News: I started this project back in october 2019 and never expected it to become that large. The project grew and grew - so did main.cpp. So it was about time to have it split into modules. This was done in march/april. After spending some time on tests, improvements and implementing new features, refactoring-branch will is NOW the new master whereas the previous master a new branch named old. It will be kept as reference but won't by maintained anymore. Please be advised that moving to refactoring-branch will re-arrange ESP32's partition. All things to know are described here in german language. Development of the new master is documented here. Have fun and don't hesitate to contact me in case of problems/questions.
- EN: I've set up a primarily German-speaking community with much documentation. Also an international corner for non-German-speakers is available at https://forum.espuino.de. Github-Login can be used there but it's not mandatory.
- DE: Ich habe ein primär deutschsprachiges Forum aufgesetzt, welches ich mit reichlich Doku versehen habe. Würde mich freuen, euch dort zu sehen: https://forum.espuino.de. Ihr könnt euch dort mit eurem Github-Login einloggen, jedoch auch "normal" anmelden. Dokumenation findet ihr insbesondere hier: https://forum.espuino.de/c/dokumentation/anleitungen/10
- Partition-layout for ESP32 is changed along with this branch. This step was necessary in order to resize (enlarge) the memory-region where especially the assignments for the RFID-tags are saved. As all permanent settings (e.g. WiFi-settings) are saved there too, it's necessary to re-enter WiFi-credentials after update. But the most important thing is to recover the assignments for the RFID-tags. Please consult my migration-document.
Last three events:
- 30.09.2021: Added feature
PAUSE_WHEN_RFID_REMOVEDfor RC522 after having it already for PN5180 (thanks @elmar-ops for contribution) - 23.07.2021: Adding new playmode: from local .m3u-file (files or webstreams)
- 13.07.2021: Adding OTA-support via webGUI
- Some webstreams don't run. Guess it's a combination of saturated connection-pool and lack of heap-memory. Works probably better if ESP32-WROVER (e.g. Lolin D32 pro) is used, as this chip has PSRAM. Advice: Don't enable modules (e.g. MQTT) if you don't need them as this could save memory (and trouble).
- For ESPuinos making use of SPI for SD (instead of SD_MMC), there's currently a problem that sometimes leads to incomplete file-transfers via webtransfer or FTP. I'm about to investigate...
The basic idea of ESPuino is to provide a way, to use the Arduino-platform for a music-control-concept that supports locally stored music-files without DRM-restrictions. This basically means that RFID-tags are used to direct a music-player. Even for kids this concept is simple: place an RFID-object (card, character) on top of a box and the music starts to play. Place another RFID-object on it and anything else is played. Simple as that.
The core of my implementation is based on the popular ESP32 by Espressif. Having WiFi-support out-of-the-box makes it possible to provide further features like an integrated FTP-server (to feed the player with music), smarthome-integration via MQTT, webradio and administration via webgui. And nonetheless Bluetooth, too! However, my primary focus was to port the project to a modular base. Having said this mp3-decoding is done in software with a dedicated µSD-card-slot and music-output is done via I2S-protocol. I did all my tests on Adafruit's MAX98357A, UDA1334 and headphone-pcb. Hopefully, not only in theory, other DACs that support I2S can be used as well.
The heart of my project is an ESP32 on a Wemos Lolin32 development-board. If ordered in China (Aliexpress, eBay e.g.) it's pretty cheap (around 4€ => ok meanwhile price has doubled...) but even in Europe it's affordable. Make sure to install the drivers for the USB/Serial-chip (CP2102 e.g.). But probably it's better to use its big brother (which has battery-measurement, µSD-slot, PSRAM already included): Wemos Lolin D32 pro.
- MAX98357A (like Adafruit's)
- µSD-card-reader; 3.3V only; supports SPI + SD-MMC or cheaper
- RFID-reader RC-522
- RFID-reader PN5180
- RFID-tags
- Neopixel-ring
- Rotary Encoder
- Buttons
- Speaker
- µSD-card: doesn't have to be a super-fast one; µC is limiting the throughput. Tested 32GB without any problems.
- Much documentation in german language.
- I recommend to install Microsoft's Visual Studio Code. This is a popular and powerful IDE that gives you the ability to install tons of (well-supported) plugins.
- Install Platformio Plugin into Visual Studio Code and make sure to have a look at the documentation. Step-by-step-manual is available here
- Install Git and make a copy ("clone") my repository to your local computer using
git clone https://github.com/biologist79/ESPuino.git. Using git you can keep your local repository easily up to date without doing copy'n'paste. To keep it up to date rungit pull origin master. Further infos here. - (Optional) Install Gitlens as plugin (to have advanced Git-support).
- Now, that the git-repository is saved locally, import this folder into Platformio as a project.
- There's a file called
platformio.ini, that contains the configuration for different develboards (e.g. env:lolin32). Platformio supports hundrets of boards out of the box. So probably you need to change/extend that configuration-file. Guess Lolin32 is described in platformio.ini but you need Lolin D32, then lookup Platformio's documentation to know what to change. - Depending on your operating system (Windows, Mac OS, Linux), you'll probably need to change
upload_portandmonitor_portas well. - Edit
src/settings.haccording your needs. - Edit board-specific (
HAL) config-file (e.g.settings-lolin32.hfor Lolin32 orsettings-lolin_d32.hfor Lolin D32). If you're running a board that is not listed there: start withsettings-custom.hand change it according your needs. - Connect your develboard via USB, click the alien-head to the left, choose the project-task that matches your desired HAL and run
Upload and Monitor. All libraries necessary should be fetched in background now followed by code-compilation. After that, your ESP32 is flashed with the firmware. Depending on your develboard it might me necessary to push a button in order to allow ESP32 to enter flashmode (not necessary für Lolin32, D32 und D32 pro). - Now have a look at the serial-output at the bottom of Visual Studio Code's windows. At the first run there might appear a few error-messages (related to missing entries in NVS). Don't worry, this is just normal. However, make sure SD is running as this is mandatory!
- If everything ran fine, at the first run, ESPuino should open an access-point with the name "ESPuino". Join this WiFi with your computer (or mobile) and enter
http://192.168.4.1to your webbrowser. Enter WiFi-credentials and the hostname. After saving the configuraton, restart ESPuino. Hint: I tried to connect this access-point via Android mobile. Basically that's no problem, but as my mobile detected there'd be no internet-connection, it kept LTE-connection open and prevented me from connecting tohttp://192.168.4.1. So if in doubts better use a computer. - After reboot ESPuino tries to join your WiFi (with the credentials previously entered). If that was successful, an IP is shown in the serial-console of Visual Studio Code. You can call ESPuino's GUI using a webbrowser via this IP; make sure to allow Javascript. If mDNS-feature is active in
src/settings.h, you can use the hostname configured extended by .local instead the IP. So if you configuredespuinoas hostname, you can usehttp://espuino.localfor webgui and FTP. - Via FTP and webGUI you can upload data (but don't expect it to be super fast).
- FTP needs to be activated after boot if you need it! Don't forget to assign action
ENABLE_FTP_SERVERinsettings.hto be able to activate it. Neopixel flashes green (1x) if enabling was successful. It'll be disabled automatically after next reboot. Means: you have to enable it every time you need it (if reboot was in between). Sounds annoying and maybe it is, but's running this way in order to have more heap-memory available (for webstream) if FTP isn't necessary. - Via webbrowser you can configure various settings and pair RFID-tags with actions. If MQTT/FTP-support was not compiled, their config-tabs won't appear.
- Much much documentation in german language.
- Open settings.h
- Choose if optional modules (e.g. MQTT, FTP, Neopixel) should be compiled/enabled.
- Make sure to edit/review button-layout. Default-design is three buttons and a rotary-encoder. All actions available are listed in
src/values.h(values with numbers >= 100). - For debugging-purposes serialDebug can be set to ERROR, NOTICE, INFO or DEBUG. I usually have DEBUG set.
- If Neopixel enabled: set NUM_LEDS to the LED-number of your Neopixel-ring and define the Neopixel-type using
#define CHIPSET - Open board-specific config-file and edit according your needs.
- If you want to monitor battery's voltage, make sure to enable
MEASURE_BATTERY_VOLTAGE. Use a voltage-divider as voltage of a LiPo is way too high for ESP32 (only 3.3V supported!). For my tests I connected VBat with a serial connection of 130k + 130k resistors (VBat(+)--130k--X--130k--VBat(-)). X is the measure-point where to connect the GPIO to. If using Lolin D32 or Lolin D32 pro, make sure to leave both resistor-values unchanged at 100k - voltage-divider is already integrated there. Same goes for GPIO: leave unchanged at 35. Please note: via GUI upper and lower voltage cut-offs for visualisation of battery-voltage (Neopixel) is available. Additional GUI-configurable values are interval (in minutes) for checking battery voltage and the cut off-voltage below whose a warning is shown via Neopixel. - If you're using a headphone-pcb with a headphone jack that has a pin to indicate if there's a plug, you can use this signal along with the feature
HEADPHONE_ADJUST_ENABLEto limit the maximum headphone-voltage automatically. As per default you have to invert this signal (with a P-channel MOSFET) and connect it e.g. to GPIO22. - Enabling
SHUTDOWN_IF_SD_BOOT_FAILSis really recommended if you run your ESPuino in battery-mode without having a restart-button exposed to the outside of ESPuino's enclosure. Because otherwise there's no way to restart your ESPuino and the error-state will remain until battery is empty (or you open the enclosure, hehe). - Enabling
PLAY_LAST_RFID_AFTER_REBOOTwill tell ESPuino to remember the last RFID-tag played after next reboot. So rebooting ESPuino will end up in autoplay.
Having SD working is mandatory! However, there are two modes available to access SD-cards: SPI and SD-MMC (1 bit).
Advantages SD-MMC (1 bit) over SPI:
- Needs only three GPIOs (instead of four)
- It's faster. FTP-upload: 298 kiB vs 178 kiB. HTTP-upload: 350 kiB vs 184 kiB. (tested with filesize of 70.7 MiB.
So why using SPI if SD-MMC seems to be better? The primary problem of SD-MMC is: you cannot choose different GPIOs. That doesn't sound bad but this can (depending on the µSD-card-reader-module) be a problem because maybe GPIO2 is pulled HIGH to 3.3V by a 10k-resistor. For example this is the case when using the reader-module named above in hardware-setup. It's a problem because if GPIO2 is pulled high at boot, ESP32 doesn't enter flash-mode (so you cannot flash new firmwares). As soon as flash-mode is entered, it's no longer a problem. However, this behaviour can be an issue if ESP32 is deeply "burried" in ESPuino's enclosure and you want to update its firmware. But fortunately there's a way to bypass this problem: remove the pullup-resistor shown in the picture. It can be removed safely because if MMC-mode is set because pullup is done in software usingpinMode(2, INPUT_PULLUP);. So it's not really a problem but you have to take note of that!
RC522 is so to say the ESPuino-standard. It's cheap and works, but RFID-tag has to be placed near the reader. PN5180 instead has better RFID range/sensitivity and can read ISO-15693 / iCode SLIX2-tags aka 'Tonies' (you need a password to read Tonies), too. You can also wake-up the board with the card. Disadvantages: it's more expensive and needs more GPIOs (6/7 instead of 4). Refer PN5180's wire-section below for further informations. Hint: if using 3.3V make sure to connect PN5180 to +5V AND 3.3V. Sounds weird but it's necessary.
- Why 3.3V? Because: if you plan to use battery-mode with a LiPo, there's no 5 V available (unless USB is connected). That's why my design's focus is on 3.3 V. If you want to use 5 V - do so, but be advised it's not compatible with LiPo-battery-mode. The Mosfet-circuit for saving power in deepsleep (see Lolin32-schematics as reference) works as well for 5 V.
- MAX98357a: provides more power at 5 V but also runs at 3.3 V. Anyway: it's still loud enough (in my opinion).
- Neopixel: specification says it needs 5 V but runs at 3.3 V as well.
- RC522: needs 3.3 V (don't power with 5 V!)
- PN5180: at 3.3 V make sure to connect both 5 V and 3.3 V-pins to 3.3 V.
- SD: needs 3.3 V but if voltage-regulator is onboard, it can be connected to 5 V as well
- Rotary encoder: 3.3 V (don't power with 5 V! Encoder doens't care if connected to 3.3 or 5 V, but GPIOs of ESP32 do!)
I really really recommend to solder all the stuff onto a PCB as wiring the components with jumperwires on a breadboard can lead to many problems. Especially for the interconnect between µC and µSD-card-reader make sure to use short wires (like 10cm or so)! So be aware of this!
Have a look at the PCB-folder and the forum. I provided PCBs for a few types of develboards (and others will follow...).
Important: you can easily connect another I2S-DACs by just connecting them in parallel to the I2S-pins (DIN, BCLK, LRC). This is true for example if you plan to integrate a line/headphone-pcb. In general, this runs fine. But unfortunately especially this board lacks of a headphone jack, that takes note if a plug is inserted or not. Best way is to use a headphone jack that has a pin that is pulled to GND, if there's no plug and vice versa. Using for example a MOSFET-circuit, this GND-signal can be inverted in a way, that MAX98357.SD is pulled down to GND if there's a plug. Doing that will mute MAX98537a and so turn off the speaker immediately if there's a plug and vice versa. Have a look at the PCB-folder in order to view the detailed solution. Here's an example for such a headphone-pcb that makes use of GND.
Uses two SPI-instances. The first one for the RFID-reader and the second for SD-card-reader. This is also the setup, I personally use primarily.
| ESP32 (GPIO) | Hardware | Pin | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3.3 (5) V | SD-reader | VCC | Connect to p-channel MOSFET for power-saving when µC is off |
| GND | SD-reader | GND | |
| 15 | SD-reader | CS | |
| 13 | SD-reader | MOSI | |
| 16 | SD-reader | MISO | |
| 14 | SD-reader | SCK | |
| 3.3 V | RFID-reader | 3.3V | Connect to p-channel MOSFET for power-saving when µC is off |
| GND | RFID-reader | GND | |
| 21 | RFID-reader | CS/SDA | |
| 23 | RFID-reader | MOSI | |
| 19 | RFID-reader | MISO | |
| 18 | RFID-reader | SCK | |
| 5 / 3.3 V | MAX98357 | VIN | Connect to p-channel MOSFET for power-saving when µC is off |
| GND | MAX98357 | GND | |
| 25 | MAX98357 | DIN | |
| 27 | MAX98357 | BCLK | |
| 26 | MAX98357 | LRC | |
| --- | MAX98357 | SD | Info: if pulled down to GND amp will turn off |
| 34 | Rotary encoder | CLK | Change CLK with DT if you want to change the direction of RE |
| 35 | Rotary encoder | DT | Change CLK with DT if you want to change the direction of RE |
| 32 | Rotary encoder | BUTTON | |
| 3.3 V | Rotary encoder | + | |
| GND | Rotary encoder | GND | |
| 4 | Button (next) | ||
| GND | Button (next) | ||
| 2 | Button (previous) | ||
| GND | Button (previous) | ||
| 5 | Button (pause/play) | ||
| GND | Button (pause/play) | ||
| 3.3 V | Neopixel | V | Connect to p-channel MOSFET for power-saving when µC is off |
| GND | Neopixel | G | |
| 12 | Neopixel | DI | |
| 17 | N-channel Mosfet | Gate | |
| 33 | Voltage-divider / BAT | Optional: voltage-divider to monitor battery-voltage | |
| 22 | Headphone jack | Optional: if pulled to ground, headphone-volume is set |
Optionally, GPIO 17 can be used to drive a Mosfet-circuit in order to switch off peripherals (SD, Neopixel, RFID and MAX98357a) if ESP32 is in deepsleep. Please refer the schematics for my Lolin32-PCB for further informations. If you need further informations on transistor-circuits visit this website.
In general I recommend using a µSD-card-reader that can be run solely with 3.3V (doesn't have a voltage-regulator - don't use it with 5V!).
| ESP32 (GPIO) | Hardware | Pin | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| -- | SD-reader | CS | no CS required |
| 15 | SD-reader | MOSI | |
| 2 | SD-reader | MISO | make sure there's no hardware-pullup for MISO |
| 14 | SD-reader | SCK |
Make sure to enable SD_MMC_1BIT_MODE if you want to use this feature. Don't(!) enable SINGLE_SPI_ENABLE. SD-MMC-mode requires these fixed PINs listed above. You can find a good comparison of different SD-card-modes here: (https://www.instructables.com/Select-SD-Interface-for-ESP32/).
Advice: Double check that above PINs are not used elsewhere (e.g. GPIO2 is used as PREVIOUS_BUTTON as per default in settings.h).
Basically the same as using 2 SPI-instances but... In this case RFID-reader + SD-reader share SPI's SCK, MISO and MOSI. But make sure to use different CS-pins. Have to admit I had problems to get this running. Seems to be connected properly, but nothing happens when an RFID-tag is applied. Maybe anybody else wants to point out :-)
| ESP32 (GPIO) | Hardware | Pin | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3.3 (5) V | SD-reader | VCC | Connect to p-channel MOSFET for power-saving when µC is off |
| GND | SD-reader | GND | |
| 15 | SD-reader | CS | Don't share with RFID! |
| 3.3 V | RFID-reader | 3.3V | Connect to p-channel MOSFET for power-saving when µC is off |
| GND | RFID-reader | GND | |
| 21 | RFID-reader | CS/SDA | Don't share with SD! |
| 23 | RFID+SD-reader | MOSI | |
| 19 | RFID+SD-reader | MISO | |
| 18 | RFID+SD-reader | SCK | |
| 5 / 3.3 V | MAX98357 | VIN | Connect to p-channel MOSFET for power-saving when µC is off |
| GND | MAX98357 | GND | |
| 25 | MAX98357 | DIN | |
| 27 | MAX98357 | BCLK | |
| 26 | MAX98357 | LRC | |
| --- | MAX98357 | SD | Info: if pulled down to GND amp will turn off |
| 34 | Rotary encoder | CLK | Change CLK with DT if you want to change the direction of RE |
| 35 | Rotary encoder | DT | Change CLK with DT if you want to change the direction of RE |
| 32 | Rotary encoder | BUTTON | |
| 3.3 V | Rotary encoder | + | |
| GND | Rotary encoder | GND | |
| 4 | Button (next) | ||
| GND | Button (next) | ||
| 2 | Button (previous) | ||
| GND | Button (previous) | ||
| 5 | Button (pause/play) | ||
| GND | Button (pause/play) | ||
| 5 / 3.3 V | Neopixel | V | Connect to p-channel MOSFET for power-saving when µC is off |
| GND | Neopixel | G | |
| 12 | Neopixel | DI | |
| 17 | N-channel Mosfet | Gate | |
| 33 | Voltage-divider / BAT | Optional: voltage-divider to monitor battery-voltage | |
| 22 | Headphone jack | Optional: if pulled to ground, headphone-volume is set |
PN5180-reader needs at least two more GPIOs: RESET and BUSY. Double check pin-conflicts! RFID_READER_TYPE_PN5180 needs to be enabled to use this feature. Make sure to disable RFID_READER_TYPE_MFRC522 if doing so!
You can enable low power card-detection with PN5180_ENABLE_LPCD, but this needs another GPIO for IRQ. With low power card detection (LPCD) you can wake-up the ESP32 from deep-sleep just by applying a card to the reader. But: you need a PN5180-firmware >= 4.0 to use this feature. Most china-boards come with an older firmware, so be advised to flash them to latest firmware using this project. There's a PCB available for PN5180: Lolin32 + SD_MMC + PN5180.
| ESP32 (GPIO) | Hardware | Pin | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3.3 V | PN5180 RFID-reader | 3.3V | Connect to p-channel MOSFET for power-saving when µC is off |
| 3.3 V | 3.3V | For low power card detection mode (LPCD) connect directly to 3.3V | |
| 5 / 3.3 V | PN5180 RFID-reader | 5V | Don't forget to connect this pin the same way as 3.3V |
| GND | PN5180 RFID-reader | GND | |
| 21 | PN5180 RFID-reader | CS/SDA | Same as MFRC522. Don't share with SD! |
| 23 | PN5180 RFID-reader | MOSI | Same as MFRC522 |
| 19 | PN5180 RFID-reader | MISO | Same as MFRC522 |
| 18 | PN5180 RFID-reader | SCK | Same as MFRC522 |
| 16 | PN5180 RFID-reader | BUSY | be aware of SD MISO if running in SPI mode |
| 22 | PN5180 RFID-reader | RST | be aware of Headphone jack PIN |
| 39 | PN5180 RFID-reader | IRQ | optional, used for low power card detection (LPCD) |
When using a develboard with SD-card-reader already integrated (Lolin D32 Pro, several TTGO-boards), the pinouts described above my not fit. Feel free to change them according your needs. Additionaly some boards may use one or some of the GPIOs I used for their internal purposes and that reason for are maybe not exposed via pin-headers. However, having them exposed doesn't mean they can be used without limits. This is because some GPIOs have to be logical LOW or HIGH at start/boot for example and this is probably not the case when connecting stuff to it. Feel free to adjust the GPIOs proposed by me (but be adviced it could take a while to get it running). If you encounter problems please refer the board's manual first.
Here I described a solution for a board with many GPIOs used internally and a very limited number of GPIOs exposed. That's why I had to use different SPI-GPIOs for RFID as well. ESPuino supports this board and there's a discussion.
WiFi is mandatory for webgui, FTP and MQTT. However, WiFi can be temporarily or permanently disabled. There are two ways to do that:
- Use a special modification-card that can be configured via webgui
- Assign action
CMD_TOGGLE_WIFI_STATUSto a button (or multi-button). Default: press previous + next-button in parallel shortly. Now release both. This toggles the current WiFi-status: if it's currently enabled, it will be disabled instantly and vice versa. Please note: this WiFi-status will remain until you change it again, which means, that ESPuino will remember this state after the next reboot. Having Wifi enabled is indicated in idle-mode (no playlist active) with four white slow rotating LEDs whereas disabled WiFi is represented by those ones coloured green. Bluetooth-mode is indicated by blue LEDs.
ESPuino can be used as bluetooth-sink (a2dp). This mode can be enabled/disabled via a RFID-modification-card or by assigning action CMD_TOGGLE_BLUETOOTH_MODE to a button (or multi-button). Applying this will restart ESPuino immediately. Two modes are available which are toggled in between: "normal" and "bluetooth". Normal means: SD + WiFi are available whereas in mode "bluetooth" only bluetooth-support can be provided. Activated bluetooth is indicated by four slow rotating blue LEDs. Now you can stream to your ESPuino e.g. with your mobile device. Tested this with Android 8 and Mac OS: worked 100% flawless. Please note: due to memory-restrictions it's not possible to run Bluetooth in parallel with WiFi.
There might be situations where you run out of GPIOs. To address this, port-expander PCA9555 can be used to extend number of input-channels (output-mode is only supported in special cases). This port-expander provides 2 ports with 8 channels each - so 16 channels in total. To activate PCA9555 you need to enable PORT_EXPANDER_ENABLE. Like GPIOs in your develboard-specific settings-file, you can assign numbers. Range is 100->115 where 100: port 0 channel 0 -> 107: port 0 channel 7; 108: port 1 channel 0 -> 115: port 1 channel 7. Via expanderI2cAddress port-expander's I2C-address can be changed. It's 0x20 if all A0, A1, A2 are wired to GND.
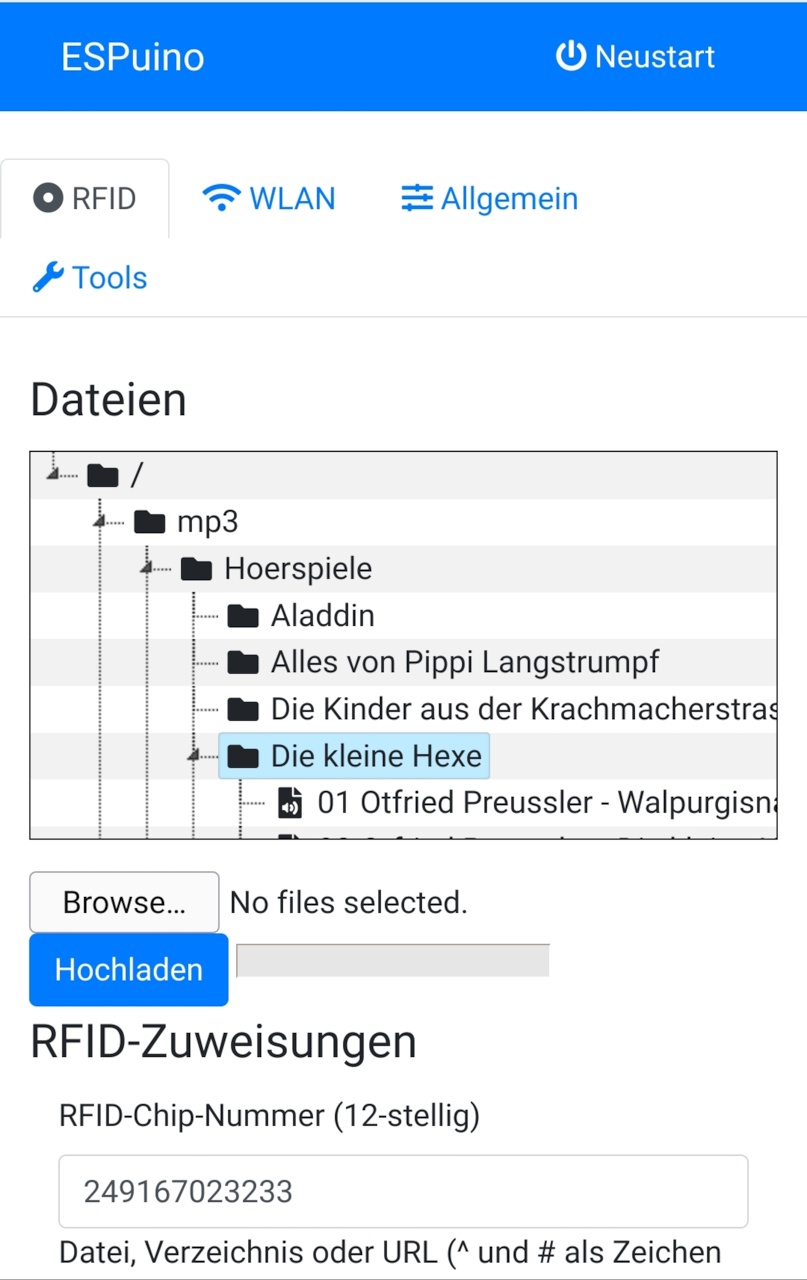
After making ESPuino part of your LAN/WiFi, the 'regular' webgui is available at the IP assigned by your router (or the configured hostname). Using this GUI, you can:
- configure WiFi
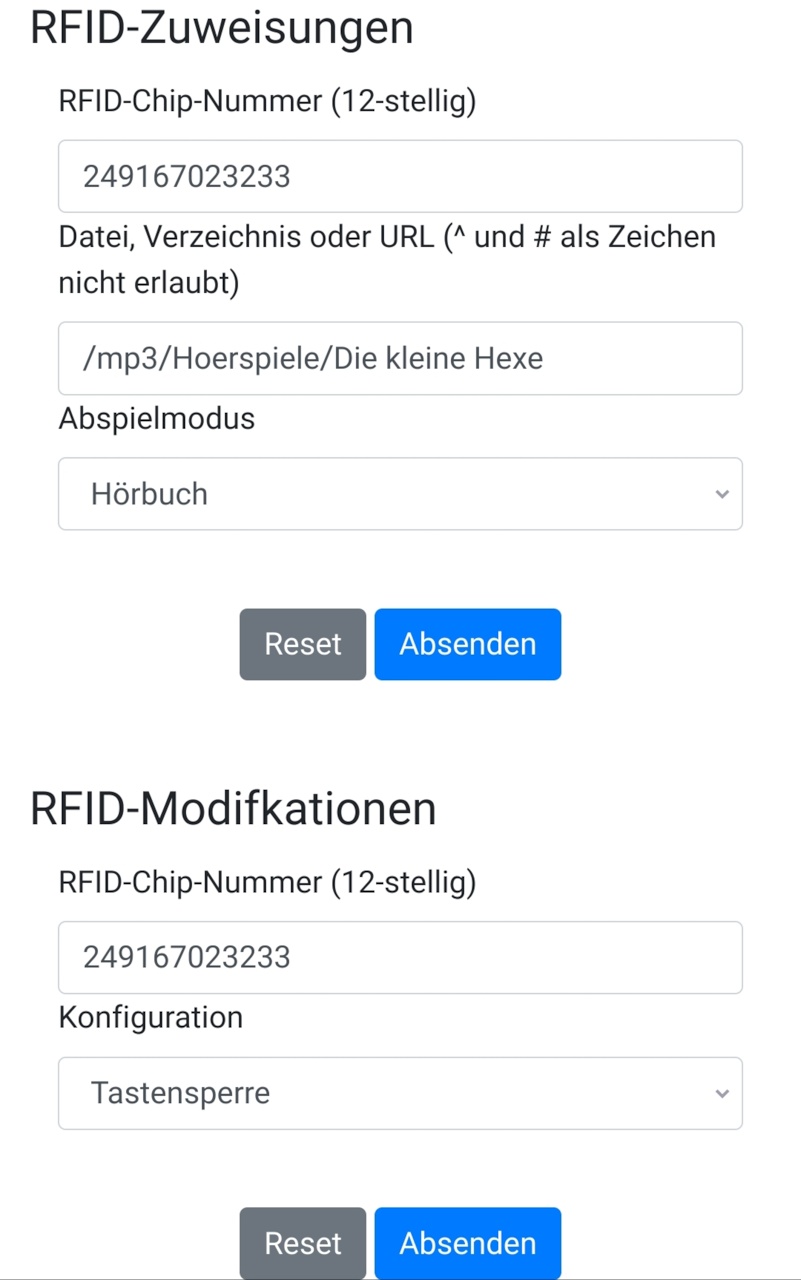
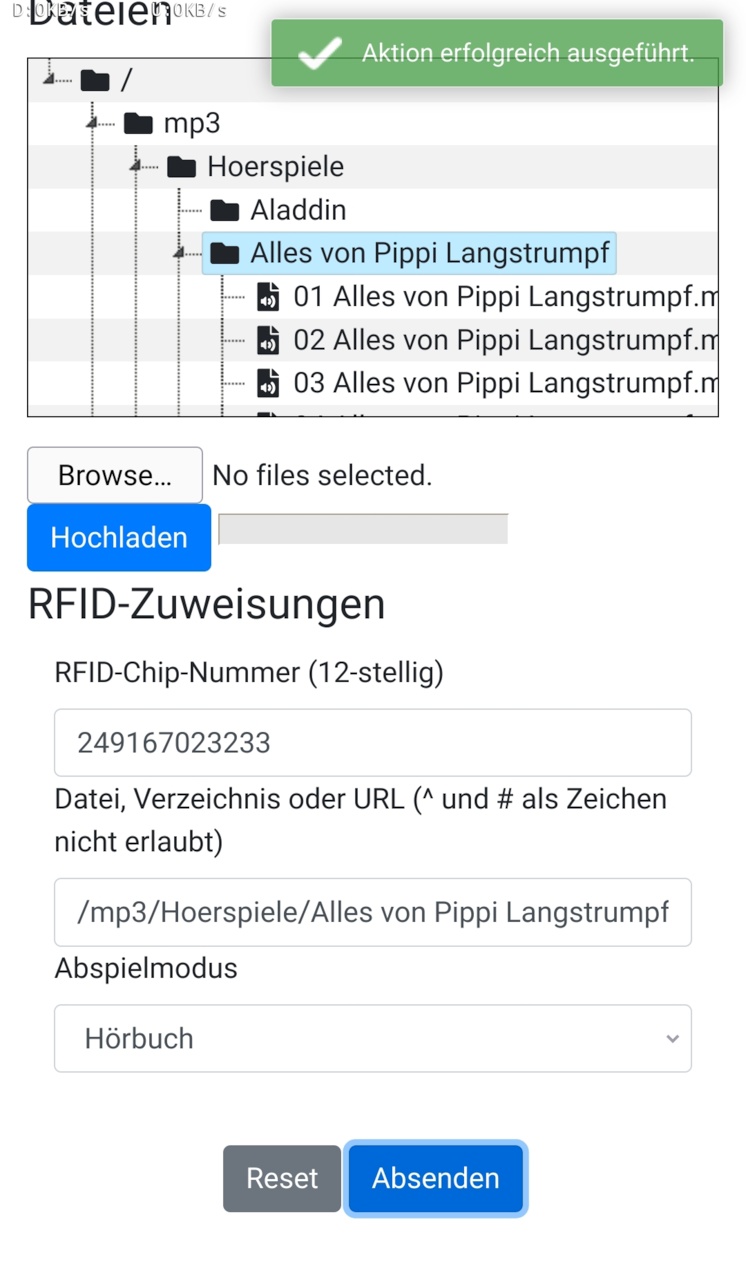
- make binding between RFID-tag, file/directory/URL and playMode
- make bindings between RFID-tag and a modification-type
- configure MQTT (if enabled)
- configure FTP (if enabled)
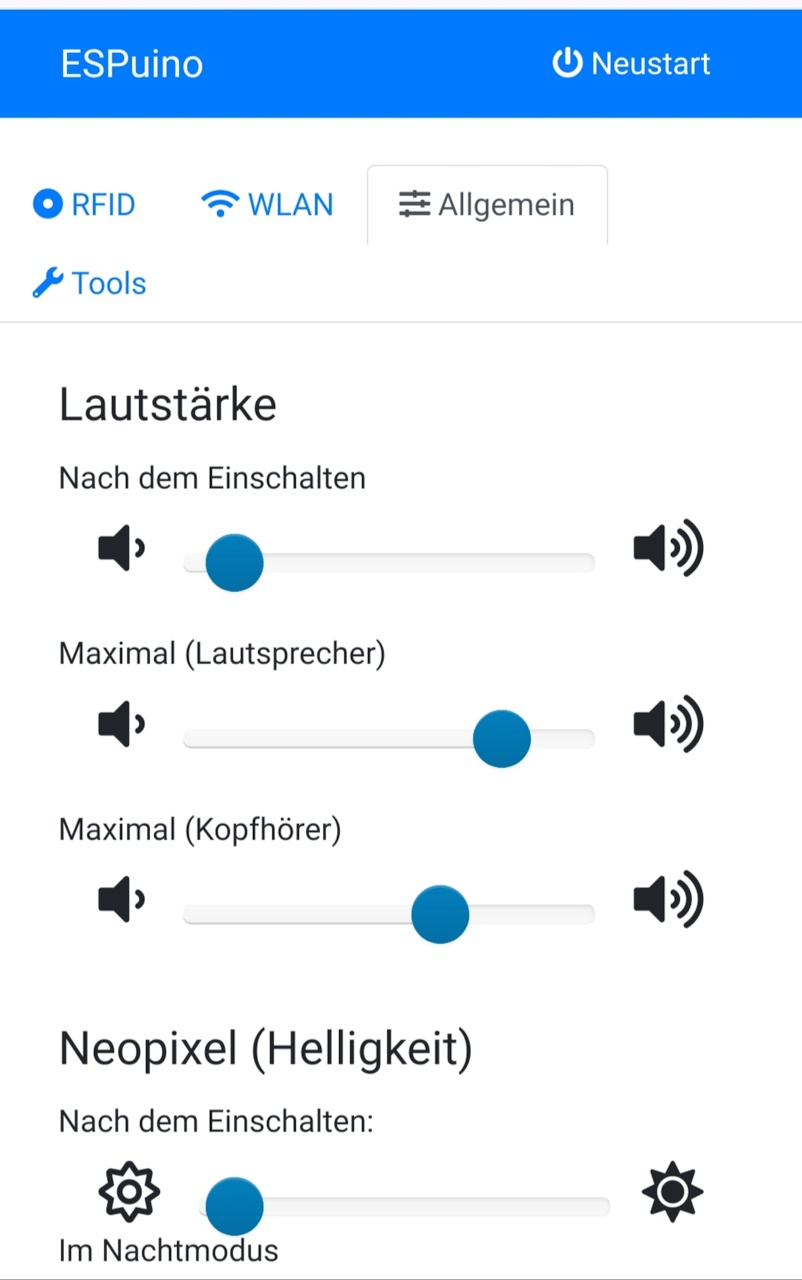
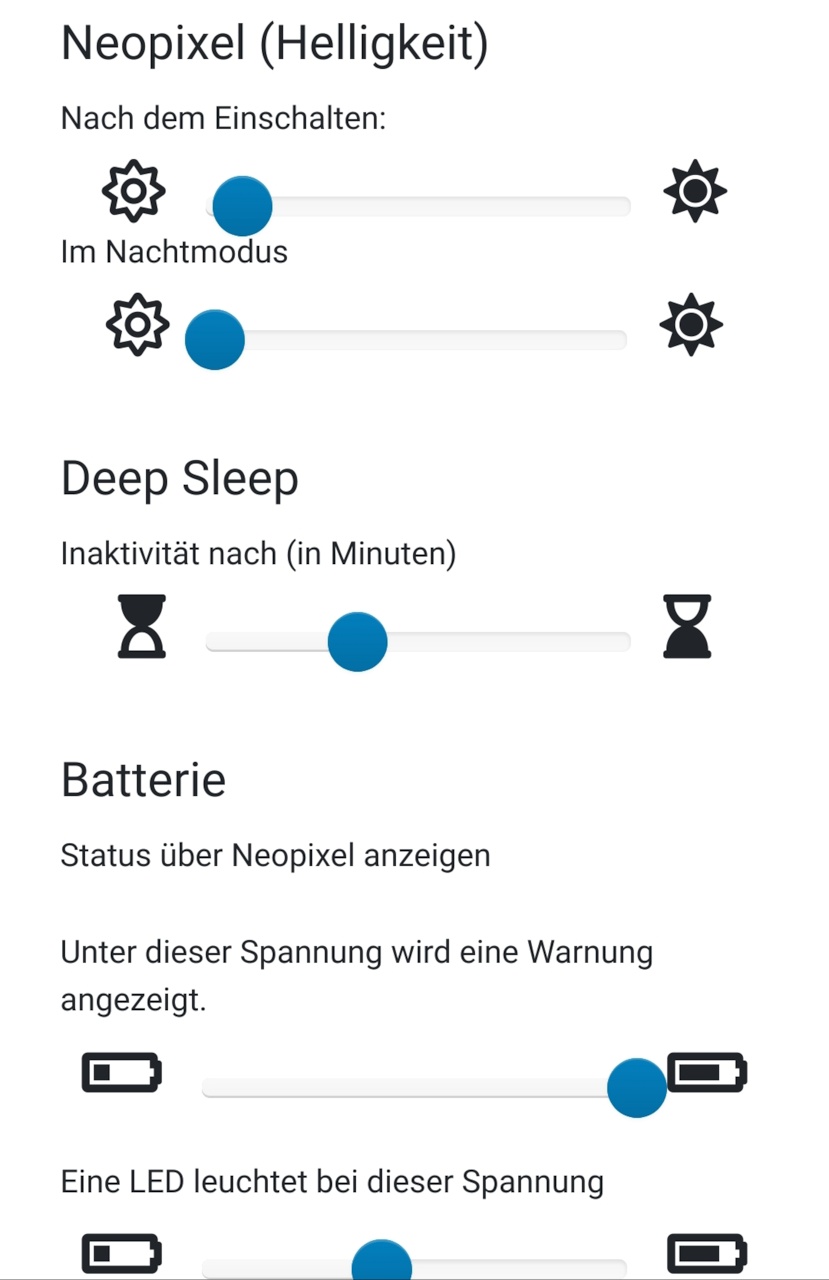
- configure nitial volume, maximum volume (speaker / headphone), brightness of Neopixel (nightmode / default) and inactivity-time
- view logs / status / current track
- control player
- upload audiofiles (called webtransfer)
- do OTA-updates (ESP32s with 16 MB of flash-memory only)
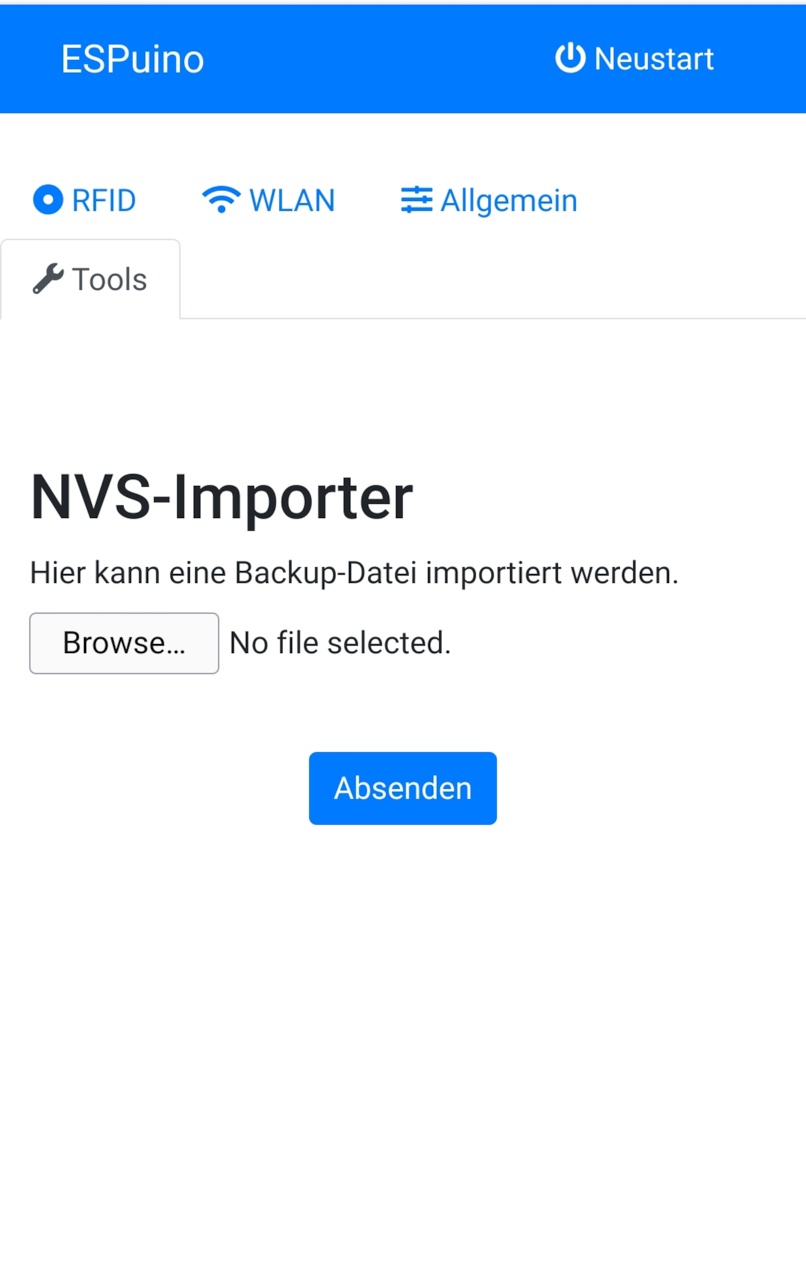
- import + delete NVS-RFID-assigments
- restart + shutdown ESPuino
Please note: as you apply a RFID-tag to the RFID-reader, the corresponding ID is pushed to the GUI. So there's no need to enter such IDs manually (unless you want to). Filepath is filled out automatically by selecting a file/directory in the filebrowser.
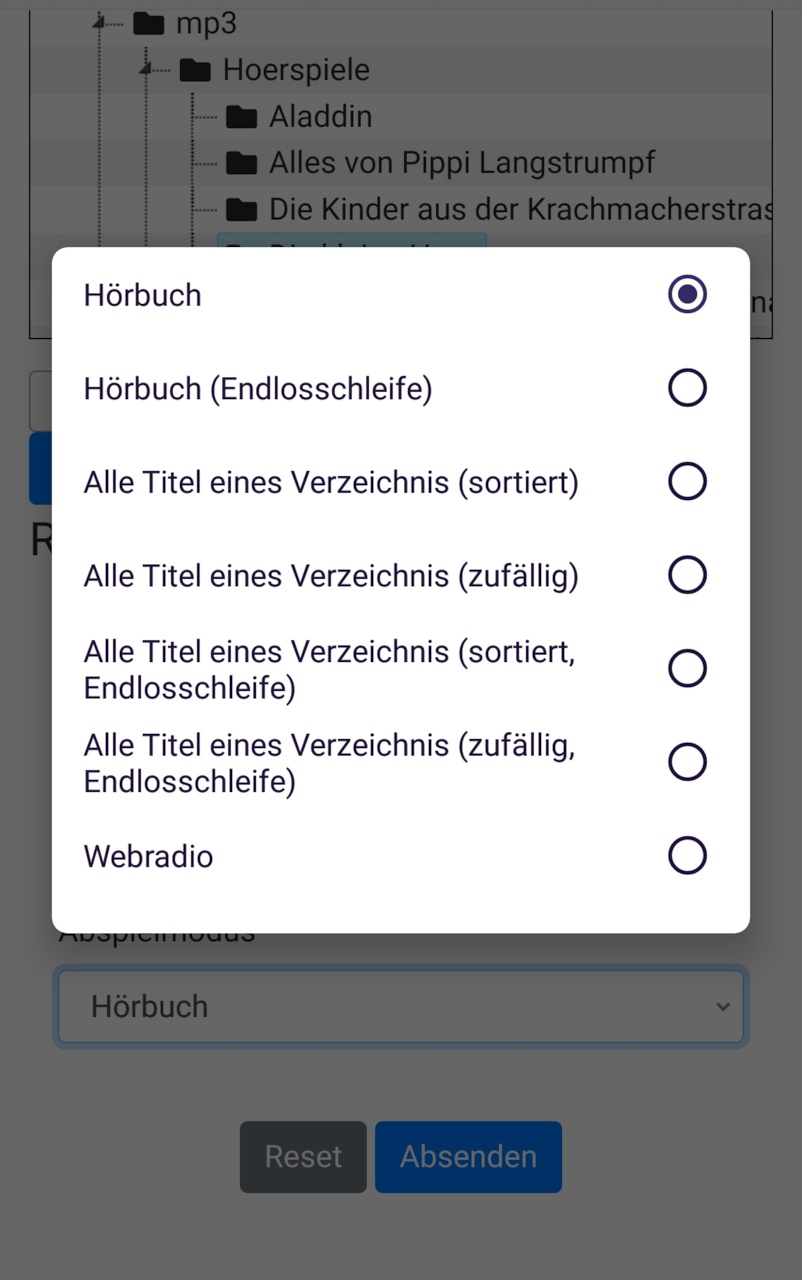
It's not just simply playing music; different playmodes are supported:
single track=> plays one track one timesingle track (loop)=> plays one track foreveraudiobook=> single file or playlist/folder; last play-position (file and playlist) is saved (when pushing pause or moving to another track) and re-used next timeaudiobook(loop) => same as audiobook but loops foreverfolder/playlist (alph. sorted)=> plays all tracks in alph. order from a folder one timefolder/playlist (random order)=> plays all tracks in random order from a folder one timefolder/playlist (alph. sorted)=> plays all tracks in alph. order from a folder foreverfolder/playlist (random order)=> plays all tracks in random order from a folder foreverwebradio=> always only one "track": plays a webstreamlist (files from SD and/or webstreams) from local .m3u-File=> can be one or more files / webradio-stations with local .m3u as sourcefile
There are special RFID-tags, that don't start music by themself but can modify things. If applied a second time, it's previous action/modification will be reversed. Please note: all sleep-modes do dimming (Neopixel) automatically because it's supposed to be used in the evening when going to bed. Well, at least that's my children's indication :-) So first make sure to start the music then use a modification-card in order to apply your desired modification:
- lock/unlock all buttons
- sleep after 5/30/60/120 minutes
- sleep after end of current track
- sleep after end of playlist
- sleep after five tracks
- dimm neopixel
- current track in loop-mode (is "stronger" than playlist-loop but doesn't overwrite it!)
- playlist in loop-mode
- track und playlist loop-mode can both be activated at the same time, but unless track-loop isn't deactivated, playlist-loop won't be effective
- Toggle WiFi (enable/disable) => disabling WiFi while webstream is active will stop a running webstream instantly!
- Toggle Bluetooth (enable/disable) => restarts ESPuino immediately
Indicates different things. Don't forget configuration of number of LEDs via #define NUM_LEDS
- While booting: every second LED (rotating orange)
- Unable to mount SD: LEDs flashing red (will remain forever unless SD-card is available or
SHUTDOWN_IF_SD_BOOT_FAILSis active) - IDLE: four LEDs slow rotating (white if WiFi enabled; green if WiFi disabled)
- BLUETOOTH: four LEDs slow rotating coloured blue
- ERROR: all LEDs flashing red (1x) if an action was not accepted
- OK: all LEDs flashing green (1x) if an action was accepted
- BUSY: violet; four fast rotating LEDs when generating a playlist. Duration depends on the number of files in your playlist.
- track-progress: rainbow; number of LEDs relative to play-progress
- playlist-progress: blue; appears only shortly in playlist-mode with the beginning every new track; number of LEDs relative to progress
- webstream: two slow rotating LEDs that change their colours rainbow-wise as the stream proceeds
- volume: green => red-gradient; number of LEDs relative from current to max volume
- switching off: red-circle that grows until long-press-time is reached
- buttons locked: track-progress-LEDs coloured red
- paused: track-progress-LEDs coloured orange
- rewind: if single-track-loop is activated a LED-rewind is performed when restarting the given track
- (Optional) Undervoltage: flashes three times red if battery-voltage is too low. This voltage-level can be configured via GUI.
- (Optional) Short press of rotary encoder's button provides battery-voltage visualisation via Neopixel. Upper und lower voltage cut-offs can be adjusted via GUI. So for example if lower voltage is set to 3.2 V and upper voltage to 4.2 V, 50% of the LEDs indicate a voltage of 3.7 V.
Please note: some Neopixels use a reversed addressing which leads to the 'problem', that all effects are shown
counter clockwise. If you want to change that behaviour, just enable NEOPIXEL_REVERSE_ROTATION.
Important: this section describes my default-design: 3 buttons + rotary-encoder. Feel free to change button-number and button-actions according your needs in settings.h and your develboard-specific config-file (e.g. settings-lolin32.h). At maximum you can activate five buttons + rotary-encoder.
Minimum duration for long press (to distinguish vom short press) in ms is defined by intervalToLongPress. All actions available are listed in src/values.h. If using GPIO >= 35 make sure to add a external pullup-resistor (10 k).
- previous (short): previous track / beginning of the first track if pressed while first track is playing
- previous (long): first track of playlist
- next (short): next track of playlist
- next (long): last track of playlist
- pause/play (short/long): pause/play
- rotary encoder (turning): vol +/-
- rotary encoder (button long): switch off (only when on)
- rotary encoder (button short): switch on (when switched off)
- rotary encoder (button short): show battery-voltage via Neopixel (when switched on and
MEASURE_BATTERY_VOLTAGEis active) - previous (long; keep pressed) + next (short) + release (both): toggle WiFi enabled/disabled
- Music starts to play right after a valid RFID-tag was applied.
- If
PLAY_LAST_RFID_AFTER_REBOOTis active, ESPuino will remember the last RFID applied => music-autoplay. - If a folder should be played that contains many mp3s, the playlist-generation can take a few seconds.
- For all playmodes that are not single tracks or webradio a filecache is available to speed up playlist-generation. The cache is generated as you apply the corresponding RFID-tag for the first time. Use
CACHED_PLAYLIST_ENABLEto enable it - I really recommend to use it. - A file's name including path isn't allowed exceed 255 characters.
- While playlist is generated Neopixel indicates BUSY-mode.
- After last track was played, Neopixel indicates IDLE-mode.
This mode is different from the others because the last playposition is saved. Playposition is saved when...
- next track starts.
- first/previous/last track requested by button.
- pause was pressed.
- track is over.
- playlist is over (playposition is set back to the first track and file-position 0).
- Please note: last playposition is not saved when applying a new RFID-tag. This is intended because otherwise you wouldn't have a possibility to not save it. If you want to save the playposition: press pause first.
- FTP needs to be activated after boot! Don't forget to assign action
ENABLE_FTP_SERVERinsettings.hor use a modification-card to to activate it! Neopixel flashes green (1x) if enabling was successful. It'll be disabled automatically after next reboot. Means: you have to enable it every time you need it (if reboot was in between). Sounds annoying and maybe it is, but's running this way in order to save heap-memory when FTP isn't needed. - Why FTP? Well: in order to avoid exposing µSD-card or disassembling ESPuino all the time for adding new music, it's possible to transfer music to the µSD-card using FTP. Another possibility is to do via webGUI (webtransfer).
- Default-user and password are set to
esp32/esp32but can be changed via GUI. - Make sure to set the max. number of parallel connections to ONE in your FTP-client and the charset to CP437. CP437 is important if you want to use german umlauts (öäüß).
- Secured FTP is not available. So make sure to disable SSL/TLS.
- Software: my recommendation is Filezilla as it's free and available for multiple platforms.
- Don't expect a super fast data-transfer; it's around 185 kB/s (SPI-mode) and 310 kB/s (MMC-mode).
- Please note: if music is played in parallel, this rate decrases dramatically! So better stop playback when doing a FTP-transfer.
As already described in the modify-section, there are different sleepmodes available. Additionaly µC will be put into deepsleep after 10 minutes of inactivity (configurable my maxInactivityTime) unless ESPuino doesn't play music, has a FTP-client connected and any input via buttons. Every button-interaction resets the counter.
Everything that can be controlled via RFID-tags and buttons, can also be controlled via MQTT (excepting toggling WiFi-status as this doesn't make sense). All manual interactions (buttons, RFID-tags) are also sent to MQTT in parallel, so everything is always in-sync (unless Wifi/MQTT-connection is broken). In my home-setup I'm using openHAB to "encapsulate" MQTT into a nice GUI, that's accessible via APP + web. I described a sample-config for openHAB2. However, meanwhile openHAB3 is available and all the stuff described can also be configured via GUI. Be advised that openHAB is pretty complex and you have to spend some time to get familiar with it.
Please refer ESP32-audioI2S, as this is the library I used for music-decoding. Make sure to update especially this library regularly as it's development is still in progress.
As all assignments between RFID-IDs and actions (playmode, file to play...) is saved in ESP's NVS, the problem is that it's all gone when the ESP is broken. So that's where a backup comes into play. So every time you change or add a new assignment between a RFID-tag and an action via GUI, a backup-file is saved on the µSD-card. The file's name can be changed via backupFile. So better don't delete it! Using the webgui you can use the upload-form to import such a file.
As already described, MQTT is supported. In order to use it it's necessary to run a MQTT-broker; Mosquitto for instance. After connecting to it, ESPuino subscribes to all command-topics. State-topics are used to push states to the broker in order to inform others if anything changed (change of volume, new playlist, new track... name it). Others, like openHAB, subscribe to state-topics end send commands via command-topics. So it's not just limited to openHAB. It's just necessary to use a platform, that supports MQTT. For further informations (and pictures) refer the subfolder.
Feel free to use your own smarthome-environments (instead of openHAB). The MQTT-topics available are described as follows. Please note: if you want to send a command to ESPuino, you have to use a cmnd-topic whereas ESPuino pushes its states back via state-topics. So guess you want to change the volume to 8 you have to send this number via topic-variable topicLoudnessCmnd. Immediately after doing to, ESPuino sends a conformation of this command using topicLoudnessState. To get hands on MQTT I recommend this one as introducton (covers more than you need for ESPuino).
| topic-variable | range | meaning |
|---|---|---|
| topicSleepCmnd | 0 or OFF | Power off ESPuino immediately |
| topicSleepState | ON or OFF | Sends ESPuino's current/last state |
| topicRfidCmnd | 12 digits | Set number of RFID-tag which 'emulates' an RFID-tag (e.g. 123789456089) |
| topicRfidState | 12 digits | ID of current RFID-tag (if not a modification-card) |
| topicTrackState | String | Sends current track number, total number of tracks and full path of curren track. E.g. "(2/10) /mp3/kinderlieder/Ri ra rutsch.mp3" |
| topicTrackControlCmnd | 1 -> 7 | 1=stop; 2=unused!; 3=play/pause; 4=next; 5=prev; 6=first; 7=last |
| topicLoudnessCmnd | 0 -> 21 | Set loudness (depends on minVolume / maxVolume) |
| topicLoudnessState | 0 -> 21 | Sends loudness (depends on minVolume / maxVolume |
| topicSleepTimerCmnd | EOP | Power off after end to playlist |
| EOT | Power off after end of track | |
| EO5T | Power off after end of five tracks | |
| 1 -> 2^32 | Duration in minutes to power off | |
| 0 | Deactivate timer (if active) | |
| topicSleepTimerState | various | Sends active timer (EOP, EOT, EO5T, 0, ...) |
| topicState | Online, Offline | Online when powering on, Offline when powering off |
| topicCurrentIPv4IP | IPv4-string | Sends ESPuino's IP-address (e.g. 192.168.2.78) |
| topicLockControlsCmnd | ON, OFF | Set if controls (buttons, rotary encoder) should be locked |
| topicLockControlsState | ON, OFF | Sends if controls (buttons, rotary encoder) are locked |
| topicPlaymodeState | 0 - 10 | Sends current playmode (single track, audiobook...; see playmodes) |
| topicRepeatModeCmnd | 0 - 3 | Set repeat-mode: 0=no; 1=track; 2=playlist; 3=both |
| topicRepeatModeState | 0 - 3 | Sends repeat-mode |
| topicLedBrightnessCmnd | 0 - 255 | Set brightness of Neopixel |
| topicLedBrightnessState | 0 - 255 | Sends brightness of Neopixel |
| topicBatteryVoltage | float | Voltage (e.g. 3.81) |
| topicWiFiRssiState | int | Numeric WiFi signal-strength (dBm) |