With the rise of powerful pre-trained vision-language models like CLIP, the community has started to investigate potential solutions to efficiently adapt these models to downstream datasets and tasks. In order to systematically organize and understand the development of this field, we summarize awesome Vision Language(VL) Prompt/Finetune/Adapter methods and models. The list of papers is in chronological order.
-
Dual Modality Prompt Tuning for Vision-Language Pre-Trained Model [CVPR] [code]
-
Dual-modality Prompt Tuning (DPT) can learn text and visual prompts for both the text and image encoder simultaneously, equipped with a Class-Aware Visual Prompt Tuning(CAVPT) scheme to help the final obtained image feature concentrate more on the target visual concept.
-
Pre-Trained Model: CLIP
-
Datasets: EuroSAT, Caltech1-1, OxfordFlowers, Food101, FGVCAircraft, DTD, OxfordPets, StandfordCars, ImagNet1K, Sun397, UCF101
-
Domain Generalization(ImageNet, ImageNetV2, ImageNet-Sketch, ImageNet-A, ImageNet-R)
-
-
Scaling & Shifting Your Features: A New Baseline for Efficient Model Tuning [NeurlPS] [code]
- SSF is a general proxy for parameter-efficient fine-tuning, where you only need to Scale and Shift your deep Features extracted by a pre-trained model for fine-tuning. It mainly has two merits: i)The scale and shift parameters do not depend on any input and have a unified learnable parameter space for different tasks. ii) It only introduces linear transformations.
- Pretrained Models:
- ViT-B/16
- Swin-B
- ConvNeXt-B
- AS-MLP-B
- Baselines:
- 2 basic fine-tuning methods:
- Full-Fine-Tuning
- Linear-Probing
- 2 Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning Methods:
- Adapter
- Bias
- VPT
- 2 basic fine-tuning methods:
- Tasks:
- Performance Comparisions on Image Classification (FGVC, VTAB-1k, CIFAR-100, ImageNet-1K, totally 26 image classification tasks)
- Impacts of Different Designs on SSF-ADA (CIFAR-100)
- Performance Comparisons on Robustness and OOD Datasets (ImageNet-A, ImageNet-R, ImageNet-C, ImageNet-1K)
-
Debiasing Vision-Language Models via Biased Prompts [arXiv] [code]
-
Debias_VL is a general approach for self-debiasing foundation vision-language models by projecting out biased directions in the text embedding.
-
Pre-Trained Model: CLIP
-
Experiments
-
Discriminative models(zero-shot classifier, text-image retrieval)
-
Generative models(text-to-image)
-
-
-
PLOT: Prompt Learning with Optimal Transport for Vision-Language Models [ICLR] [code]
- PLOT is a prompt model based on CLIP and CoOp that uses optimal transport (OT) theory and two-stage optimization to learn multiple comprehensive prompts for describing different features of a category.
- Pretrained Model:
- CLIP
- CoOp
- Task:
- few-shot recognition (Caltech101, ImageNet, OxfoldPets, StanfordCars, Flowers102, Food101, FGVCAircraft, DTD, EuroSAT, UCF101, sun397)
- domain generalization (ImageNet, ImageNetV2, ImageNet-Sketch, ImageNet-A, ImageNet-R).
-
VoLTA: Vision-Language Transformer with Weakly-Supervised Local-Feature Alignment [arXiv]
-
VoLTA (Vision-Language Transformer with weakly-supervised local-feature Alignment) is only utilizes image-caption data but achieves fine-grained region-level image understanding, eliminating the use of expensive box annotations.
-
Foundational Objective: Barlow Twins
-
Pre-Training & Downstream datasets: COCO, ImageNet, VOC07, LVIS, NLVR, Flicker30k
-
-
CLIP-ViP: Adapting Pre-trained Image-Text Model to Video-Language Representation Alignment [ICLR] [code]
-
CLIP-ViP model is proposed in three aspects:
-
adopt an image captioning model instead of using video captioning model
-
equip with Video Proxy mechanism
-
use Omnisource Cross-modal Learning(OCL)
-
-
Preliminary:
-
post-pretraining with different data-scale
-
pre-trained models: CLIP-ViT-B/32, CLIP4Clip
-
dataset: WebVid-2.5M, HD-VILA-100M, HD-VILA-10M, MSR-VTT
-
-
language domain gap with downstream data
-
datasets: MSR-VTT, DiDeMo, HD-VILA-100M, webVid-2.5M, MS-COCO, Conceptual Caption 12M
-
pre-trained model: CLIP
-
-
Tasks:
-
Video-Text Post-Pretrainig(HD-VILA-100M)
-
Fine-tuning Training(MSR-VTT, DiDeMo, LSMDC, ActivityNet)
-
-
-
SgVA-CLIP: Semantic-guided Visual Adapting of Vision-Language Models for Few-shot Image Classification [arXiv]
-
Semantic-Guided Visual Adapting (SgVA) extends vision-language pre-trained models to produce discriminative adapted visual features with the guidance of the fine-grained cross-modal knowledge learned by the pre-trained model.
-
Baselines and Benchmarks
-
PEMnE-BMS*, HCTransformers, CLIP_LP+LN, P>M>F, cluster-FSL, PT+MAP, EPNet and EASY(miniImagenet and tieredImagenet)
-
Zero-shot CLIP, CoOp, CLIP-Adapter, ProGrad(ImageNet, StandfordCars, UCF101, Caltech101, Flowers102, SUN397, DTD, EuroSAT, FGVCAircraft, OxfordPets, Food101)
-
-
-
Understanding and Mitigating Overfitting in Prompt Tuning for Vision-Language Models [arXiv] [code]
-
Subspace Prompt Tuning(SubPT) and Novel Feature Learner(NFL) boost the performance of CoOp and outperform the state-of-art CoCoOp approach
-
SubPT projects the gradients in back-propagation onto the low-rank subspace spanned by the early-stage gradient flow eigenvectors durning the entire training process and successfully eliminate the overfitting problem.
-
NFL enhances the generalization ability of the learned prompts onto novel categories beyond the training set, needless of image training data.
-
-
Pre-Trained Model: CoOp
-
Tasks:
-
Datasets(ImageNet, Caltech101, Oxford Pets, Stanford Cars, Flowers 102, Food 101, FGVC Aircraft, SUN 397, DTD, EuroSAT, UCF 101)
-
Base-to-Novel Generalization(first half of categories as base classes and the second half as novel classes within each dataset)
-
Domain Generalization(source domain: ImagNet, target domain: ImageNet-V2, ImageNet-Sketch, ImageNet-A, ImageNet-R)
-
-
-
Re-ViLM: Retrieval-Augmented Visual Language Model for Zero and Few-Shot Image Captioning [arXiv]
-
Retrieval-augmented Visual Language Model (Re-ViLM) supports retrieving the relevant knowledge from the external database for zero and in-context few-shot image-to-text generations.
-
Baseline: Flamingo
-
Benchmarks: MSCOCO, Flickr30k, NoCaps
-
-
VoP: Text-Video Co-operative Prompt Tuning for Cross-Modal Retrieval [CVPR] [code]
-
Text-Video Co-operative Prompt Tuning is an end-to-end framework with both video and text prompts introducing, offering position-specific, context-specific and function-specific video prompt.
-
Pre-Trained Model: CLIP
-
Benchmarks: MSR-VTT, DiDeMo, ActivityNet, LSMDC
-
-
Contrastive Prompt Tuning Improves Generalization in Vision-Language Models [ICLR]
-
Contrastive Prompt Tuning(CPT) can augment the standard cross-entropy loss with two additional contrastive loss terms driven by a hypothesis that contrastive losses can improve generalization by making the model output invariant to small input perturbations.
-
Pre-Trained Model: CLIP
-
Datasets:ImageNet, Caltech101, OxfordPets, StanfordCars, Flowers102, Food101, FGVCAircraft, SUN397, DTD, DuroSAT, UCF101, ImageNetV2, ImageNet-Sketch, ImageNet-A, ImageNet-R
-
Baselines: Zero-shot CLIP, CoOp, CoCoOp, CLIP-Adapter, Tip-Adapter
-
-
Vision Transformer Adapter for Dense Predictions [ICLR] [code]
-
Vision Transformer Adapter(ViP-Adapter) introduces vision-specific inductive biases into the plain ViT (3 tailored modules: spatial prior, spatial feature injector, multi-scale feature extractor) and develops an adapter to close the performance gap between the plain ViT and vision-specific backbones for dense prediction tasks.
-
Backbone: Plain ViT
-
Benchmarks: MMDetection, COCO, ADE20K
-
-
T2I-Adapter: Learning Adapters to Dig out More Controllable Ability for Text-to-Image Diffusion Models [arXiv] [code]
-
T2I-Adapter can well align the internal knowledge of T2I models and external control signals with a low training cost, providing more accurate controllable guidance to existing T2I models while not affecting their original generation ability.
-
Pre-Trained Model: Stable Diffusion (SD)
-
Tasks:
-
Sketch Map: COCO
-
Semantic Segmentation Map: COCO_Stuff
-
Keypoints Map: LAION-AESTHETICS, MMPose
-
-
-
Debiased Fine-Tuning for Vision-language Models by Prompt Regularization [arXiv]
-
Prompt Regularization(ProReg)can fine-tune the resultant model, neither biased towards the pretrained knowledge which is represented with the “soft“ label of the downstream data nor towards the downstream knowledge which is formulated as the ground-truth annotations in downstream tasks.
-
Pre-Trained Models: CLIP, ViLT
-
Tasks:
-
image classification: BAR, NICO, PACS, DomainNet
-
visual question answering: VQA-CP
-
-
-
Fine-tuned CLIP Models are Efficient Video Learners [CVPR] [code]
-
Video Finetuned CLIP (ViFi-CLIP) is a simple but strong baseline for adapting image-based CLIP to video-specific tasks and also proposes a two-stage ‘bridge and prompt‘ approach to first bridge the modality gap through fine-tuning followed by prompt learning in both visual and language branches of the CLIP model for low-data regimes.
-
Pre-Trained Model: ViT-B/16 based CLIP
-
Benchmarks: Kinetics-400 and 600, HMDB-51, UCF-101, Something Something V2(SSv2)
-
-
Multimodality Helps Unimodality: Cross-Modal Few-Shot Learning with Multimodal Models [CVPR] [code]
-
The cross-modal adaptation approach treats examples from different modalities as additional few-shot examples, encoding different modalities to the same representation space.
-
Pre-trained Models:
-
CLIP
-
AudioCLIP
-
-
Task:
-
Vision-Language Adaption(Caltech101, OxfordPets, StanfordCars, Flowers102, Food101, FGVCAircraft, SUN397, DTD, EuroSAT, UCF101)
-
Vision-Audio Adaption(ImageNet, ESC-50)
-
-
-
Not All Features Matter: Enhancing Few-Shot CLIP with Adaptive Prior Refinement [arXiv][code]
-
Adaptive Prior Refinement method (APE) directly utilizes the refined cache model for inference and explore the trilateral affinities between the text image, the refined cache model and textual representations for robust training-free recognition.
-
Training-required APE-T simply trains lightweight category residuals on top other than costly fine-tuning the entire cache model.
-
Pre-Trained Models:
-
CLIP
-
CoOp
-
Tip-Adapter
-
-
Tasks
-
Comprehensive Evaluation(ImageNet, Caltech101, DTD, EuroSAT, FGVCAircraft, Flowers102, Food101, OxfordPets, StandfordCars, SUN397, UCF101)
-
Generalization Ability(ImageNet-V2, ImageNet-Sketch)
-
-
-
Exploring Vision-Language Models for Imbalanced Learning [arXiv] [code]
-
Imbalance-VLM uses supervised imbalanced methods in conjunction with VLMs to improve the performance of VLMs on tail classes, incorporating lightweight decoder after the ViT of VLMs to save memory and capture subtle features for tail classes.
-
Pre-Trained Models:
-
CLIP
-
Laion-CLIP
-
-
Datasets(ImageNet-LT, Places-LT, iNaturalist2018)
-
-
Prompt Pre-Training with Twenty-Thousand Classes for Open-Vocabulary Visual Recognition [arXiv] [code]
-
POMP is a memory and computation efficient model and enables the learned prompt to condense semantic information for a rich set of visual concepts with over twenty-thousand classes.
-
Backbone: CLIP(ViT/B-16)
-
Dataset: ImageNet-21K
-
-
Chain of Thought Prompt Tuning for Vision-Language Models [[arXiv]] (https://arxiv.org/pdf/2304.07919.pdf)
-
Chain of Thought for prompt tuning combines visual and textual embeddings in vision domain and is consistent with the human learning paradigm, providing unique insight in vision domain.
-
Pre-Trained Model: CLIP
-
Datasets: ImageNet, Caltech101, OxfordPets, StanfordCars, Flowers102, Food101, FGVCAircraft, SUN39, UCF101, DTD, EuroSAT
-
Tasks
-
Base-to-New Generalization
-
Cross-dataset Evaluation
-
Domain Gneralization
-
Image-Text Retrieval
-
Visual Question Answering
-
-
-
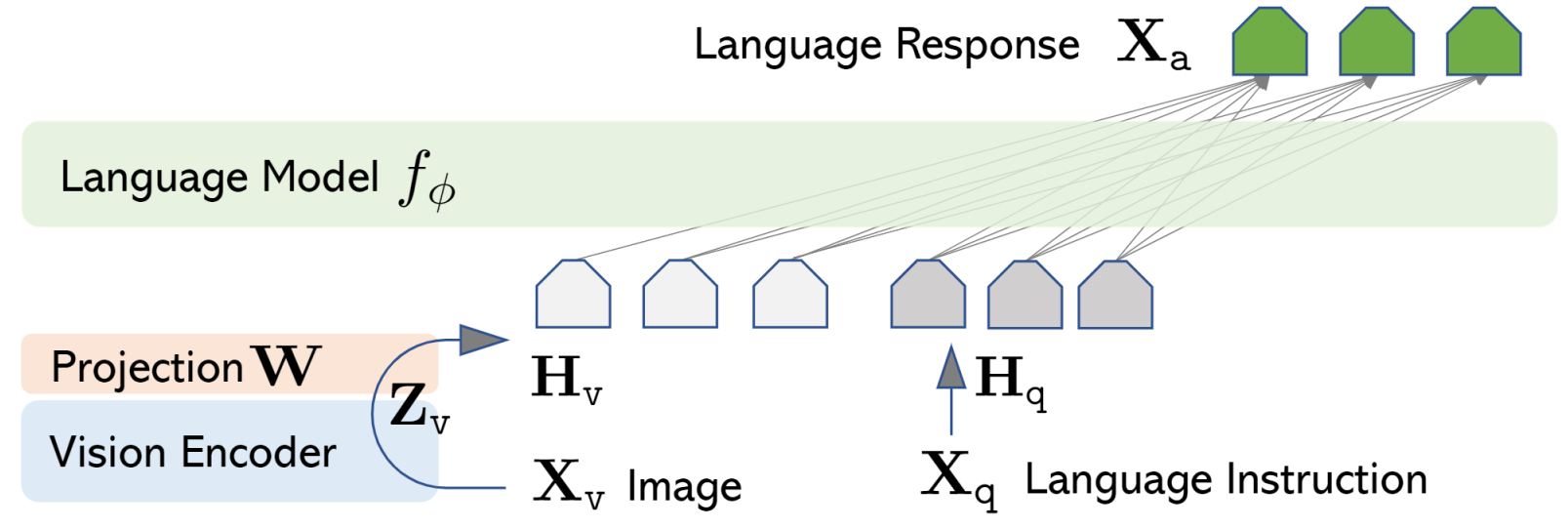
Visual Instruction Tuning [arXiv] [code]
-
Large Language and Vision Assistant (LLaVA) is an end-to-end trained large multimodal model that connects the open-set visual encoder of CLIP and large language models (LLM) for general purpose visual and language understanding.
-
Pre-Trained Model: CLIP
-
GPT-assisted Visual Instruction Data Generation: leverage language only GPT-4 or ChatGPT as the strong teacher to create instruction0following data involving visual content
-
Conversation
-
Detailed Description
-
Complex Reasoning
-
-
-
Towards Robust Prompt on Vision-Language Models [arXiv]
-
Robust Prompt Learning(ProL) improves robustness to both base and novel classes by integrating multi-scale features of an image into the prompt compared to existing in-context learning (IcoL) and ProL approaches, which is motivated by the robust multi-scale network architecture.
-
VLM: MEGMA(visual encoder NF_RN20x16 and language model GPT-Neo)
-
Datasets:
-
in-distribution data:ImageNet-1k
-
out-of-distribution(OOD) data: ImageNet-V2(re-collected ImageNet-like images), ImageNet-R(rendition images), ImageNet-C(natural corrupted images), ImageNet-S(sketch images), ImageNet-A(natural adversarial images)
-
-
-
Progressive Visual Prompt Learning with Contrastive Feature Re-formation [arXiv]
-
Progressive Visual Prompt (ProVP) demonstrates the effectiveness of visual prompts in V-L pre-trained models. It also prevents the serious deviation of the prompted visual feature form CLIP visual feature distribution.
-
Pre-Trained Model: CLIP
-
Tasks:
-
Few-Shot Learning(train on 1,2,4,8,shots and test on full test sets)
-
Base-to-Novel Generalization(train on 16 shots )
-
Datasets(11 benchmarks:ImageNet, Caltech101, FGVCAircraft, Flowers102, Food101, OxfordPets, StandfordCars, EuroSAT, DTD, SUN397, UCF101)
-
-
-
Improving Visual Prompt Tuning for Self-supervised Vision Transformers [ICML] [code]
-
The authors propose a simple yet effective method that learns a gate for each ViT block to adjust its intervention into the prompt tokens, with which prompt tokens are selectively influenced by blocks that require steering for task adaptation.
-
Tasks:
-
Image Classification:FGVC(CUB, Oxford Flowers, Stanford Cars, Stanford Dogs, NABirds), VTAB-1K(Natural, Specialized, Structured) benchmark
-
Semantic Segmentation: ADE20K benchmark and SETR-PUP segmentation model.
-
-
Self-supervised Vision Transformers: MAE, MoCo pretrained on ImageNet-1K
-
-
Task Residual for Tuning Vision-Language Models[CVPR][code]
-
Task Residual Tuning (TaskRes)bperforms directly on the textbased classifier and explicitly decouples the prior knowledge of the pre-trained models and new knowledge regarding a target task by keeping the original classifier weights from the VLMs frozen and obtains a new classifier for the target task by tuning a set of prior-independent parameters as a residual to the original one, which enables reliable prior knowledge preservation and flexible task-specific knowledge exploration.
-
Tasks:
-
Few-shot learning: ImageNet, Caltech101, OxfordPets, StanfordCars, Flowers102, Food101, FGVCAircraft, SUN397, DTD, EuroSAT, UCF101
-
Domain generalization: ImageNetV2, ImageNet-Sketch, ImageNet-A, ImageNet-R
-
-
-
ConES: Concept Embedding Search for Parameter Efficient Tuning Large Vision Language Models [arXiv]
-
Concept Embedding Search (ConES) approach optimizes prompt embeddings—without the need of the text encoder—to capture the ‘concept’ of the image modality through a variety of task objectives, which not only significantly speed up the learning process but is also orthogonal to current existing tuning methods since the searched concept embeddings can be further utilized in the next stage of fine-tuning the pre-trained large models for boosting performance.
-
Pre-trained Model: GLIP, UNIEXT, Stable Diffusion
-
Datasets: ISIC 2016, DFUC 202, BCCD, CPM-17, TBX11k, LUNA16, ADNI, TN3k, Cityscapes, DFUC2022, Kavsir-SEG
-
-
Contextual Prompt Learning for Vision-Language Understanding [CVPR]
-
Contextual Prompt Learning (CoPL) framework is capable of aligning the prompts to the localized features of the image, include using local image features as part of the prompt learning process, and more crucially, learning to weight these prompts based on local features that are appropriate for the task at hand.
-
Pre-trained Model: CLIP
-
Datasets:
-
generic classification: ImageNet Caltech-101
-
curated fine-grained: OxfordPets, StanfordCars, Flowers102, Food101 FGVCAircraft
-
scene, action, texture and satellite image recognition: SUN397, UCF101, DTD, EuroSat
-
-
-
Learning to Prompt for Continual Learning [CVPR] [code]
-
Learning to dynamically prompt(L2P) is a novel continual learning framework based on prompts for continual learning, providing a new mechanism to tackle contiunal learning challenges through learning a prompt pool memory space, which are served as parameterized “instructions“ for pre-trained models to learn tasks sequentially.
-
Datasets
-
class-incremental setting: Split CIFAR-100, CIFAR-10, MNIST, Fashion-MNIST, SVHN, notMNIST
-
domain-incremental setting: CORe50
-
task-agnostic setting: Gaussian scheduled CIFAR-100
-
-
-
Visual Prompt Tuning [ECCV] [code]
-
Visual Prompt Tuning (VPT) introduces a small amount of task-specific learnable parameters into the input space while freezing the entire pre-trained Transformer backbone during downstream training.
-
Pre-trained Model: Vision Transformers(ViT) and Swin Transformers(Swin)
-
Tasks:
-
FGVC(5 benchmarked Fine-Grained Visual Classification): CUB-200-2011, NABirds, Oxford Flowers, Stanford Dogs, Stanford Cars
-
VTAB-1k(19 diverse visual classification): Natural, Specialized and Structured Groups.
-
-
-
Unified Vision and Language Prompt Learning [CVPR] [code]
-
Unified Prompt Tuning(UPT) learns a tiny neural network to jointly optimize prompts across different modalities and thus presents a unified prompt method for VL models to tune both visual and text modality representations.
-
Baselines: Zero-shot CLIP, Single-modal Prompt Tuning(CoOp, CoCoOp, VPT)
-
Tasks:
-
Few-Shot Learning(ImageNet, Caltech101, OxfordPets, StanfordCars, Flowers102, Food101, FGVC-Aircraft, SUN397, UCF101, DTD, EuroSAT)
-
Domain Generalization(ImageNet, ImageNet-V2, ImageNet-Sketch, ImageNet-A, ImageNet-R)
-
-
-
AdaptFormer: Adapting Vision Transformers for Scalable Visual Recognition [NeurlPS] [code]
-
AdaptFormer can adapt vision transformers to a large variety of downstream visual recognition tasks and avoid catastrophic interference with each other.It also introduces lightweight modules that only add less that 2% extra parameters to a ViT.
-
Pre-Trained Backbone:
-
Vision Transformer(ViT)
-
Image:supervised pre-trained model(ImageNet-21k), self0supervised model(MAE)
-
Video: supervised and self-supervised pre-trained models(VideoMAE)
-
-
Downstream tasks:
-
Image Domain(CIFAR-100, SVHN, Food-101)
-
Video domain(SSv2, HDMB51)
-
-
-
Neural Prompt Search [arXiv] [code]
-
The concept of Neural Prompt Search (NOAH) is a novel approach that learns, for large vision models like Adapter, LoRA and VPT, the optimal design of prompt modules through a neural architecture search (NAS) algorithm, specifically for each downstream dataset.
-
Baselines:
-
Adapter(language models)
-
LoRA(language models)
-
VPT(vision models)
-
-
Tasks:
-
VTAB-1k(clustered into Natural Specialized and Structured groups)
-
Few-shot learning(Food101, OxfordFlowers102, StandfordCars, OxfordPets, FGVCAircraft)
-
Domain Generalization(ImageNet, ImageNetV2, ImageNet-Sketch, ImageNet-A, ImageNet-R)
-
-
-
Convolutional Bypasses Are Better Vision Transformer Adapters [arXiv] [code]
-
Convolutional Bypasses(Convpass) is an effective parameter-efficient transfer learning(PETL)method which leverages trainable convolutional blocks as bypasses to adapt pretrained ViT to downstream visual tasks.
-
Tasks
-
Transfer Learning
-
Datasets: VTAB-1K
-
Baselines: Full finetuning, Linear evaluation, VPT, Adapter, Adaptformer, LoRA, NOAH
-
-
Few-Shot Learning(FGVCAircraft, OxfordPets, Food101, StanfordCars, OxfordFlowers102)
-
Domain Generalization
-
Datasets:ImageNet-1K, ImageNet-V2, ImageNet-Sketch, ImageNet-A, ImageNet-R
-
Baselines: CLIP, CoOp, CoCoOp, Tip-Adapter-F
-
-


-
-
Conv-Adapter: Exploring Parameter Efficient Transfer Learning for ConvNets [arXiv]
-
Conv-Adapter is a light-weight and plug-and-play PET module designed for ConvNets in CV tasks, along with four adapting variants and following tow design dimensions - transferability and parameter efficiency.
-
Tasks:
-
Datasets:VTAB-1k and FGVC
-
Transferability: Full Fine-tuning, Linear Probing Bias Tuning, Visual Prompt Tuning
-
Universality: ResNet50, ConvNext-B, ConvNext-L, CLIP MoCov3
-
Few-shot Classification:ResNet50, ConvNext-B
-
Object Detection and Semantic Segmentation: ResNet50, ConvNext-S
-
-
-
ST-Adapter: Parameter-Efficient Image-to-Video Transfer Learning [NeurlPS] [code]
-
Parameter-effiicient Spatio-Temporal Adapter(ST-Adapter) is capable of extracting and leveraging the pre-trained knowledge of a large image model to achieve superior video understanding at a small parameter cost while is also easy to implement and friendly to deployment by grounding all the primitive on standard operators.
-
Datasets: Kinetics-400, Something-Something-v2, Epic-Kitchens-100
-
Pre-trained model: ViT
-
-
Parameter-efficient Model Adaptation for Vision Transformers [arXiv]
-
The parameter-efficient model adaptation framework first selects submodules by measuring local intrinsic dimensions and then projects them into subspace for further decomposition via a novel Kronecker Adaptation(KAdaptation) method.
-
Baselines: ViTs
-
Tasks:
-
Few-shot: ELEVATER benchmark
-
full-shot: CIFAR10, CIFAR100, SUN397, DTD, STL10, FGVCAircraft, FER2013
-
-
-
VL-Adapter: Parameter-Efficient Transfer Learning for Vision-and-Language Tasks [CVPR] [code]
-
The authors benchmark different types of parameter-efficient training techniques(Adapter, Hyperformer and Compacter) for diverse challenging downstream image-text and video-text tasks and analyze the freezing CLIP.
-
V&L Models: VL-BART, VL-T5
-
Datasets:
-
image-text: VQAv2, GQA, NLVR2, MSCOCO
-
video-text: VALUE, TVQA, How2QA, TVC, YC2C
-
-
-
Prompt Vision Transformer for Domain Generalization [arXiv]
-
Domain generalization algorithm DoPrompt for vision transformers with Domain Prompt Learning(DPL) and Prompt Adatper Learning(PAL) embed the knowledge of source domains in domain prompts for target domain prediction.
-
Baseline: ERM with ViT backbone
-
Datasets: PACS, VLCS, OfficeHome, DomainNet
-
-
Visual Prompt Tuning for Generative Transfer Learning [arXiv]
-
Generative visual transfer learning framework for vision transformers with prompt tuning proposes a prompt token generator design and a prompt engineering method for image synthesis.
-
Tasks
-
Baselines: GAN-based generative transfer learning methods
-
Generative Transfer on visual task adaptation benchmark(VTAB):Caltech-101, CIFAR-100, SUN397, SVHN, Flowers102, Pet, DTD, EuroSAT, Resisc45, Patch Camelyon, Diabetic Retinopathy, Kitti, Smallnorb (azimuth, elevation), Dsprites (x position, orientation), Clevr (object distance, count), DMLab
-
Few-shot Generative Transfer
-
NAR transformer
-
Dataset: Places, ImageNet, Animal Face
-
-
-
-
Learning Domain Invariant Prompt for Vision-Language Models [arXiv]
-
MetaPrompt directly generates domain invariant prompt generalizable to unseen domains by proposing a episodic prompt tuning algorithm.
-
Pre-trained model: CLIP
-
Tasks:
-
base-to-new generalization: ImageNet, Caltech101, OxfordPets, StanfordCars, Flowers102, Food101, FGVCAircraft, SUN397, UCF101, DTD, EuroSAT
-
conventional domain generalization: DomainBed(VLCS, PACS, OfficeHome, DomainNE)
-
-
-
Domain-Unified Prompt Representations for Source-Free Domain Generalization [arXiv] [code]
-
Source-free domain generalization(SFDG) method achieves domain generalization(DG) for visual tasks by learning domain-unified text encodings.
-
Pretrained Model: CLIP
-
Dataset: PACS, VLCS, OfficeHome, TerraIncognita, DomainNet
-
-
Prompt-Matched Semantic Segmentation [arXiv]
-
Stage-wise Prompt-Matched Framework is proposed to effectively and efficiently fine-tune those pre-trained foundation backbones with frozen parameters.Plus, a lightweight SPM is introduced to progressively learn reasonable visual prompts between different stages of the backbone through a recurrent mechanism.
-
Downstream Datasets: ADE20k, Vaihingen, CHASE-DB1, STARE
-
Backbone Network: ReNet-101(pretrained on ImageNet-1K)
-
-
Visual Prompting via Image Inpainting [arXiv]
-
The authors provide a new dataset that allows a model to learn grid structures which are given a few examples of task inputs and outputs and a query image without any labeling, task descriptions, or any additional information about the grid structure.
-
Models and Baselines: VQGAN, BEiT, MAE
-
-
Unleashing the Power of Visual Prompting At the Pixel Level [arXiv] [code]
-
Enhanced Visual Prompting(EVP) includes two designs: first, the authors treat the prompt as an extra and independent learnable component. Second, they re-introduce input diversity and gradient normalization which often used in building transferable adversarial examples into visual prompting.
-
Baselines:
-
TP (text prompting)=zero-shot in CLIP
-
VP,
-
VPT,
-
LP (linear probing): uses a linear layer as the classification head
-
FT (fully fine-tuning):updates all parameters of the backbone and the classification head
-
-
Datasets:
-
classification datasets: CIFAR100, CIFAR10, Flowers102, Food101, EuroSAT, SUN397, SVHN, DTD, OxfordPets, Resisc45, CLEVR, and DMLab
-
out-of-distribution datasets: Camelyon17, FMoW, and iWildCAM
-
corruption datasets: CIFAR100-C and CIFAR10-C
-
-
-
Exploring Visual Prompts for Adapting Large-Scale Models [arXiv] [code]
-
The authors demonstrates that visual prompting is particularly effective for CLIP and robust to distributions shift, achieving performance competitive with standard linear probes.
-
Pre-trained Models:
-
Instagram-pretrained ResNeXt (Instagram)
-
Big Transfer (BiT-M)
-
ResNet trained on ImageNet-1k (RN50)
-
CLIP
-
-
Baselines:fine-tuning, linear probes, and text prompting (i.e., zero-shot transfer)
-
Datasets
-
CIFAR100, CIFAR10, Flowers102, Food101, EuroSAT, SUN397, DTD, UCF101, SVHN , OxfordPets, Resisc45, and CLEVR
-
3 image classification datasets in WILDS: Camelyon17, FMoW, and iWildCAM
-
-
-
Visual Prompt Tuning for Test-time Domain Adaptation [arXiv]
-
To tackle the test-time adaptation(TTA) problem, Data-efficient Prompt Tuning(DePT) is proposed with 2 key ingredients: first, visual prompts are plugged into the ViT and only tunes source-initialized prompts during adaptation. Second, DePT bootstraps the source representation to the target domain by memory bank-based online pseudo-labeling.
-
Domain Adaptation Benchmarks:
-
VisDA-C
-
ImageNet-C
-
DomainNet-126
-
-
Backbone: ViT-B
-
Baselines
-
UDA: DANN, CDAN, CAN, SWD, MCC
-
TTA: Tent, SHOT, CFA, AdaContrast
-
-
-
Test-Time Prompt Tuning for Zero-Shot Generalization in Vision-Language Models [NeurlPS] [code]
-
Test-Time Prompt Tuning (TPT)can learn adaptive prompt on the fly with a single test sample in a zero-shot manner, and confidence selection is a simple plug-and-play module of TPT for image classification.
-
Pre-Trained Model: CLIP
-
Tasks:
-
Robustness to Natural Distribution Shifts: ImageNet-V2, ImageNet-A, ImageNet-R, ImageNet-Sketch
-
Cross-Datasets Generalization: Flower102, OxfordPets, SUN397, DTD, Food101,StanfordCars, Aircraft, UCF101, EuroSAT, Caltech101
-
Contest-dependent Visual Reasoning on Bongard-HOI
-
-
-
Prompt Generation Networks for Efficient Adaptation of Frozen Vision Transformers [arXiv] [code]
-
Prompt Generation Network (PGN) generates input-dependent visual prompts by sampling items from a learned Token Library.
-
Pre-Trained Model: CLIP
-
Datasets: CIFAR100&CIFAR10, Oxford Flowers, Food101, EuroSAT, SUN397, UCF101, SVHN, Oxford-IIIT Pets, DTD, RESISC, CLEVR
-
-
Multitask Vision-Language Prompt Tuning [arXiv] [code]
-
Multitask vision-language prompt tuning (MVLPT) framework incorporates cross-task knowledge into prompt tuning for vision-language models, incuding multitask prompt initialization and multitask prompt adaptation.
-
Pre-Trained Model: CLIP
-
Source Tasks: ImageNet, Caltech101, OxfordPets, StanfordCars, Flowers102, Food101, FGVCAircraft, SUN397, UDF101, DTD, EuroSAT
-
Target Tasks: 12 non-overlapped tasks in ELEVATER as Hateful Memes, PatchCamelyon, Rendered-SST2, KITTI Distance, FER 2013, CIFAR-10/100, VOC 2007 Classification, Country-211, MNIST, GTSRB, and Resisc45
-
-
Prompt Tuning with Soft Context Sharing for Vision-Language Models [arXiv]
-
Soft Context Sharing for Prompt Tuning(SoftCPT) can fine-tune pre-trained vision-language models on multiple target few-shot tasks, which consists of a novel meta network that transforms task name to prompt vector.
-
A new few-shot fashion classification dataset is constructed to test the effectiveness of multi-task prompt tuning in real industrial scenario.
-
Pre-Trained Model: CLIP
-
Datasets: General-10, Plant-6, Fashion-20
-
-
Learning to Prompt for Vision-Language Models [IJCV] [code]
- Based on continuous prompt learning and provided 2 implementations that handle different tasks, Context Optimization(CoOp) models a prompt’s context words with learnable vectors while the entire pre-trained parameters are kept fixed, improving the deployment efficiency compared with proposed vision-language models.
- Pretrained Models: CLIP
- Tasks
- Few-Shot Learning(ImageNet, Caltech101, OxfordPets, StanfordCars, Flowers102, Food101, FGVCAircraft, SUN397, DTD, EuroSAT, UCF101)
- Domain Generalization(ImageNet, ImageNetV2, ImageNet-Sketch, ImageNet-A, ImageNet-R)
-
Language-Aware Soft Prompting for Vision & Language Foundation Models [arXiv]
-
Language-Aware Soft Prompting (LASP) learning method enforces the learned prompts to be correctly classified with respect to the hand-engineered ones by means of a cross-entropy regularization loss. The authors also propose LASP+ by training LASP with virtual classes by including, during training, class names for which no visual samples are available.
-
Pre-Trained Model: CLIP
-
Datasets: ImageNet, Caltech101, Oxford-Pets, Stanford Cars, Flowers102, Food101, FGVC Aircraft, SUN397, DTD, EuroSAT and UCF-101.
-
-
Supporting Vision-Language Model Inference with Causality-pruning Knowledge Prompt [arXiv]
-
Causality-pruning Knowledge Prompt(CapKP) derives label-related semantic information by retrieving an ontological knowledge graph and introduces causality-pruning by following the first principle of Granger causality.
-
Few-Shot Learning
-
Datasets: ImageNet, Caltech101, StandfordCars, FGVCAircraft, Flowers102, OxfordPets, Food101, SUN397, UCF101, DTD, and EuroSAT
-
Baselines: CLIP, CoOp
-
-
Domain Generalization
- Datasets: ImageNetV2, ImageNet-Sketch, ImageNet-A and ImageNet-R
-
-
Learning to Prompt for Open-Vocabulary Object Detection with Vision-Language Model [CVPR] [code]
-
Detection prompt (DetPro) can learn continuous prompt representations for open-vocabulary object detection based on the pre-trained vision-language model equipped with a background interpretation scheme for negative proposal inclusion, which optimizes the embedding of negative proposals to be away from all other class embedding and a context grading scheme with tailored positive proposals, which tailors the prompt representation learning with different positive proposal sets corresponding to different context levels.
-
Pre-Trained Model: CLIP
-
Datasets: LVIS V1, Pascal VOC, COCO, Objects365
-
-
A Good Prompt Is Worth Millions of Parameters: Low-resource Prompt-based Learning for Vision-Language Models [ACL] [code]
-
FEWVLM is pre-train on a sequence-to-sequence transformer model with prefix language modeling (PrefixLM) and masked language modeling (MaskedLM) for prompt-based low-resource learning of VL tasks.
-
Visual Question Answering Tasks:
- VQAv2, OKVQA, GQA
-
Image Captioning:
- NoCaps, Flickr30k
-
Categoical Learning
- miniImageNet
-
-
Prompting through Prototype: A Prototype-based Prompt Learning on Pretrained Vision-Language Models [arXiv]
-
A method of prompting through prototype(PTP) on pretrained vision-language models (PVLMs) is a prototype-based prompting method which only updates parameters related to prompting while freezing the weights of PVLM.
-
Image Classification Datasets: Caltech101, StanfordCars, OxfordPets ,UCF101, Food101, SUN397, FGVCAircraft
-
PVLM models: bi-encoder CLIP, single-encoder ViLT
-
Image Encoder Backbone: ViT-B/32
-
-
Unsupervised Prompt Learning for Vision-Language Models [arXiv] [code]
-
Unsupervised prompt learning (UPL) framework can avoid time-consuming prompt engineering and better adapt vision-language models (e.g. CLIP) for the downstream image recognition task.
-
Pre-Model: CLIP
-
Datasets:ImageNet , Caltech101, DTD, EuroSAT, FGVCAircraft, Food101, Flowers102, OxfordPets, SUN397, StandfordCars, UCF101
-
-
Prompt Distribution Learning [CVPR]
-
Prompt Distribution Learning (ProDA) learns the soft prompts from a few downstream samples, discovering the task-related content with less bias than manual design and estimates a distribution over diverse and informative prompts to capture the variance of visual representations rather than learning one soft prompt.
-
Pre-Trained Model: CLIP
-
Datasets:
-
General Object Recognition: ImageNet-1k, CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100, STL10, Caltech-101
-
Fine-Grained Object Recognition: Oxford-IIIT Pets, Food-101, Stanford Cars, Oxford Flowers 102, and FGVC Aircraft
-
Remote Sensing Recognition: EuroSAT
-
Texture Recognition: DTD
-
-
-
Conditional Prompt Learning for Vision-Language Models [CVPR] [code]
- Conditional Context Optimization(CoCoOp) extends CoOp by further learning a lightweight neural network(Meta-Net) to generate for each image an input-conditional token(vector), allowing the gap between manual and learning-base prompts to be substantially reduced.
- Pretrained Model: CLIP
- Tasks:
- Generalization from Base to New Classes(ImageNet, Caltech101, OxfordPets, StanfordCars, Flowers102, Food101, FGVCAircraft, SUN397, DTD, EuroSAT, UCF101)
- Cross-Dataset Transfer(ImageNet, Caltech101, OxfordPets, StanfordCars, Flowers102, Food101, FGVCAircraft, SUN397, DTD, EuroSAT, UCF101)
- Domain Generalization(ImageNet, ImageNetV2, ImageNet-Sketch, ImageNet-A, ImgaeNet-R)
-
DenseCLIP: Language-Guided Dense Prediction with Context-Aware Prompting [CVPR] [code]
-
DenseCLIP is a new language-guided dense prediction framework designed for various Dense prediction tasks by implicitly and explicitly leveraging the pre-trained knowledge from CLIP models.
-
Tasks:
-
Semantic Segmentation: ADE20K
-
Object Detection and Instance Segmentation: ImageNet1K
-
-
-
CLIP also Understands Text: Prompting CLIP for Phrase Understanding [arXiv]
-
Because the text encoder trained with only image-text contrastive learning can achieve competitive or even better results on downstream text understanding tasks compared to popular language models pretrained with MLM, the authors design an automatic prompting method with a language model as the knowledge base to boost performance on phrase understanding for both language models and CLIP.
-
Datasets:
-
entity clustering: CoNLL2003, BC5CDR, WNUT 2017
-
entity set expansion: WIKI
-
-
-
Bridge-Prompt: Towards Ordinal Action Understanding in Instructional Videos [CVPR] [code]
-
Bridge-Prompt(Br-Prompt) can model the semantics across adjacent actions, so that it simultaneously exploits both out-of-context and contextual information from a series of ordinal actions in instructional videos.
-
Pre-trained Model: CLIP, Action-CLIP
-
Datasets: 50Salads, Georgia Tech Egocentric Activities (GTEA), Breakfast
-
-
Prompting Visual-Language Models for Efficient Video Understanding [ECCV]
-
The authors present a simple but strong baseline to efficiently adapt the pre-trained I-VL model, and exploit its powerful ability for resourcehungry video understanding tasks, with minimal training.
-
Pre-Trained Model: CLIP(ViT0B/16)
-
Tasks:
-
Action Recognition: HMDB-51, UCF-101, Kinetics-400, Kinetics-700, Something-Something V2
-
Action Localisation: THUMOS14, ActivityNet1.3
-
Text-Video Retrieval: LSMDC, DiDeMo, SMIT
-
-
-
PointCLIP V2: Adapting CLIP for Powerful 3D Open-world Learning [CVPR] [code]
-
PointCLIP V2 is a powerful 3D open-world learner which can fully unleash the potential of CLIP on 3D point cloud data.
-
Tasks:
-
Zero-Shot Classification: ModelNet10, ModelNet40, ScanObjectNN(OBJ ONLY, OBJ BG, and PB T50 RS)
-
Few-Shot Classification: ModelNet40, ScanObjectNN
-
Zero-Shot Part Segmentation: ShapeNetPart
-
Zero-Shot 3D Object Detection: ScanNet V2
-
-
-
SVL-Adapter: Self-Supervised Adapter for Vision-Language Pretrained Models [BMV] [code]
-
SVL-Adapter combines the complementary strengths of both vision-language pretraining and self-supervised representation learning and address the issue that remedies under-deliver on classification tasks with images differ significantly from those commonly found online.
-
Pre-Trained Model: CLIP
-
Datasets: Caltech101, OxfordPets, StanfordCars, Flowers102, Food101, FGVCAircraft, SUN397, DTD, UCF101, and EuroSAT, FMoW, OCT, MMCT, CCT20, Serengeti
-
-
Localized Latent Updates for Fine-Tuning Vision-Language Models [arXiv]
-
In this paper, the authors suggest a lightweight adapter which only updates the models predictions close to seen datapoints.
-
Datasets
-
Generic Object Classification: ImageNet, Caltech101
-
More Specific Object Classification: OxfordPets, StanfordCars, Flowers102, Food101, FGVCAircraft
-
Other Diverse Set of Tasks: SUN397, DTD, EuroSAT, UCF101
-
Domain Generalization: ImageNet, ImageNetV2, ImageNet-Sketch, ImageNet-A, ImageNet-R
-
-
-
EfficientVLM: Fast and Accurate Vision-Language Models via Knowledge Distillation and Modal-adaptive Pruning [arXiv] [code]
-
EfficientVLM is trained on a distilling then prning framework, which can compress large vision-language models into smaller, faster and more accurate ones.
-
Baselines: MiniVLM, DistillVLM
-
Datasets: COCO and Visual Genome(VG), SBU Captions, Conceptual Captions(CC), X-VLM, MSCOCO, ALBEF
-
-
Can Language Understand Depth? [ACM MM] [code]
-
DepthCLIP apply CLIP for zero-shot monocular depth estimation, which surpasses existing unsupervised methods and even approaches the early fully-supervised networks.
-
Datasets: NYU Depth v2
-
-
Prompting for Multi-Modal Tracking [ACM MM]
-
ProTrack can transfer the multi-modal inputs to a single modality by the prompt paradigm and perform well on multi-modal tracking by only altering the inputs and employing the tracking ability of pretrained RGB trackers learning at scale.
-
Tasks:
-
RGB-Depth object tracking: CDTB, DepthTrack
-
RGB-Thermal object tracking: LasHeR, RGBT234
-
RGB-Event object tracking: VisEvent
-
-
-
Expanding Language-Image Pretrained Models for General Video Recognition [ECCV] [code]
-
The authors adapts the pretrained language-image models to video recognition directly, propose a cross-frame attention mechanism that explicitly exchanges information across frames to capture the long-range dependencies of frames along the temporal dimension and design a video-specific prompting technique to yield instance-level textual representation automatically.
-
Pre-trained model: CLIP and Florence
-
Dataset: Kinetics-400&600, UCF-101, HMDB-51
-
-
Tip-Adapter: Training-free Adaption of CLIP for Few-shot Classification [ECCV] [code] ECCV*
-
Tip-Adapter with Fine-tuning(Tip-Adapter-F) is the fine-tuned version of Tip-Adatper. It unfreezed the cached keys as a good initialization for learnable parameters and further fine-tuned them via SGD.
-
Pre-Trianed Models:
-
CLIP
-
CoOp
-
Tip-Adapter
-
-
Experiments(ImageNet, StandfordCars, UCF101,Caltech101, Flowers102, SUN397,DTD, EuroSAT, FGVCAircraft, OxfordPets, Food101)
-
-
Adapting CLIP For Phrase Localization Without Further Training [arXiv] [code]
-
The authors not only adapt CLIP to generate high-resolution spatial feature maps without human annotations or additional training, but also extract feature maps from both ViT and ResNet CLIP model while maintaining the semantic properties.
-
Datasets:
-
Flickr: Flickr-S0, Fliker-S1, Flickr-All, Flickr-Other
-
Visual Genome(VG): VG-S0, VG-S1
-
-
-
CPT: Colorful Prompt Tuning for Pre-trained Vision-Language Models [arXiv] [code]
-
Cross-modal Prompt Tuning (CPT, alternatively, Colorful Prompt Tuning), is a novel paradigm for tuning VL-PTMs, which reformulates visual grounding into a fill-in-blank problem with color-based co-referential markers in image and text, maximally mitigating the gap.
-
datasets: MSCOCO (RefCOCO, RefCOCO+, RefCOCOg)
-
-
Domain Prompt Learning for Efficiently Adapting CLIP to Unseen Domains [arXiv] [code]
-
Domain Prompt Learning (DPL) adopts CLIP for domain generalization(DG) problems in image classification and domain inference in the form of conditional prompt generation.
-
Datasets: VLCS, OfficeHome, TerraIncognita
-
Baselines: CLIP (ViT-B16) using ERM, CORAL, DANN
-
-
Clip-Tuning: Towards Derivative-free Prompt Learning with a Mixture of Rewards [EMNLP]
-
Clip-Tuning adopts diverse frozen “thinned” networks of pretrained language models to obtain a mixture of rewards and thus advance the derivative-free prompt learning, consisting of all the hidden units that survive a stationary dropout strategy.
-
Datasets: SST-2, Telp polarity, AG’s News DBPedia, SNLI, RTE, MRPC
-
-
Prompt-aligned Gradient for Prompt Tuning [arXiv] [code]
-
Prompt-aligned Gradient (ProGrad) prevents prompt tuning from forgetting the general knowledge learned from VLMs and updates the prompt whose gradient is aligned (or non-conflicting) to the “general direction“.
-
Pretrained Model: CLIP
-
Datasets:
-
few-shot learning and base-to-new generalization: ImageNet Caltech101 OxfordPets StanfordCars Flowers102 Food101 FGVCAircraft EuroSAT UCF101 DTD SUN397
-
domain generalization: ImageNetV2 ImageNet-Sketch ImageNet-A ImageNet-R
-
-
-
DualCoOp: Fast Adaptation to Multi-Label Recognition with Limited Annotations [arXiv]
-
Delving into the Openness of CLIP [arXiv]
-
OrdinalCLIP: Learning Rank Prompts for Language-Guided Ordinal Regression [NeurlPS] [code]
-
Prompt Tuning for Generative Multimodal Pretrained Models [arXiv] [code]
-
Contrastive Demonstration Tuning for Pre-trained Language Models [EMNLP] [code]
-
PPT: Pre-trained Prompt Tuning for Few-shot Learning [ACL] [code]
-
Pro-tuning: Unified Prompt Tuning for Vision Tasks [arXiv]
-
Multi-Prompt Alignment for Multi-Source Unsupervised Domain Adaptation [arXiv]
-
An Empirical Study of GPT-3 for Few-Shot Knowledge-Based VQA [AAAI] [code]
-
VisualGPT: Data-efficient Adaptation of Pretrained Language Models for Image Captioning [CVPR] [code]
-
Flamingo: a Visual Language Model for Few-Shot Learning [arXiv]
-
Visual Clues: Bridging Vision and Language Foundations for Image Paragraph Captioning [arXiv]
-
DU-VLG: Unifying Vision-and-Language Generation via Dual Sequence-to-Sequence Pre-training [ACL]
-
GroupViT: Semantic Segmentation Emerges from Text Supervision [CVPR] [code]
-
Finetune like you pretrain: Improved finetuning of zero-shot vision models [arXiv] [code]
-
CPL: Counterfactual Prompt Learning for Vision and Language Models [arXiv]* [code] arXiv
-
Zero-Shot Temporal Action Detection via Vision-Language Prompting [ECCV] [code]
-
AdaViT: Adaptive Vision Transformers for Efficient Image Recognition [CVPR]
-
Unified Multimodal Pre-training and Prompt-based Tuning for Vision-Language Understanding and Generation [arXiv]
-
Learning Transferable Visual Models From Natural Language Supervision [arXiv] [code]
-
CLIP-Adapter: Better Vision-Language Models with Feature Adapters [arXiv] [code]
-
CLIP-Adapter conducts residual-style feature blending to achieve efficient few-shot transfer learning via fine-tuning.
-
Baseline Models:
-
Linear probe CLIP
-
Zero-shot CLIP
-
CoOp
-
-
Experiments
-
Few-Shot Learning(ImageNet, StanfordCars, UCF101, Caltech101, Flowers102, SUN397, EuroSAT, FGVCAircraft, OxfordPets, Food101)
-
Visualization of Manifold(t-SNE, EuroSAT)
-
Ablation Studies(DTD, ImageNet)
-
-
-
Tip-Adapter: Training-free CLIP-Adapter for Better Vision-Language Modeling [arXiv] [code]
-
Trianing-Free CLIP-Adapter (Tip-Adapter) has strong performance on few-classification via directly setting the weights of adapter with a cache model to avoid the conventional SGD fine-tuning.
-
Pre-Trianed Models:
-
Zero-shot CLIP
-
Linear-porbe CLIP
-
CLIP-Adapter
-
CoOp
-
-
Tasks:
-
Efficiency Comparison(ImageNet, StandfordCars, UCF101, Caltech101, Flowers102, SUN397, DTD, EuroSAT, FGVCAircraft, OxfordPets, Food101)
-
Ablation Studies(ImageNet)
-
-
-
ActionCLIP: A New Paradigm for Video Action Recognition [arXiv] [code]
-
Multimodal Few-Shot Learning with Frozen Language Models [NeurlPS]
-
ClipCap: CLIP Prefix for Image Captioning [arXiv] [code] arXiv*
-
Unifying Vision-and-Language Tasks via Text Generation [ICML] [code]
-
StyleCLIP: Text-Driven Manipulation of StyleGAN Imagery [ICCV] [code]
-
Align and Prompt: Video-and-Language Pre-training with Entity Prompts [CVPR] [code]