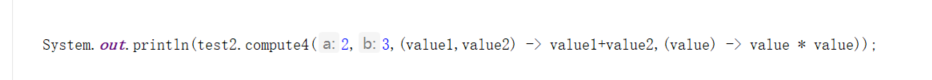Jdk 8 新特性
public class SwingTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("hello world");
JFrame jFrame = new JFrame("My Jframe");
JButton jButton = new JButton("My JButton");
//增加事件处理器 点击触发事件
jButton.addActionListener(e -> System.out.println("Button Pressed"));
jFrame.add(jButton);
jFrame.pack();
jFrame.setVisible(true);
jFrame.setDefaultCloseOperation(jFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
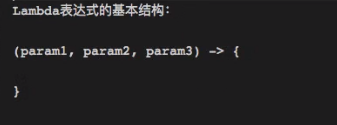
}(param1 , param2 , param3) -> {
system.out.println("hello world");
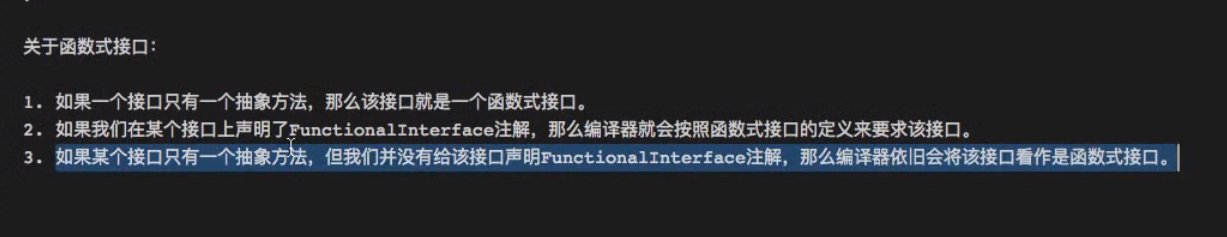
}; The type is an interface type and not an annotation type, enum, or class.
The annotated type satisfies the requirements of a functional interface.public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//集合
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8);
System.out.println("---------普通遍历list-----------");
//普通遍历list
for (int i = 0 ; i <list.size();i++){
System.out.print(list.get(i));
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("----------增强for循环 外部迭代------------");
//增强for循环
for (Integer i : list){
System.out.print(i);
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("---------Consumer内部迭代-------------");
//jdk8 Consumer 匿名内部类
list.forEach(new Consumer<Integer>() {
@Override
public void accept(Integer integer) {
System.out.print(integer);
}
});
System.out.println();
System.out.println("---------lambda-------------");
//jdk8 lambda 表达式
list.forEach( (integer) -> {
System.out.print(integer);
});
System.out.println();
System.out.println("------方法引用---------");
list.forEach(System.out::print);
}
} MyInterface myInterface = () -> {
System.out.println("hello");
};- lambda表达式引用
- 方法引用
- 构造方法引用
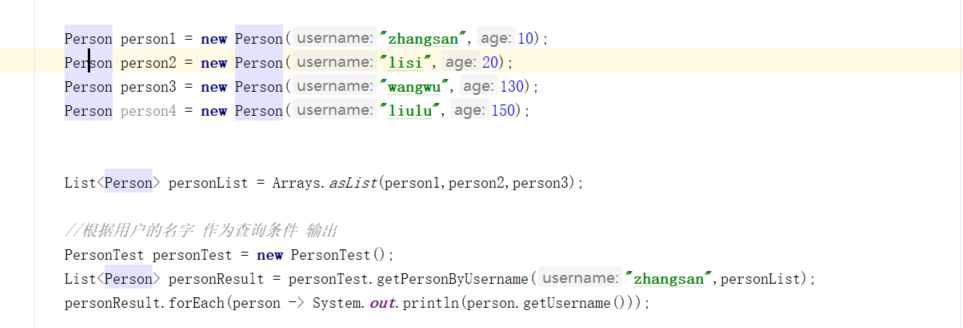
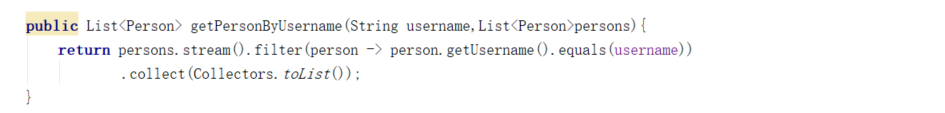
public boolean createList(List<WishManager> managers, String wishApplyId, String userId) { List<WishAuthorize> list = new ArrayList<>(); managers.forEach(wishManager -> { WishAuthorize wishAuthorize = new WishAuthorize(); wishAuthorize.setCreateUserId(userId); wishAuthorize.setUserId(wishManager.getUserId()); wishAuthorize.setWishApplyId(wishApplyId); list.add(wishAuthorize); }); return worthServiceprovider.getWishAuthorizeService().insertBatch(list); }
compose andThen 方法的调用
compose : 先操作最后一个参数,然后再操作前一个参数 andThen : 先操作第一个参数,然后再操作后一个参数
函数式编程:四则运算
函数式编程:四则运算
函数式编程 Function 、BiFunction实现的多种方式
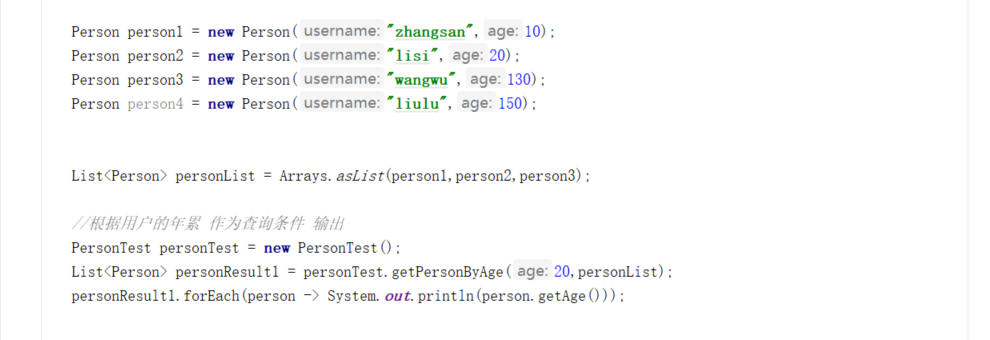
函数式编程 Predicate 判断 true Or false
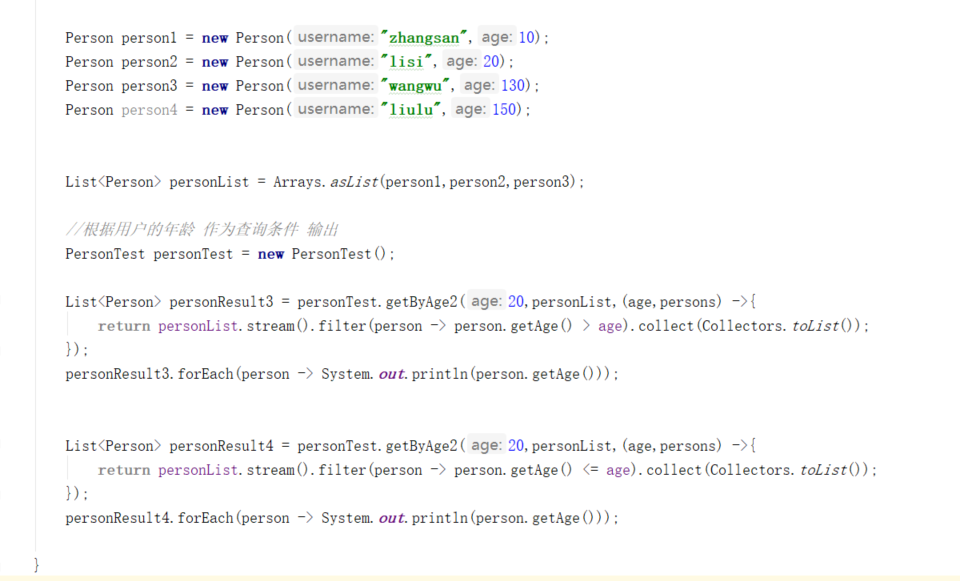
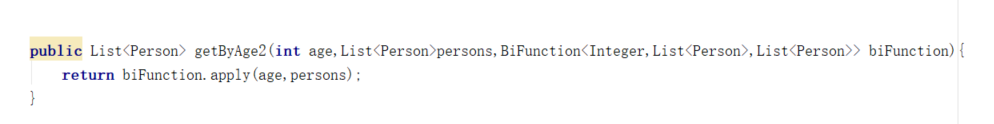
Predicate 进阶
public class PredicateTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10);
PredicateTest2 predicateTest2 = new PredicateTest2();
//找到集合所有的奇数
predicateTest2.conditionFilter(list,item ->item % 2 != 0);
System.out.println("------------------");
//找到集合所有的偶数
predicateTest2.conditionFilter(list,item ->item % 2 == 0);
System.out.println("------------------");
//找到集合大于5的数
predicateTest2.conditionFilter(list,item -> item > 5);
System.out.println("------------------");
//打印集合所有元素
predicateTest2.conditionFilter(list,item -> true );
}
//函数式编程 传递行为不传递值 传递2个值 一个数组,第二个行为
public void conditionFilter(List<Integer> list, Predicate<Integer> predicate){
for (Integer integer : list){
if (predicate.test(integer)){
System.out.print(" "+integer);
}
}
System.out.println();
}
//面向对象
public void findAllEven(List<Integer> list){
for(Integer i : list){
if(i % 2 == 0){
System.out.print(" "+integer);
}
}
}
}Predicate And Or Negate
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
/**
* @Auther: 梓
* @Date: 2019/3/8 15:14
* @Description:
*/
public class PredicateTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//要求找出当前集合所有大于5 而且是偶数的集合
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10);
PredicateTest3 predicateTest3 = new PredicateTest3();
System.out.println("------------AND----------------------");
predicateTest3.conditonFilter(list,item -> item > 5 ,item -> item % 2 ==0);
System.out.println("-------------OR----------------------");
predicateTest3.conditonFilter2(list,item -> item > 5 ,item -> item % 2 ==0);
System.out.println("-------------Negate------------------");
predicateTest3.conditonFilter3(list,item -> item > 5 ,item -> item % 2 ==0);
System.out.println("------------equls---------------------");
String a = "test";
if ("test".equals(a)){
System.out.println(a);
}
System.out.println("----------------isEqual----------------");
System.out.println(Predicate.isEqual("test").test("a"));
}
public void conditonFilter(List<Integer> list, Predicate<Integer> predicate,Predicate<Integer> predicate2){
for(Integer integer : list){
if (predicate.and(predicate2).test(integer)){
System.out.print( " "+integer);
}
}
System.out.println();
}
public void conditonFilter2(List<Integer> list, Predicate<Integer> predicate,Predicate<Integer> predicate2){
for(Integer integer : list){
if (predicate.or(predicate2).test(integer)){
System.out.print(" "+integer);
}
}
System.out.println();
}
public void conditonFilter3(List<Integer> list, Predicate<Integer> predicate,Predicate<Integer> predicate2){
for(Integer integer : list){
if (predicate.and(predicate2).negate().test(integer)){
System.out.print(" "+integer);
}
}
System.out.println();
}
public Predicate<String> isEqual (Object object){
return Predicate.isEqual(object);
}
}Supplier 函数式接口 : get()
实际场合常用于 工厂类
public class StudentTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("----------Supplier---");
Supplier<Student> studentSupplier = () -> new Student();
System.out.println(studentSupplier.get().getAge());
System.out.println("---构造方法引用----");
Supplier<Student> studentSupplier1 = Student::new;
System.out.println(studentSupplier1.get().getName());
}
}BinaryOpertor : 比较二个参数
public class BinaryOpertorTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryOpertorTest binaryOperator = new BinaryOpertorTest();
System.out.println(binaryOperator.compute(1,2,(value,value2) -> value + value2));
System.out.println("------minBy--长度--------");
System.out.println(binaryOperator.getShort("hello123","hello4567", (a,b) -> a.length() - b.length() ));
System.out.println("------minBy--首字母--------");
System.out.println(binaryOperator.getShort("hello","aorld",(a,b) ->a.charAt(0) - b.charAt(0)));
}
public int compute (int a ,int b , BinaryOperator<Integer> binaryOperator){
return binaryOperator.apply(a,b);
}
public String getShort (String a ,String b,Comparator<String> comparator){
return BinaryOperator.minBy(comparator).apply(a,b);
}
}
Optional :函数式判断NPE 从数据库取出来的数据 不一定知道为空使用isNotable
public class OptionalTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Optional<String> optional = Optional.of("hello");
Optional<String> optional = Optional.empty();
//取值
if (optional.isPresent()){
System.out.println(optional.get());
}
//推薦使用 構建一個為空的Optional
optional.ifPresent(item -> System.out.println(item));
System.out.println("---------------");
System.out.println(optional.orElse("world"));
System.out.println("----------------");
System.out.println(optional.orElseGet(() -> "nihao"));
}
}Optional 推荐用法
public class Employee {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}public class Comany {
private String name;
private List<Employee> employeeList;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public List<Employee> getEmployeeList() {
return employeeList;
}
public void setEmployeeList(List<Employee> employeeList) {
this.employeeList = employeeList;
}
}public class OptionalComany {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setName("zhangshan");
Employee employee1 = new Employee();
employee1.setName("lisi");
Comany comany = new Comany();
comany.setName("comany1");
List<Employee> employees = Arrays.asList(employee,employee1);
comany.setEmployeeList(employees);
//如果存在則返回,不存在返回空數組
// List<Employee> list = comany.getEmployeeList();
// if (null != list){
// return list;
// }else
// return new ArrayList<Employee>();
Optional<Comany> optional = Optional.ofNullable(comany);
System.out.println(optional.map(theCompany -> theCompany.getEmployeeList())
.orElse(Collections.emptyList()));
}
//不要試圖將Optional作為方法參數 或者在類中聲明optional的成員變量
public void test(Optional optional){
}
}方法引用 lamda 表达式的语法糖 :: lamdba表达式只有一个语句而刚好jdk里面又有方法实现
方法引用分类 :
- 类名::静态方法名
- 引用(对象名)::实例方法名
- 类名::实例方法名
- 构造方法引用::类名::new
我们可以方法引用看作【函数指针】 function pointer 指向另外一个函数
classname::staticmethod (方法引用 类似函数指针 指向方法)
classname.staticmethod (方法调用) List<String> list = Arrays.asList("0","12");
list.forEach(item -> System.out.println(item));
list.forEach(System.out::print);public class Student {
private String name;
private int score;
public Student(String name, int score) {
this.name = name;
this.score = score;
}
//排序方法[分数] 升序规则 -正 0 同 1倒序
public static int compareStudentByScore(Student s1 ,Student s2){
return s1.getScore() - s2.getScore();
}
//根据名字asrcl
public static int compareStudentByName(Student s1 ,Student s2){
return s1.getName().compareToIgnoreCase(s2.getName());
}
public int compareByScore(Student student){
return this.getScore() - student.getScore();
}
public int compareBySName(Student student){
return this.getName().compareToIgnoreCase(student.getName());
}
}public class StudentComparator {
public int comparatorStudentByScore(Student s1,Student s2){
return s1.getScore() - s2.getScore();
}
public int comparatorStudentByName(Student s1 , Student s2 ){
return s1.getName().compareToIgnoreCase(s2.getName());
}
}public class StudentMethondRefTest {
public String getString(Supplier<String> supplier){
return supplier.get()+"test";
}
public String getString2 (String str , Function<String,String> function){
return function.apply(str);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student1 = new Student("zhangsan",4);
Student student2 = new Student("lisi",5);
Student student3 = new Student("wangwu",3);
Student student4 = new Student("zhaoliu",6);
List<Student> studentList = Arrays.asList(student1,student2,student3,student4);
//lambda 集合排序
studentList.sort((s1,s2) -> Student.compareStudentByScore(s1,s2));
studentList.forEach(student -> System.out.print(" "+student.getScore()));
System.out.println();
System.out.println("-----------1.类名::静态方法名-------------");
//方法引用
studentList.sort(Student::compareStudentByScore);
studentList.forEach(student -> System.out.print(" "+student.getScore()));
System.out.println();
System.out.println("-----------2.引用(对象名)::实例方法名-------------");
//lambda表达式写法
StudentComparator studentComparator = new StudentComparator();
studentList.sort((s1,s2)-> studentComparator.comparatorStudentByScore(s1,s2));
studentList.forEach(student -> System.out.print(" "+student.getScore()));
//方法引用
studentList.sort(studentComparator::comparatorStudentByScore);
studentList.forEach(student -> System.out.print(" "+student.getScore()));
System.out.println();
System.out.println("-----------3.类名::实例方法名-------------");
//lambda表达式写法
studentList.sort(Student::compareByScore);
studentList.forEach(student -> System.out.print(" "+student.getScore()));
System.out.println();
System.out.println("-----------4.jdk自带的排序-------------");
List<String> cities =Arrays.asList("qiandao","chongqing","tianjin","beijing");
Collections.sort(cities,(ctiy1,city2) -> ctiy1.compareToIgnoreCase(city2));
cities.forEach(city-> System.out.print(" "+city));
//等价于
Collections.sort(cities,String::compareToIgnoreCase);
cities.forEach(city-> System.out.print(" "+city));
System.out.println();
System.out.println("-----------5.构造方法引用::类名::new-------------");
StudentMethondRefTest studentMethondRefTest = new StudentMethondRefTest();
System.out.println(studentMethondRefTest.getString(String::new));
System.out.println(studentMethondRefTest.getString2("hello",String::new));
}
}默认构造方法
public interface MyInterface {
default void myMythod(){
System.out.println("MyMethod");
}
}
public interface MyInterface2 {
default void myMythod(){
System.out.println("MyMethod2");
}
}
public class MyInterfaceImpl implements MyInterface {
@Override
public void myMythod() {
System.out.println("MyImpl");
}
}
public class MyClass implements MyInterface,MyInterface2 {
@Override
public void myMythod() {
MyInterface.super.myMythod();
MyInterface2.super.myMythod();
System.out.println("Myclass");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyClass myClass = new MyClass();
myClass.myMythod();
}
}
MyMethod
MyMethod2
Myclass
public class MyClass extends MyInterfaceImpl implements MyInterface2 {
// @Override
// public void myMythod() {
// MyInterface.super.myMythod();
// MyInterface2.super.myMythod();
// System.out.println("Myclass");
// }
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyClass myClass = new MyClass();
myClass.myMythod();
}
}
MyImplStream stream能更好的操作集合
流操作
- 源
- 零个或多个中间操作
- 终止操作
流操作的分类
- 惰性求值
- 及早求值
stream.xxx().yyy().zzz().count();
-("惰性求值 (中间操作): xxx().yyy().zzz()" )
-中间操作什么时候被发起 : 只有当 "count()"发起时,中间操作才会被执行
- ("及早求值 : count(): 立马求出值" )public void getPublishListHash(Map<String, Object> map, List<Skill> list) {
if (list == null || list.size() <= 0)
return;
List<String> skillIds = list.stream().map(Skill::getId).collect(Collectors.toList());
List<SkillRegister> skillRegisters = worthServiceprovider.getSkillRegisterService().getRegList(skillIds);
Map<String, Long> registerCountHash = skillRegisters.stream()
.collect(groupingBy(SkillRegister::getSkillId, Collectors.counting()));
Map<String, Long> registerSuccessCountHash = skillRegisters.stream()
.filter(e -> e.getStatus().equals(SkillRegisterStatus.SUCCESS.status))
.collect(groupingBy(SkillRegister::getSkillId, Collectors.counting()));
map.put("registerCountHash", registerCountHash);
map.put("registerSuccessCountHash", registerSuccessCountHash);
}