The AirBnB clone (hbnb), is a project in which the students of Holberton deploy on a server a simple copy of the AirBnB website, in order to cover all fundamental concepts of the higher level programming track.
The web application is composed by:
-
A command interpreter to manipulate data without a visual interface, like in a Shell (perfect for development and debugging)
-
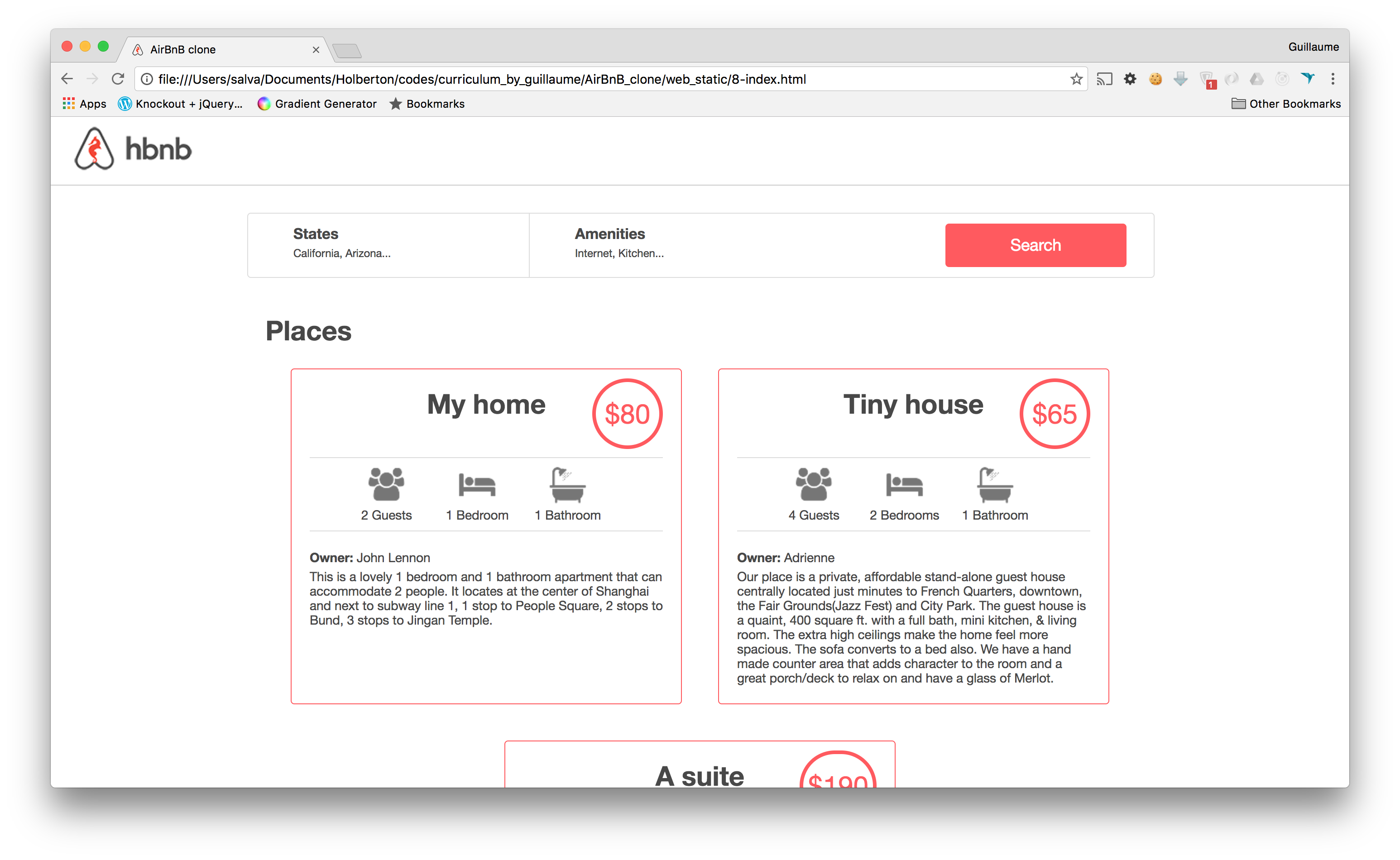
A website (the front-end) that shows the final product to everybody: static and dynamic
-
A database or files that store data (data = objects)
-
An API that provides a communication interface between the front-end and your data (retrieve, create, delete, update them)
The console is a command line interpreter but limited to a specific use-case. In this case it will be able to manage the objects of our AirBnb clone project:
-
Create a new object (ex: a new User or a new Place)
-
Retrieve an object from a file, a database etc…
-
Do operations on objects (count, compute stats, etc…)
-
Update attributes of an object
-
Destroy an object
The shell works like this in interactive mode:
$ ./console.py
(hbnb)
But also in non-interactive mode:
$ echo "help" | ./console.py
(hbnb)
NOTE: you can use the help option with all the commands implemented to see the respective documentation.
(hbnb) help
Documented commands (type help <topic>):
========================================
EOF help quit
i.e.
(hbnb) help quit
Quit command to exit the program
quitandEOFto exit the program
i.e.
$ ./console.py
(hbnb) quit
$
create: Creates a new instance ofBaseModel, saves it (to the JSON file) and prints theid.
Syntax: $ create [CLASS]
i.e.
(hbnb) create BaseModel
49faff9a-6318-451f-87b6-910505c55907
show: Prints the string representation of an instance based on the class name andid.
Syntax: $ show [CLASS] [ID]
i.e.
(hbnb) show BaseModel 49faff9a-6318-451f-87b6-910505c55907
[BaseModel] (49faff9a-6318-451f-87b6-910505c55907) {'created_at': datetime.datetime(2017, 10, 2, 3, 10, 25, 903293), 'id': '49faff9a-6318-451f-87b6-910505c55907', 'updated_at': datetime.datetime(2017, 10, 2, 3, 10, 25, 903300)}
destroy: Deletes an instance based on the class name andid(save the change into the JSON file).
Syntax: $ destroy [CLASS] [ID]
i.e.
(hbnb) destroy BaseModel 49faff9a-6318-451f-87b6-910505c55907
all: Prints all string representation of all instances based or not on the class name.
Syntax: $ all [CLASS] or $ all
i.e.
(hbnb) all BaseModel
["[BaseModel] (2dd6ef5c-467c-4f82-9521-a772ea7d84e9) {'id': '2dd6ef5c-467c-4f82-9521-a772ea7d84e9', 'created_at': datetime.datetime(2017, 10, 2, 3, 11, 23, 639717), 'updated_at': datetime.datetime(2017, 10, 2, 3, 11, 23, 639724)}", "[BaseModel] (49faff9a-6318-451f-87b6-910505c55907) {'first_name': 'Betty', 'id': '49faff9a-6318-451f-87b6-910505c55907', 'created_at': datetime.datetime(2017, 10, 2, 3, 10, 25, 903293), 'updated_at': datetime.datetime(2017, 10, 2, 3, 11, 3, 49401)}"]
update: Updates an instance based on the class name andidby adding or updating attribute (save the change into the JSON file).
Syntax: $ update [CLASS] [ID] [ATTRIBUTE] [VALUE]
i.e.
(hbnb) update BaseModel 49faff9a-6318-451f-87b6-910505c55907 first_name "Betty"
If a command is missing an argument or it does not exist, a message will be displayed:
i.e.
(hbnb) all MyModel
** class doesn't exist **
(hbnb) destroy
** class name missing **




![Linked[in] alt text](https://i.imgur.com/TJRr1iY.png)