
/
2
/ \
1 1
/ \
3 1
Note:
The given d is in range [1, maximum depth of the given tree + 1].
The given binary tree has at least one tree node.
1684. Count the Number of Consistent Strings
You are given a string allowed consisting of distinct characters and an array of strings words. A string is consistent if all characters in the string appear in the string allowed.
Return the number of consistent strings in the array words.
Example 1:
Input: allowed = "ab", words = ["ad","bd","aaab","baa","badab"]
Output: 2
Explanation: Strings "aaab" and "baa" are consistent since they only contain characters 'a' and 'b'.
Example 2:
Input: allowed = "abc", words = ["a","b","c","ab","ac","bc","abc"]
Output: 7
Explanation: All strings are consistent.
Example 3:
Input: allowed = "cad", words = ["cc","acd","b","ba","bac","bad","ac","d"]
Output: 4
Explanation: Strings "cc", "acd", "ac", and "d" are consistent.
Constraints:
1 <= words.length <= 104
1 <= allowed.length <= 26
1 <= words[i].length <= 10
The characters in allowed are distinct.
words[i] and allowed contain only lowercase English letters.
1295. Find Numbers with Even Number of Digits
Given an array nums of integers, return how many of them contain an even number of digits.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [12,345,2,6,7896]
Output: 2
Explanation:
12 contains 2 digits (even number of digits).
345 contains 3 digits (odd number of digits).
2 contains 1 digit (odd number of digits).
6 contains 1 digit (odd number of digits).
7896 contains 4 digits (even number of digits).
Therefore only 12 and 7896 contain an even number of digits.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [555,901,482,1771]
Output: 1
Explanation:
Only 1771 contains an even number of digits.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 500
1 <= nums[i] <= 10^5
100. Same Tree
Given the roots of two binary trees p and q, write a function to check if they are the same or not.
Two binary trees are considered the same if they are structurally identical, and the nodes have the same value.
Input: p = [1,2,3], q = [1,2,3]
Output: true
Input: p = [1,2], q = [1,null,2]
Output: false
Input: p = [1,2,1], q = [1,1,2]
Output: false
Constraints:
The number of nodes in both trees is in the range [0, 100].
-104 <= Node.val <= 104
Recommend Projects
-
 React
React
A declarative, efficient, and flexible JavaScript library for building user interfaces.
-
Vue.js
🖖 Vue.js is a progressive, incrementally-adoptable JavaScript framework for building UI on the web.
-
 Typescript
Typescript
TypeScript is a superset of JavaScript that compiles to clean JavaScript output.
-
TensorFlow
An Open Source Machine Learning Framework for Everyone
-
Django
The Web framework for perfectionists with deadlines.
-
Laravel
A PHP framework for web artisans
-
D3
Bring data to life with SVG, Canvas and HTML. 📊📈🎉
-
Recommend Topics
-
javascript
JavaScript (JS) is a lightweight interpreted programming language with first-class functions.
-
web
Some thing interesting about web. New door for the world.
-
server
A server is a program made to process requests and deliver data to clients.
-
Machine learning
Machine learning is a way of modeling and interpreting data that allows a piece of software to respond intelligently.
-
Visualization
Some thing interesting about visualization, use data art
-
Game
Some thing interesting about game, make everyone happy.
Recommend Org
-
Facebook
We are working to build community through open source technology. NB: members must have two-factor auth.
-
Microsoft
Open source projects and samples from Microsoft.
-
Google
Google ❤️ Open Source for everyone.
-
Alibaba
Alibaba Open Source for everyone
-
D3
Data-Driven Documents codes.
-
Tencent
China tencent open source team.