DISCONTINUATION OF PROJECT.
This project will no longer be maintained by Intel.
Intel has ceased development and contributions including, but not limited to, maintenance, bug fixes, new releases, or updates, to this project.
Intel no longer accepts patches to this project.
If you have an ongoing need to use this project, are interested in independently developing it, or would like to maintain patches for the open source software community, please create your own fork of this project.
The JavaScript* Runtime for the Zephyr™ OS project (ZJS for short) provides an IoT web runtime environment with JavaScript APIs for the Zephyr operating system, based on the JerryScript engine. It is intended for systems with little memory where Node.js with V8 is too big.
This code requires a local copy of JerryScript and Zephyr OS source. We will upstream patches to those projects as appropriate, but this repo is for everything else.
- Getting Started
- Developing with the Web-based IDE
- Classical 'Build and Flash' development
- Increase space on A101
- JS Minifier
- Other HW Platforms
- Running the JS app on Linux or Mac
- Networking with QEMU
- Networking with BLE
- Adding New Modules
- Contributing
- Repo Organization
ZJS should work on most of the boards supported by the Zephyr OS, though it does have higher memory / flash requirements so it won't work on the very smallest boards. So far we've had our hands on these boards: Arduino 101 / tinyTILE, FRDM-K64F, nRF52-DK, Arduino Due, NUCLEO-F411RE, STM32F4DISCOVERY, 96Boards Carbon, and OLIMEX STM32 E407. Please do try it with any other boards Zephyr supports and let us know what works and what doesn't.
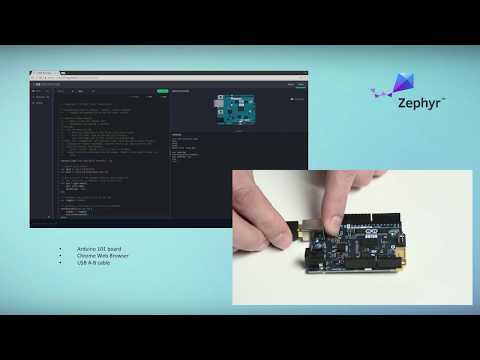
Up until recently, the Web IDE which makes ZJS development very easy only worked on Arduino 101. So the following instructions are still specific to Arduino 101 but we'll try to update them soon; until then please ask for help on IRC if you have questions about working with a particular board.
This section will walk you through building and running your first ZJS application on Arduino 101*.
- Arduino 101 board
- Ubuntu* 16.04 host; adapt as necessary for other platforms.
- If you're behind a proxy, go through all the usual pain to get ssh working to github.com and http working to zephyrproject.org.
- If you wish to use the Web IDE (highly recommended!), please follow the Zephyr Project JavaScript & WebIDE Tutorial.
The easiest way to develop your JavaScript app on Zephyr is using our Web-based IDE which allows you to write JS apps on the fly in our online editor and upload them directly to the Arduino 101 board through WebUSB. Please follow our Zephyr Project JavaScript & WebIDE Tutorial to get started with the Web IDE and check out the ashell guide for more advanced usages.
Windows and OSX users: These instructions are for Ubuntu 16.04. Be sure to also consult Zephyr Project's Getting Started documentation for Windows or OSX.
First, install these packages that you will need beyond those installed by default with Ubuntu:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install cmake dfu-util git python3-yaml screen uglifyjsNote: python3-yaml is a recent requirement for the frdm-k64f build due to a change in Zephyr, so it could be left out currently if you don't use k64f. Before that, for a while python-yaml was needed when the script was using Python 2.
You may also need to install pip3 to get pyelftools:
$ sudo apt install python3-pip
$ sudo pip3 install pyelftoolsNext, clone this git repo:
git clone http://github.com/intel/zephyr.js.gitIf you want to use a stable release version, the latest is 0.5:
git checkout v0.5If you do nothing and remain on master, you will be looking at the very latest
changes which may have regressions or instability. You can read the version
file in the root of the source tree to see what version you're on. If you're on
the master development branch it will just say 'devel'.
Download the latest Zephyr SDK, then:
chmod +x /path/to/zephyr-sdk-<VERSION>-setup.run
sudo /path/to/zephyr-sdk-<VERSION>-setup.runFollow the prompts, but the defaults should be fine.
Add the following two lines to your ~/.bashrc. If you installed your Zephyr
SDK elsewhere, adjust as needed.
export ZEPHYR_GCC_VARIANT=zephyr
export ZEPHYR_SDK_INSTALL_DIR=/opt/zephyr-sdkThen source the .bashrc :
source ~/.bashrcAdd your user to the plugdev group with this command:
sudo usermod -a -G plugdev USERNAMECopy these two files into your /etc/udev/rules.d directory (/etc/udev.rules for Ubuntu 14.04):
- 60-openocd.rules (from this Arduino github project)
- 99-dfu.rules (from this 01org github project)
Then run this command:
sudo udevadm control --reload-rulesThis should cause your /dev/tty* entries to have the plugdev group, which will
let you use them without root privileges. Otherwise, you will have to run some
of the following commands with sudo.
Whenever you open a new terminal to work with this repo, you need to set up environment variables.
First, the ZJS variables:
cd zephyr.js
source zjs-env.shNext, this command will check out additional git repos into the deps/ subdirectory, if you haven't done so before:
make update(If this is the first time you've run this, will see an error.)
As the previous command will complain, you need to set up some Zephyr OS environment variables, too. Here's the right way to do that:
source deps/zephyr/zephyr-env.shNote: cmake 3.8.2 or later is required, and your system might install an older version, if this is the case, you'll have to manually install the latest version of cmake:
$ mkdir $HOME/cmake && cd $HOME/cmake
$ wget https://cmake.org/files/v3.8/cmake-3.8.2-Linux-x86_64.sh
$ yes | sh cmake-3.8.2-Linux-x86_64.sh | cat
$ echo "export PATH=$PWD/cmake-3.8.2-Linux-x86_64/bin:\$PATH" >> $HOME/.zephyrrc
$ source $ZJS_ROOT/deps/zephyr/zephyr-env.sh
$ cmake --versionNow you're ready to build the x86 and ARC images. The x86 image includes the JerryScript engine and the ZJS runtime support, along with your JavaScript application, and the ARC support image acts as a helper library that channels some of the data needed from the ARC processor to the x86 processor.
Note: you'll need to build both the x86 and ARC images with the same JS file so the required sub-modules are enabled on both images.
You can build both with a single command:
make JS=samples/TrafficLight.jsThe JS= argument lets you provide the path to your application. The TrafficLight sample is a good first choice because you don't need to wire up any additional hardware. It just blinks onboard LEDs on your Arduino 101. Also, for many of the samples you will want to hook up the serial console (see below), but for this one it's not really needed.
Then connect the Arduino 101 to your host with a USB A/B cable. Press the Master Reset button on the Arduino 101 and within a few seconds type:
make dfuThis will flash both the images to the device using the dfu-util program.
If you get a permission error, make sure you followed the plugdev group
instructions above for this user. You shouldn't need to run this command with sudo.
After this flashing completes successfully, reboot the device with the Master Reset button to start the application. After a few seconds the onboard LEDs should start cycling.
You have built and run your first ZJS application!
If you want to make changes to the application, or run a different .js sample, you just need to repeat the steps the desired JavaScript filename.
Without the serial console set up, you won't be able to see error messages and other output from your ZJS application. To hook up the serial console, you need a USB to TTL Serial Cable, such as the TTL-232R-3V3. On that particular cable, you wire the black wire to ground on the Arduino 101 board, the orange wire to GPIO pin 0 (RX), and the yellow wire to GPIO pin 1 (TX). The other three are unused.
When you plug this in, the device should show up as something such as
/dev/ttyUSB0. You can then use the screen command to connect to the device
with a command such as this:
watch screen /dev/ttyUSB0 115200The watch utility will restart screen when you disconnect and reconnect your
Arduino 101, so you shouldn't miss anything. You can leave a dedicated terminal
running to watch the output.
In screen, you can scroll back the output with Ctrl-A, Esc, followed by
PgUp/PgDn. Then Esc again to get back to the latest output (out of "Copy Mode").
See Zephyr's
supported boards documentation
for information on debugging with a specific board. For the Arduino 101, ZJS has
special make targets: use the commands make adebug and make agdb in two
separate terminals to connect to the device with a debugger. Then you can set
breakpoints such as b main and run to start debugging as usual with gdb.
JerryScript has a built-in remote debugger which allows debugging JavaScript programs. At the moment only a Websocket-based implementation is provided by JerryScript which transmits messages over TCP/IP networks, but it currently only supports ethernet, so you'll need to run it on a board that has ethernet support, for example, the FRDM-K64F or Linux.
To enable the remote debugger for a particular JS application:
make BOARD=frdm_k64f DEBUGGER=on JS=xxx.jsWhen you flash and run the JS application, it will start in debugging mode, running on 192.168.1.101:5001, and you will see the following on serial output:
Debugger mode: connect using jerry-client-ws.py
Waiting for client connectionyou might need to add a route on your PC to connect to the network if you are connecting the board directly to your PC:
ip route add 192.168.1/24 dev eno1Then you can use the jerryscript command line or html client to connect to the debugger to debug your JS application:
python jerryscript/jerry-debugger/jerry-client-ws.py --display 10 192.168.1.1
In the client, type 'help' to get a list of debugger commands, such as adding breakpoints, stepping through JS sources, etc.
Alternatively, we've created a client that integrates with Chome DevTools, which lets you use the Chrome's built-in debugger to connect and you can use it to set breakpoints and step through source from all within the browser. Please see installation instructions on how to set it up from here
To enable the remote debugger on Linux:
make BOARD=linux DEBUGGER=on
outdir/linux/release/jslinux app.js --debuggerIt will then be run on debugger mode waiting for client connection, you can then in another terminal, you can connect to it by running the python client in JerryScript:
python jerryscript/jerry-debugger/jerry-client-ws.py --display 10 localhostSee below for a few more tips, such as increasing the space available for your application on the Arduino 101, or how to use ZJS with the FRDM-K64F.
Arduino 101 comes with a 144K X86 partition, but we're able to use more space by telling Zephyr there is more space and then splicing the images we flash to the device. You can control this with the ROM= flag to make. So if you want to allocated 256KB for x86, use ROM=256.
You can also just build without it until you see a message like this:
lfiamcu/5.2.1/real-ld: region `ROM' overflowed by 53728 bytes
That implies you need an extra 53K of space, so you could try passing ROM=200. If it's the ARC image that needs more space, you should decrease the ROM you're passing instead.
Note: Earlier, we would physically repartition the device and install a new bootloader that knew about it. This is no longer necessary, so if you have such a device you should restore it to factory condition with the 256-to-144 flashpack.
You can also influence the amount of RAM allocated to the X86 side with a new RAM= argument. Here the default is 55 but it can theoretically go as high as 79 if ARC was disabled; realistically up to maybe 75 or so depending on how few modules you require in the ARC build.
The RAM and ROM sizes being used are now displayed at the top of the make output when you do build for Arduino 101.
To save space it is recommended to use a minifier. In convert.py, the script
used to encode your JS into a source file, we use uglifyjs. If you didn't
install this earlier, you can do so with the command:
sudo apt install node-uglifyThis is an experimental ZJS platform and has not been tested. There should be no expectation that any given sample/test/application will work at all on this platform. The good news is that there have been ZJS networking samples run on the nRF52 board with success therefore we mention it here so anyone can try it out and contribute fixes to anything that does not work, potentially getting it stable enough to adopt as a supported board in the future. The nRF52 board we have tested is nRF52 DK (nrf52_pca10040). Please see Zephyr's project page to see the supported nRF5x variant boards, since each board will have different instructions to flash. To flash to the nRF52 DK, you'll need to downloand and install the JLink Software and Documentation Pack and the nRF5x command-line tools.
See the Zephyr docs for general information about running Zephyr OS on the nRF52.
Connecting to serial output is quite similar to the Arduino 101, except the nRF52 will have an ACM port rather than USB. You can connect with minicom by doing:
minicom -D /dev/ttyACM0Building is the same as any other ZJS platform, just use nrf52_pca10040 as
the BOARD name:
make JS=samples/HelloWorld.js BOARD=nrf52_pca10040You should now have a Zephyr binary in outdir/nrf52_pca10040/. You can flash
it to the nRF52 DK board with the nRF5x command line tools:
-
Connect the micro-USB cable to the nRF52 DK and to your computer and turn on the power switch.
-
Erase the flash memory in the nRF52832:
$ nrfjprog --eraseall -f nrf52- Flash the application using the nrfjprog tool:
$ nrfjprog --program outdir/nrf52_pca10040/zephyr.hex -f nrf52You should see the lights flashing on the nRF52 board. When it stops you can reset the board and you should see your application output on /dev/ttyACM0. If you don't see any output, try pressing the BOOT/RESET button next to the power switch to boot it again.
From here the device can be connected with BLE to a Linux machine as you do with an Arduino 101.
See the Zephyr docs for general information about running Zephyr OS on the FRDM-K64F.
The instructions below assume Ubuntu 14.04 on the host PC.
Connect a micro-USB cable from the device to your PC.
If you hit the Reset switch and wait about five seconds, you should be able to start up a serial console. Either:
screen /dev/ttyACM0 115200or
minicom -D /dev/ttyACM0(I typically had to try either command several times before it would work.) The benefit of minicom is it will keep running even if you unplug the cable and then plug it back in later.
Check your dmesg output or watch your /dev directory to know what device it shows up as.
Then, follow these instructions to update your firmware.
Next, you can try to build ZJS for the platform:
make BOARD=frdm_k64f JS=samples/HelloWorld.js
cp outdir/frdm_k64f/zephyr/zephyr.bin /media/<USERNAME>/MBED/After you copy the new .bin file to that directory, the device will reboot,
blink an LED quickly as it writes the image, and then you should see
the device reconnect as a USB storage device to your PC. Then you can press the
Reset button to run the Zephyr image. You should see "Hello, ZJS world!" output
on the serial console in less than a second.
If something doesn't work, you may want to establish that you're able to upload the K64F hello world application.
Then, you could try the Zephyr OS hello_world sample to narrow down the
problem:
cd deps/zephyr/samples/hello_world/
mkdir build && cd build
cmake -DBOARD=frdm_k64f ..
make
cp zephyr/zephyr.bin /media/<USERNAME>/MBED/Using the same procedure as above, once you hit Reset you should see "Hello World!" within a second on your serial console.
See the Zephyr Project Wiki for general information about running Zephyr OS on the STM32F4DISCOVERY.
Building is the same as any other ZJS platform, just use stm32f4_disco as
the BOARD name:
make BOARD=stm32f4_disco ideYou should now have a Zephyr binary in outdir/stm32f4_disco/. You can flash
it to the STM32F4DISCOVERY board with the openocd:
-
Connect the Mini USB cable from the device(CN1) to your PC.
-
Connect a micro-USB cable from the device (CN5) to your PC.
-
Flash the application using the following command:
make BOARD=stm32f4_disco flashYou should see the lights flashing on the STM32F4DISCOVERY board. When it stops you should see WebIDE url notification from Chrome.
From here the device can be connected with WebIDE and upload JS code to the device.
See the Zephyr Project Wiki for general information about running Zephyr OS on the OLIMEX-STM32-E407.
Building is the same as any other ZJS platform, just use olimex_stm32_e407 as
the BOARD name:
make BOARD=olimex_stm32_e407 ideYou should now have a Zephyr binary in outdir/olimex_stm32_e407/. You can flash
it to the OLIMEX-STM32-E407 board with the openocd:
- Connect the ST-Link USB dongle to your host computer and to the JTAG port of the OLIMEX-STM32-E407 board.
- Connect the Mini USB cable to the device(OTG1 near LAN connector) to your PC.
- Flash the application using the following command:
make BOARD=olimex_stm32_e407 flashYou should see the lights flashing on the ST-Link USB dongle. When it stops you should see WebIDE url notification from Chrome.
From here the device can be connected with WebIDE and upload JS code to the device.
In addition to Zephyr there is a "linux" target which does not use Zephyr at all and instead uses the host OS. This can be built on Linux or MacOS using the command:
make BOARD=linuxThe executable will be outputted to outdir/linux/<variant>/jslinux. Where
<variant> is either debug or release. This is specified the same as the
Zephyr target by passing in VARIANT= when running make. The default is
release.
Note: To build on MacOS using BOARD=linux, see instructions in the next section.
What makes the linux target convenient is that a JS script does not have to be
bundled with the final executable. By default samples/HelloWorld.js will be
bundled but you can always just pass in a script on the command line when
running jslinux e.g.:
./outdir/linux/release/jslinux samples/Timers.jsIf a script is passed in on the command line it will take the priority over any
script bundled with the executable (using JS=).
By default jslinux will exit when there are no pending events but if this is
not desired, there are two flags which can be used to cause jslinux to run
longer (or forever). The first is the --noexit flag. If this flag is used,
jslinux will run indefinitely. The second flag (-t) will cause jslinux to
run until a specified timeout (in milliseconds) is met.
This flag can be used like:
./outdir/linux/release/jslinux -t <ms>It should be noted that the Linux target has only very partial support to hardware compared to Zephyr. This target runs the core code, but most modules do not run on it, specifically the hardware modules (AIO, I2C, GPIO etc.). There are some modules which can be used though like Events, Promises, Performance an OCF. This list may grow if other modules are ported to the Linux target.
Mac support is still limited at this point. As Zephyr does not provide the SDK/toolchain to compile on MacOS natively, you will have to build your own or use a 3rd-party toolchain. Currently the targets we support building on Mac are "linux", "qemu_x86", with limited support for "arduino_101" and "frdm-k64f" boards. You'll need to have a recent version of MacOS and XCode command line tools from App store to get you started. Depending on your system setup and target, you might have to perform additional steps, but if you run into build issues, you should first make sure that you can build Zephyr native apps on Mac using the toolchain you installed. Once you verify that it works, then our project should also build and link correctly, but we'll try to update the document as we find these kinds of issues. Currently we enable Travis CI to build the linux target only against a recent version of MacOS (10.12) and XCode Command Line Tools (provided by XCode SDK) for sanity check purposes.
The basic requirement for building Zephyr boards is that you'll need to install and setup the correct cross-compiler toolchain on your Mac for the boards you are trying to build. You need to install crosstool-ng, which allows you to build the x86 images you can run on QEMU, and for Arduino 101, you need to install the ARC compiler, which can be found by installing the Arduino IDE for Mac, this is used to build the ARC support image.
Requirements:
- MacOS 10.12 (Sierra) or later
- XCode Command Line Tools: 8.1 or later (clang)
- Python: 2.7 or later
- Homebrew
- Crosstool-ng
- ARC cross-compiler (for building Arduino 101)
- Python-yaml
First, make sure you have Homebrew installed, instructions here, and then install the following brew packages:
brew install cmake ninja dfu-util doxygen qemu dtc python3 gperfInstall tools needed for building the toolchain:
brew install binutils gawk gettext help2man mpfr gmp coreutils wget
brew tap homebrew/dupes
brew install grep --with-default-names
brew install gnu-sedIf you have installed these packages before, make sure you update to the latest:
brew update
brew upgradeNext, you'll need to update to the latest MacOS and install/upgrade to the latest XCode Command Line Tools (we tested MacOS Sierra 10.12 and XCode 9.1) from App store.
To install XCode Command Line Tools, open a terminal and type the following, it should pop up a window to ask you to install the tools:
xcode-select --installYou'll then set up the environment variables:
cd zephyr.js
source zjs-env.sh
make update
source deps/zephyr/zephyr-env.shInstall Zephyr dependencies:
curl -O 'https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py'
sudo python ./get-pip.py
rm get-pip.py
cd deps/zephyr
pip3 install --user -r scripts/requirements.txtBuild Kconfig in $ZEPHYR_BASE/build and add it to path
brew install gtk+ libglade
cd $ZEPHYR_BASE
mkdir build && cd build
cmake ../scripts
make
echo "export PATH=$PWD/kconfig:\$PATH" >> $HOME/.zephyrrc
source $ZEPHYR_BASE/zephyr-env.shNote: You only need to do this once after cloning the git repository.
You can build the "linux" target on MacOS using BOARD=linux, follow instructions for "Building and running on Linux". This will create the jslinux ouput.
You can build QEMU with BOARD=qemu_x86 and Arduino 101 with BOARD=arduino_101, you'll need to install crosstool-ng (1.23 or later) and ARC compiler from Arduino IDE.
Install crosstool-ng:
wget http://crosstool-ng.org/download/crosstool-ng/crosstool-ng-1.23.0.tar.bz2
tar xvf crosstool-ng-1.23.0.tar.bz2
cd crosstool-ng-1.23.0/
./configure
make
make installAfter installing crosstool-ng, create and mount the image using our script osxmountzephyr.sh:
osxmountzephyr.shOnce you've created the image the first time, you can subsequently re-mount and un-mount the images with:
hdiutil mount CrossToolNG.sparseimage
diskutil umount force /Volumes/CrossToolNGThis will create an image mounted under /Volumes/CrossToolNG. You can then configure crosstool-ng:
cd /Volumes/CrossToolNG
mkdir build
cd buildIn the Zephyr kernel source tree we provide configurations that can be used to preselect the options needed for building the toolchain.
The configuration files can be found in $ZEPHYR_BASE/scripts/cross_compiler/.
Currently the following configurations are provided:
i586.config: for standard ABI, for example for Galileo and qemu_x86 iamcu.config: for IAMCU ABI, for example for the Arduino 101
(replace i586.config with iamcu.config for Arduino 101)
cp ${ZEPHYR_BASE}/scripts/cross_compiler/i586.config .config
ct-ng oldconfigAfter you are done, edit the generated .config, and make sure you have these settings, or you will run into build errors later:
...
CT_LOCAL_TARBALLS_DIR="/Volumes/CrossToolNG/src"
# CT_SAVE_TARBALLS is not set
CT_WORK_DIR="${CT_TOP_DIR}/.build"
CT_BUILD_TOP_DIR="${CT_WORK_DIR}/${CT_HOST:+HOST-${CT_HOST}/}${CT_TARGET}"
CT_PREFIX_DIR="/Volumes/CrossToolNG/x-tools/${CT_TARGET}"
CT_INSTALL_DIR="${CT_PREFIX_DIR}"
# Following options prevent link errors
CT_WANTS_STATIC_LINK=n
CT_CC_STATIC_LIBSTDCXX=n
...If you experience issue building Cross GDB at the end, you can ignore it or comment out the following:
# CT_GDB_CROSS=yNow you can build crosstool-ng. It will take 20~30 mins:
ct-ng buildWhen finished, you should have the toolchain setup in /Volumes/CrossToolNG/x-tools directory. now go back to the project's directory and set some environment variables:
export ZEPHYR_GCC_VARIANT=xtools
export XTOOLS_TOOLCHAIN_PATH=/Volumes/CrossToolNG/x-toolsTo use the same toolchain in future sessions, you can set the variables in the file $HOME/.zephyrrc. For example:
cat <<EOF > ~/.zephyrrc
export XTOOLS_TOOLCHAIN_PATH=/Volumes/CrossToolNG/x-tools
export ZEPHYR_GCC_VARIANT=xtools
EOFFor a new environment, create a symlink for Python2.7:
ln -s /usr/bin/python2.7 /usr/local/bin/python2Now, you can build and run on QEMU using this command:
make JS=samples/HelloWorld.js BOARD=qemu_x86 qemuYou should see output (To exit from QEMU enter: 'CTRL+a, x') :
SeaBIOS (version rel-1.11.0-0-g63451fca13-prebuilt.qemu-project.org)
Booting from ROM..
Hello, ZJS world!Note: There are currently some cmake issues and crosstool-ng using the latest Zephyr (1.10.0), and here are some of the work-arounds.
If you see an compile error like:
No such file or directory: CMAKE_READELF:
'/Volumes/CrossToolNG/x-tools/i586-zephyr-elfiamcu/bin/i586-zephyr-elfiamcu-readelf'edit ${ZEPHYR_BASE}/cmake/toolchain-xtools.cmake and change the line:
set(CROSS_COMPILE_TARGET_x86 i586-zephyr-elfiamcu)to
set(CROSS_COMPILE_TARGET_x86 i586-zephyr-elf)and append the following line:
set(TOOLCHAIN_INCLUDES ${TOOLCHAIN_HOME}/${CROSS_COMPILE_TARGET}/${CROSS_COMPILE_TARGET}/include)If you see a QEMU error like, it could be the qemu package on your system were installed to /usr/local/share/ :
qemu-system-i386: -L -bios: Could not open 'bios.bin': No such file or directoryedit ${ZEPHYR_BASE}/boards/x86/qemu_x86/board.cmake and change the line:
-L ${QEMU_BIOS}to
-L /usr/share/local/qemuTo build for Arduino 101, you'll need to download the latest Arduino IDE here. Once you have the IDE installed, open the IDE and click on Tools->Board->Board Manager, and install the latest version of the board support package "Intel Curie Boards". This will install the arc-elf compiler located in the following directory:
$HOME/Library/Arduino15/packages/Intel/tools/arc-elf32/
Then copy the compiler to where you installed the crosstool-ng toolchain:
cp -pR $HOME/Library/Arduino15/packages/Intel/tools/arc-elf32 /Volumes/CrossToolNG/The compiler is in a subdirectory, such as 1.6.9+1.0.1. You'll need to set this path in cmake to make to find the right bin file.
Edit deps/zephyr/cmake/toolchain-xtools.cmake, and change the following:
set(CROSS_COMPILE ${TOOLCHAIN_HOME}/${CROSS_COMPILE_TARGET}/bin/${CROSS_COMPILE_TARGET}-)to
set(CROSS_COMPILE /Volumes/CrossToolNG/arc-elf32/1.6.9+1.0.1/bin/arc-elf32-)You can now build for Arduino 101 (without setting BOARD=, it builds arduino_101 by default)
make JS=samples/HelloWorld.jsNote: There's currently a bug that you'll run into a build issue when buiding for the Arduino 101 using the latest Zephyr (1.10.). See bug
These also have limited support currently. The requiremenet is that you'll need to install the GCC ARM Embedded cross compiler here
After you download it, set these environment variables:
export GCCARMEMB_TOOLCHAIN_PATH="/Users/<USERNAME>/Downloads/gcc-arm-none-eabi-6-2017-q1-update"
export ZEPHYR_GCC_VARIANT=gccarmembThen you can build like this:
make JS=samples/HelloWorld.js BOARD=frdm_k64f CROSS_COMPILE=~/Downloads/gcc-arm-none-eabi-6-2017-q1-update/bin/arm-none-eabi-For additional information, see here on how to setup third-party compilers.
See board summary for some basic comparison information about the boards we've tested on.
There is only partial support for modules on Linux compared to Zephyr. Any hardware specific module (I2C, UART, GPIO, ADC etc.) is not supported on Linux. Trying to run a Zephyr specific module on Linux will result in the JavaScript not running successfully. Below is a complete table of modules and target support. Some Zephyr targets listed are experimental and have not been fully tested. For this reason we have the following possibilities for support:
- X - Supported
- E - Experimental, not formally tested by QA but basic functionality verified.
- NT - Not tested at all
- Blank - Not Supported
| Module | Linux | A101/tT | K64F | nRF52 | Due | F411RE | STM32F4 | OLIMEX E407 | Carbon |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HelloWorld | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| ADC | X | X | |||||||
| BLE | X | X | |||||||
| Buffer | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Console | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| Dgram | X | X | |||||||
| Event | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| File System | X | X | |||||||
| GPIO | X | X | |||||||
| I2C | X | X | |||||||
| Net | X | X | |||||||
| OCF | X | X | X | NT | |||||
| Performance | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| PME | X | ||||||||
| PWM | X | ||||||||
| Sensor | X | X | |||||||
| Timers | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
| UART | X | NT | |||||||
| WebSocket | X | X | |||||||
| WebUSB | X |
QEMU has support for networking features that can be tested on your Linux desktop. To do this you will need to build a separate "net-tools" project:
git clone https://github.com/zephyrproject-rtos/net-tools
cd net-tools
makeIf the build fails, you may need to install the libpcap-dev package:
sudo apt install libpcap-devOpen up 2 terminals to run the tools from the net-tools directory: Terminal 1:
./loop-socat.shIf this fails, you may need to install the socat package:
sudo apt install socatTerminal 2:
sudo ./loop-slip-tap.shThen run QEMU as your normally would e.g.
make BOARD=qemu_x86 JS=samples/OcfServer.js qemuNote: At this point, this setup is relatively unstable. You may experience crashes or things just not working in general. If the behavior does not seem normal you can usually fix it by restarting the two scripts and running QEMU again.
The original instructions document can be found on the Zephyr website here
It is possible to use IP networking over BLE using 6LowPAN. This is explained in a dedicated document.
This SPI Ethernet board is now supported for use with the Arduino 101. To configure it, wire IO10-IO13 (the SPI pins) to CS, SI, SO, SCK on the board, respectively. Then wire VCC to 3.3V power (somewhere online I saw a reference that some of these boards tolerate 5V and some do not) and GND to ground. Finally, wire INT on the board to pin IO4; this is a GPIO used to communicate with the board as well.
Then when building a networking application, use FORCE=zjs_net_l2_enc28j60.json on your make command line to override the default Bluetooth/6LoWPAN networking.
For a simple test configuration, connect the Ethernet port to a secondary Ethernet on your host PC (I use a USB Ethernet device). Configure that interface on your PC with static IPv4 or IPv6 addresses that work with what's configured on the device. With the TCPEchoServ[46].js samples at present, you would use something like 192.168.201.2 w/ 255.255.255.0 mask for IPv4, and 2001:db8::2 w/ 64 prefix for IPv6.
(The simple board doesn't do auto-crossover detection so if your host Ethernet adapter doesn't either, you may need to use a crossover cable or hook them both up to a dedicated switch as I've done.)
If you want to contribute code to the ZJS project, first you need to fork the project. The next step is to send a pull request (PR) for review to the ZJS repository. The PR will be reviewed by the project team members. You need at least two plus-ones (+1) , "Look Good To Me (LGTM)" or other positive signals for the project members. Once you have gained the required signals the project maintainers will merge the PR.
To report a security issue, please follow the procedure described here.
We run a series of tests on each pull request and merged commit using Travis.
This relies on a script in the repo called trlite. One easy way to run these
tests on your local $ZJS_BASE git tree is to use make check or
make quickcheck for a faster subset of the tests. These run with your code as
it stands in your tree. This will not catch a problem like you failing to
add a new file to your commit.
For a slightly safer sanity check, which might catch that kind of problem, you
can run trlite directly or trlite linux for the "quick subset". This will
clone a second copy of your git tree into a .trlite subdirectory, apply changes
that git diff knows about, and run the build tests. Another option trlite -j
will cause it to run four threads of tests to speed up execution; these will
use four directories named .trlite[1-4]. If there is a test failure, the
affected .trlite* trees are left in place so that you can investigate.
zjs-env.sh- Source this file to set environment variables and path to be able to use tools fromscripts/anywhere.prj.conf- The main configuration file for a Zephyr application; overrides settings from a defconfig file in the Zephyr tree. In the ZJS builds, we assemble the prj.conf file at build time from other fragments.
arc/- Contains sensor subsystem code for ARC side of the Arduino 101.cmake/- Contains CMake build files for building Zephyr and JerryScriptdeps/- Contains dependency repos and scripts for working with them.docs/- Documentation in Markdown format (use API.md as index).fragments/- Contains project file fragments for project configuration.modules/- Contains different Javascript modules that can be loaded.outdir/- Directory generated by build, can be safely removed.samples/- Sample JavaScript files that can be built with make JS=.scripts/- Subdirectory containing tools useful during development.src/- JS API bindings for JerryScript written directly on top of Zephyr.tests/- JavaScript unit tests (incomplete).tools/- Helper utility for building JS using snapshot.
Zephyr is a trademark of the Linux Foundation. *Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.