标签: 算法考试
##1. C/C++语言常见问题
scanf以空格和换行结束,读入除字符外的数据时可自动跳过空格long long的读入和输出格式均为“%lld”;double的读入格式时“%lf”,输出格式为“%f”.- 输出如01,02这种格式的数据用“
%02d” - 使用getchar()接收字符时,要注意过滤空格和换行
- 幂函数的使用:
pow(double r,double p)---> r^p - 计算
ln(4) --> log(4)计算logab ---> log(b)/log(a) - 判定
if(a == 0) ---> if(!a)判定if(a!=0) --> if(a) - 数组大小只可以时常量 如
int a[10] - 冒泡排序算法:
/*
* 冒泡排序属于比较排序的一种;
* 时间复杂度与数据的初始排列有关,最好的为O(N),最坏的为O(N^2);
* 空间复杂度为O(1);
* 冒泡排序是稳定的排序算法。
*/
void BubbleSort(int a[],int n){
for(int i = 0; i < n-1; i++){
for(int j = i; j < n; j++){
if(a[j]>a[j+1])
swap(a[j],a[j+1]);
}
}
}- 二维数组的每一个元素都是一维数组
- 当一个整数小于10^9时,用
int,当大于10^9时,用long long,浮点数一律用double - 当数组需要申请的空间太大时(10^6),需要将其定义在主函数外。
#include<stdio.h>
int a[1000000];
int main(){
······
}memset(数组名,值(0/-1),sizeof(数组名))对数组中的每一个元素赋相同的值。注:使用时要加string.h头文件
//a数组全赋为0
int a[5];
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));gets(string)识别换行作为结束符,因此,在使用完scanf()时应用getchar()将换行吸收掉。puts()输出时自动在字符串末尾加上换行。- string.h 中常见方法
char str[] = "PAT";
strlen(str);//获取str中字符的个数(不包括末尾的结束符‘\0‘)
int res = strcmp(str1,str2);//比较字符串str1与str2的大小(字典序),如果 res>0 则str1>str2,如果 res == 0,则str1 == str2,如果 res < 0 ,则 str1 < str2;
strcpy(str1,str2);//把字符数组str2复制给str1;
strcat(str1,str2);//把字符数组str2接到str1上;
- 数组名是常量,不能进行运算;指针变量可以进行运算。
int a[10];
int *p;
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
p = a;
//*(p+i) 与 a[i] 的作用是一样的- C++中的引用,可以在不使用指针的情况下实现局部变量的修改,从而引起原变量的改变。
//输出结果为 1
void change(int &x){
x = 1;
}
int main(){
int x = 10;
change(x);
printf("%d\n",x);
return 0;
}- 结构体的用法
struct student{
int age;
char name[20];
char major[20];
}stu,*p;
scanf("%d%s%s",&stu.age,stu.name,stu.major);
scanf("%d%s%s",&p->age,p->name,p->major);- C++中的输入与输出 cin 与 cout
cin >> n;
cout << n << endl;- 浮点数的比较
const double eps = 1e-8;
#define Equ(a,b) (fabs((a)-(b))<(eps))
#define More(a,b) (((a)-(b))>(eps))
#define Less(a,b) (((a)-(b))<(-eps))
#define MoreEqu(a,b) (((a)-(b))>(-eps)) //大于与等于的结合
#define LessEqu(a,b) (((a)-(b))<(eps)) //小于与等于的结合- 多点测试结束代码
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF){
}
----------------------------------------
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--){
}
- 输出一组数据,最后一个数据后不要空格
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
printf("%d",a[i]);
if(i < n-1)
printf(" ");
}- 日期处理:求两个日期之间的差,需要判定平年和闰年。
//month[][0] 表示平年的每个月份,month[][1] 表示闰年的每个月份
int month[13][2] = {
{0,0},{31,31},{28,29},{31,31},{30,30},{31,31},{30,30},{31,31},{31,31},{30,30},{31,31},{30,30},{31,31}
};
//判定是否是闰年
bool isLeap(int year){
return (year%4==0 && year % 100 != 0)||(year %400 == 0);
}- 进制转换
//将P进制数x转换为十进制数y
int y = 0,product = 1;
while(x != 0){
y = y + (x%10)*product;
x = x/10;
product = product * p;
}
//将数组a[n]转换为十进制数y 注:数组低位存的是十进制的高位
int y = 0;
int product = 1;
for(int i = n-1; i >= 0; i--){
y = y+a[i]*product;
product = product*10;
}
//将十进制数y转换为Q进制数Z 注:正常顺序应为高位到低位输出
int z[40],num = 0;
do{
z[num++] = y%Q;
y = y/Q;
}while(y!=0);- 字符串反转
void reverse(char str[],int n){
for(int i = 0; i <= n/2; i++){
swap(str[i],str[n-i-1]);n
}
}- 判定输入单词的个数
int num = 0;
char ans[90][90];
while(scanf("%s",ans[num])!=EOF){
num++;
}##2. 常见算法
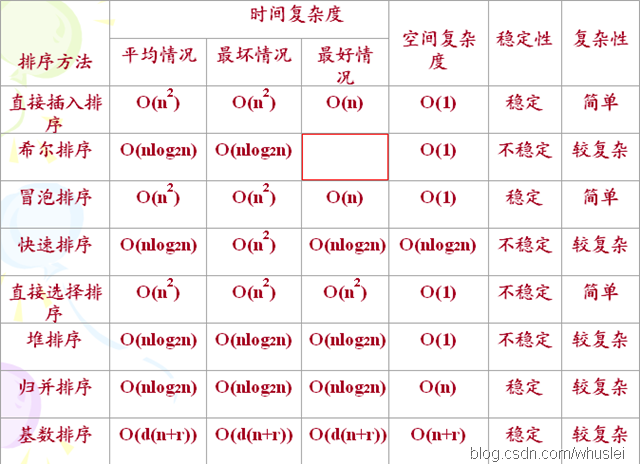
27. 常见排序算法总结:
28. 
void SelectSort(int a[],int n){
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
int k = i;
for(int j = i; j < n; j++){
if(a[j] < a[k]){
k = j;
}
}
swap(a[i],a[k]);
}
}- 插入排序:时间复杂度:O(N^2) 空间复杂度:O(1) 稳定性:稳定
int A[maxn],n;
void insertSort(){
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++){
int temp = A[i],j = i;
while(j > 1 && temp < A[j-1]){
A[j] = A[j-1];
j--;
}
A[j] = temp;
}
}- c++ 中的sort()函数使用技巧
sort()函数的使用必须加上头文件“#include”和“using >namespace std;”默认递增排序 sort(元素首地址,尾元素的下一个地址,比较函数(选填)); int a[10]; sort(a,a+4);//将a[0]~a[3]递增排序
//排名的实现
stu[0].r = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){
if(stu[i].score == stu[i-1].score){
stu[i].r = stu[i-1].r;
}else{
sru[i].r = i+1;
}
}- hash 的常见技巧
//总体思路是空间换时间。
bool hashtable[1000];
hashtable[x] == true;//表示x在N个正整数中出现过,反之没出现过
hashtable[x]++;//表示x在N个正整数中出现过的次数
3. 字符串转整数
//全大写字母
int hashFunc(char str[],int len){
int id = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
id = id*26 + (str[i]-'A');
}
return id;
}
//既有大写又有小写字母
int hashFunc(char str[],int len){
int id = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
if(str[i] <= 'Z' && str[i] >= 'A'){
id = id * 52 + (str[i] - 'A');
}else if(str[i] <= 'z' && str[i] >= 'a'){
id = id * 52 + (str[i] - 'a') + 26;
}
}
return id;
}- 二分查找
//默认a[]是递增的 传入的是[0,n-1]
int binarySearch(int a[],int left,int right,int x){
int mid;
while(left <= right){
mid = (left+right)/2;
if(a[mid] == x) return mid;
else if(a[mid] > x) right = mid -1;
else left = mid + 1;
}
return -1;
}
寻找序列中第一个满足某条件的位置 [0,n]
int solve(int a[],int left, int right,int x){
int mid;
while(left < right){
mid = (left + right)/2;
if(条件成立){
right = mid;
}else{
left = mid + 1;
}
}
return left;
}- int型整数转换成int型数组
//int型整数转换成int型数组
void to_array(int n,int num[]){
int len = 0;
do{
num[len++] = n % 10;
n = n/10;
}
}
//int型数组转换成int型整数
int to_number(int num[],int len){
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
sum = sum * 10 + num[i];
}
return sum;
}-最大公约数/最小公倍数
//最大公约数
int gcd(int a,int b){
if(b == 0) return a;
else return gcd(b,a%b);
}
//最小公倍数
int lcm(int a,int b){
return (a*b)/gcd(a,b);
}- 分数的表示与化简
struct Fraction{
int up,down;//分子,分母
}
//约分函数
Fraction reduction(Fraction result){
if(result.down < 0){
result.up = -result.up;
result.down = -result.down;
}
if(result.up == 0){
result.down = 1;
}else{
int d = gcd(abs(result.up),abs(result.down));
result.up /= d;
result.down /= d;
}
}
//分数加法
Fraction add(Fraction f1,Fraction f2){
Fraction result;
result.up = f1.up * f2.down + f1.down * f2.up;
result.down = f1.down *f2.down;
return reduction(result);
}
//分数减法
Fraction minu(Fraction f1,Fraction f2){
Fraction result;
result.up = f1.up * f2.down - f1.down * f2.up;
result.down = f1.down *f2.down;
return reduction(result);
}
//分数乘法
Fraction multi(Fraction f1,Fraction f2){
Fraction result;
result.up = f1.up * f2.up;
result.down = f1.down *f2.down;
return reduction(result);
}
//分数除法
Fraction divide(Fraction f1,Fraction f2){
Fraction result;
result.up = f1.up * f2.down;
result.down = f1.down *f2.up;
return reduction(result);
}
//分数输出
void showResult(Fraction f){
f = reduction(f);
if(f.down == 1) printf("%lld",f.up);
else if(abs(f.up)>abs(f.down)){
printf("%d %d/%d",f.up/f.down,abs(f.up)%f.down);
}else{
printf("%d/%d",f.up,f.down);
}
}- 素数
//判定素数
bool isPrime(int n){
if(n <= 1) return false;
int sqr = (int)sqrt(1.0*n);
for(int i = 2; i <= sqr; i++){
if(n % i == 0) return false;
}
return true;
}
//获取素数表
const int maxn = 101;
int prime[maxn],pNum = 0;
bool p[maxn] = {0};
void Find_Prime(){
for(int i = 1; i < maxn; i++){
if(isPrime[i] == true){
p[i] = true;
prime[pNum++] = i;
}
}
}- 大整数运算
//大整数表示
struct bign{
int d[1000];
int len;
bign(){
memset(d,0,sizeof(d));
len = 0;
}
};
//将字符串储存到bign中
bign change(char str[]){
bign a;
a.len = strlen(str);
for(int i = 0; i < a.len; i++){
a.d[i] = str[a.len - i - 1] - '0';
}
return a;
}
//比较大小
int compare(bign a,bign b){
if(a.len < b.len) return -1;
else if(a.len > b.len) return 1;
else{
for(int i = a.len - 1; i >= 0; i--){
if(a.d[i] > b.d[i]) return 1;
else if(a.d[i] < b.d[i]) return -1;
}
return 0;
}
}
//大整数输出
void print(bign a){
for(int i = a.len-1; i >= 0; i--){
printf("%d",a.d[i]);
}
}
//高精度加法
bign add(bign a,bign b){
bign c;
int carry = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < a.len || i < b.len; i++){
int temp = a.d[i] + b.d[i] + carry;
c.d[c.len++] = temp % 10;
carry = temp /10;
}
if(carry != 0) c.d[len++] = carry;
return c;
}
//高精度减法
bign sub(bign a,bign b){
bign c;
for(int i = 0; i < a.len || i < b.len; i++){
if(a.d[i] < b.d[i]){
a.d[i+1]--;
a.d[i] += 10;
}
c.d[i] = a.d[i] - b.d[i];
}
while(c.len - 1 >= 1 && c.d[c.len-1] == 0){
c.len--;
}
}- C++标准模板库(STL)学习
- vector
//vector 叫做变长数组
//使用vector需要添加#include<vector>和using namespace std;
//vector定义操作
vector<int> name;
vector<double> name;
struct node{
int value;
struct node* next;
};
vector<node> name;
//vector数组
vector<int> vi[1000];
//vector访问 和数组一样可通过下标访问 范围:0 - vi.size()-1
vector<int> vi;
vi[0];
//增删数据
vi.push_back(5);//在vi容器末尾添加一个数据
vi.pop_back();//删除vi容器的末尾数据
vi.size();//获取vi容器中的数据个数
vi.clear();//清除所有数据- set
//set是一个内部自动升序排序且不含重复数据的容器
//使用时要添加 #include<set> 和 using namespace std;
//set 定义
set<int> name;
set<int> a[100];//set 数组
//set 数据访问:使用迭代器it 并通过*it 来访问具体数据
set<int>::iterator it;
set<int> st;
for(it = st.begin(); it != st.end(); it++){
printf("%d",*it);
}
//插入数据,插入后将自动升序排序且去重
insert(5);
//查找
find(5);//返回的是其迭代器
st.size();//获取vi容器中的数据个数
st.clear();//清除所有数据- string 用法(重点)
//使用时要添加 #include<string> 和 using namespace std;
//string 定义
string str;
string str1 = "abc";
//访问:可通过下标访问
printf("%c",str1[1]);
//注:读入和输出只能用cin 和 cout
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string str;
cin>>str;
cout << str;
return 0;
}
//或用string.c_str();
prinf("%s\n",str.c_str());
//string 类型的变量可以直接比大小、直接用“+”拼接
str.size();//放回长度
//插入
str.insert(pos,string);//向str[pos]处开始插入string,且原字符向后移
//迭代器
string::iterator it;
//可用*(it+i)访问具体元素
//删除it所指向的元素
str.erase(it);
//删除从str[pos]开始到str[pos+length]的元素
str.erase(pos,length);
str.clear();//删除所有数据
//查找
str.find(str1);//放回str1在str中第一次出现的位置,如果不存在则放回string::npos;- map(映射) 注:在建立映射时会自动按键的升序排列
//map常见用法是实现 string 到 int 的映射
//map使用要添加#include<map> 和 using namespace std;
map<string,int> mp;
map<set<int>,string> mp;
//访问:1.通过下标访问 2.通过迭代器访问
map<string,int> mp;
mp["yangchen"] = 23;//其中键是唯一的
map<string,int>::iterator it;
for(it = mp.begin(); it != mp.end(); it++){
printf("%s-->%d\n",it->first,it->second);
}
//find(key)返回键为key的映射的迭代器,如果不存在则返回mp.end();
mp.find(key);
//删除键为key 的映射
mp.erase(key);
mp.clear();//清除所有数据
mp.size();//获得映射数目- queue(队列) 先进先出
//使用时要添加 #include<queue> 和 using namespace std;
queue<int> q;
//添加数据
q.push(i);
//获取队首和队尾
q.front();
q.back();
//出队列
q.pop();
//判定队列是否为空
q.empty();
//返回对内元素个数
q.size();
//队列的清空
while(!q.empty()){
q.pop();
}- stack (栈) 后进先出
//使用时要添加#include<stack> 和 using namespace std;
stack<int> st;
//入栈
st.push(i);
//出栈
st.pop();
//获取栈顶元素
st.top();
//判空
st.empty();
//大小
st.size();
//栈的清空
while(!st.empty()){
st.pop();
}- algorithm 头文件下的常用函数
//使用下列函数时要添加#include<algorithm>
max(a,b);//返回a,b中的最大值
min(a,b);//返回a,b中的最小值
swap(a,b);//交换a,b的值
int a[10];
reverse(a,a+4);//将a[0]~a[3]反转
fill(a,a+4,233);//将a[0]~a[3]均赋值为233
lower_bound(first,last,val);//在[first,last)中寻找第一个大于等于val的元素的位置,如果是数组则返回该位置的指针,如果是容器,则则返回该位置的迭代器;
upper_bound(first,last,val);//在[first,last)中寻找第一个大于val的元素的位置,如果是数组则返回该位置的指针,如果是容器,则则返回该位置的迭代器;- 链表
//考试中一般以静态链表为主
//new 关键字的使用
node* node1 = new node;//返回的是指向node类型的指针
delete(node1);//new 需与delete()配套使用
struct Node{
typename data;
int next;
bool flag;
}node[maxn];
for(int i = 0; i < maxn; i++){
node[i].flag = false;
}
int count;
int p = begin;
while(p != -1){
count++;
node[p].flag = true;
p = node[p].next;
}
void cmp(Node a,Node b){
if(a.flag == false || b.flag == false){
return a.flag > b.flag;
}else {
return a.data < b.data;
}
}- 二叉树
//二叉树的储存结构
struct node{
typename data;
struct node* lchild;
struct node* rchild;
};
//新建结点
node* newNode(int v){
node* Node = new node;
Node.data = v;
Node.lchild = Node.rchild = NULL;
return Node;
}
//查找结点,并修改结点值
void search(node* root,int x,int newdata){
if(root == NULL) retrun;
if(root->data == x) root->data = newdata;
search(root->lchild,x,newdata);
search(root->rchild,x,newdata);
}
//插入结点,需要修改root,故要加引用
void insert(node* &root,int x){
if(root == NULL){
root = newNode(x);
return;
}
if(){
insert(root->lchild,x);
}else{
insert(root->rchild,x);
}
}
//二叉树的创建
node* create(int data[],int n){
node* root = NULL;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
insert(root,data[i]);
}
return root;
}
//完全二叉树用数组存放的顺序和该二叉树层序遍历的结果一致
//二叉树的遍历
//先序遍历 根->左->右 一般二叉树的建树是按先序序列建立的
void preoreder(node* root){
if(root == NULL){
return;
}
visit(root->data);
preorder(root->lchild);
preorder(root->rchild);
}
//中序遍历 左->根->右
//知道中序序列和其他任一遍历的序列都可以建立一颗二叉树
void inorder(node* root){
if(root == NULL){
return;
}
preorder(root->lchild);
visit(root->data);
preorder(root->rchild);
}
//后序遍历 左->右->根
void postorder(node* root){
if(root == NULL){
return;
}
preorder(root->lchild);
preorder(root->rchild);
visit(root->data);
}
//层序遍历
#include<string.h>
#include<queue>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
void layerOrder(node* root){
queue<node*> q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()){
node* now = q.front();
q.pop();
visit(now->data);
if(now->lchild!=NULL) q.push(lchild);
if(now->rchild != NULL) q.push(rchild);
}
}
//层序遍历带层数
//重新定义二叉树结点
struct node{
typename data;
int layer;
struct node* lchild;
struct node* rchild;
}
void layerOrderWithLayerNum(node* root){
queue<node*> q;
root->layer = 1;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()){
node* now = q.front();
q.pop();
visit(now->data);
if(now->lchild != NULL){
now->lchild->layer = now->layer+1;
q.push(now->lchild);
}
if(now->rchild != NULL){
now->rchild->layer = now->layer+1;
q.push(now->rchild);
}
}
}
//已知先序序列和中序序列,重新建立二叉树
node* create(int preL,int preR,int inL,int inR){
if(preL > preR) return NULL;
node* root = new node;
root->data = pre[preL];
int k;
for(k = inL; k <= inR; k++){
if(in[k] == pre[preL]) break;
}
int numLeft = k - inL;
root->lchild = create(preL + 1,preL + numLeft,inL,k-1);
root->rchild = create(preL + numLeft + 1,preR,k+1,inR);
return root;
}
//BST 排序二叉树
//查找
void search(node* root,int x){
if(root == NULL) return;
if(x == root->data) {
visit(root->data);
}else if(x > root->data) search(root->rchild,x);
else if(x < root->data) search(root->lchild,x);
}
//其他操作与一般二叉树一致
//二叉树的中序遍历序列是递增的
//二叉查找数的删除
node* findMax(node* root){
while(root->rchild != NULL){
root = root->rchild;
}
return root;
}
node* findMin(node* root){
while(root->lchild != NULL){
root = root->lchild;
}
return root;
}
void deleteNode(node* &root,int x){
if(root == NULL) return;
if(root->data == x){
if(root->lchild == NULL && root->rchild == NULL){
root = NULL;
}else if(root->lchild != NULL){
node* pre = findMax(root->lchild);
root->data = pre->data;
deleteNode(root->lchild,pre->data);
}else if(root->rchild != NULL){
node* next = findMin(root->rchild);
root->data = next->data;
deleteNode(root->rchild,next->data);
}
}else if(root->data > x){
deleteNode(root->lchild,x);
}else {
deleteNode(root->rchild,x);
}
}
//一般数的静态写法
struct node{
typename data;
vector<int> child;
}Node[maxn];
int index = 0;
int newNode(int v){
Node[index].data = v;
Node[index].chlid.clear();
return index++;
}
//数的先根遍历
void preOrder(int root){
visit(Node[root].data);
for(int i = 0; i < Node[root].child.size(); i++){
preOrder(Node[root].child[i]);
}
}
//树的层序遍历
void layerOrder(int root){
queue<int> q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()){
int now = q.front();
q.pop();
visit();
for(int i = 0; i < Node[now].child.size(); i++){
q.push(Node[now].child[i]);
}
}
}- 并查集
//1.初始化
int father[N];
for(int i = 0; i <= N; i++){
father[i] = i;
}
//2.查找
int findFather(int x){
while(x != father[x]){
x = father[x];
}
return x;
}
//3.合并
void Union(int a,int b){
int faA = findFather(a);
int faB = findFather(b);
if(faA != faB){
father[faA] = faB;
}
}
//4.路径压缩
int findFather(int x){
int a = x;
while(x != father[x]){
x = father[x];
}
while(a != father[a]){
int z = a;
a = father[a];
father[z] = x;
}
return x;
}
//带秩的并查集(一个根结点下有几个孩子结点)
//1.初始化
int num[N];
int father[N];
int max = -10000000000;
for(int i = 0; i <= N; i++){
father[i] = i;
num[i] = 1;//开始时每个根结点下只有一个孩子
}
//2.查找
int findFather(int x){
while(x != father[x]){
x = father[x];
}
return x;
}
//3.合并
void Union(int a,int b){
int faA = findFather(a);
int faB = findFather(b);
if(faA == faB) return;
if(num[faA] > num[faB]){
father[faB] = faA;
num[faA] += num[faB];
if(num[faA] > max){
max = num[faA];
}
}else{
father[faA] = faB;
num[faB] += num[faA];
if(num[faB] > num[faA]){
max = num[faB];
}
}
}
//4.路径压缩
int findFather(int x){
int a = x;
while(x != father[x]){
x = father[x];
}
while(a != father[a]){
int z = a;
a = father[a];
father[z] = x;
}
return x;
}- 图
//邻接矩阵的表示
int G[N][N];
//邻接表的表示
//只表示顶点,不表示权值
vector<int> Adj[N];
//表示顶点,表示权值
struct node{
int v;
int w;
};
vector<node> Adj[N];
//赋值操作
node temp;
temp.v = 8;
temp.w = 9;
Adj[0].push_back(temp);
//图的遍历
//DFS 邻接矩阵 如果是无向图,则DFS次数就是图的联通快数
const int MAXV = 1000;
const int INF = 10000000;
int n,G[MAXV][MAXV];
bool vis[MAXV] = {false};
void DFS(int u,int depth){
vis[u] = true;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(vis[i] == false && G[u][i] != INF){
DFS(i,depth++);
}
}
}
void DFSTrave(){
for(int u = 0; u < n; u++){
if(vis[u] == false){
DFS(u,1);
}
}
}
//DFS 邻接表版
const int MAXV = 1000;
vector<int> Adj[MAXV];
bool vis[MAXV] = {false};
void DFS(int u,int depth){
vis[u] = true;
for(int i = 0; i < Adj[u].size(); i++){
int v = Adj[u][i];
if(vis[v] == false)
DFS(v,depth++);
}
}
void DFSTrave(){
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(vis[i] == false)
DFS(i,1);
}
}
//BFS 广度遍历
//邻接矩阵版
const int MAXV = 1000;
const int INF = 1000000;
int n;
int G[MAXV][MAXV];
bool vis[MAXV] = {false};
void init(){
fill(G[0],G[0]+MAXV*MAXV,INF);
}
void BFS(int u){
queue<int> q;
q.push(u);
vis[u] = true;
while(!q.empty()){
int v = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(vis[i] == false && G[v][i] != INF){
q.push(i);
vis[i] = true;
}
}
}
}
void BFSTrave(){
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(vis[i] == false) BFS(i);
}
}
//邻接表版
const int MAXV = 1000;
int n;
bool vis[MAXV] = {false};
vector<int> Adj[MAXV];
void BFS(int u){
queue<int> q;
q.push(u);
vis[u] = true;
while(!q.empty()){
int v = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < Adj[u].size(); i++){
int t = Adj[u][i];
if(vis[t] == false) q.push(t);
}
}
}
void BFSTrave(){
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(vis[i] == false) BFS(i);
}
}
//遍历的同时记录层号
struct Node{
int v;
int layer;
};
vector<Node> Adj[N];
void BFS(int s){
queue<Node> q;
Node start;
start.v = s;
start.layer = 0;
q.push(start);
vis[start.v] = false;
while(!q.empty()){
Node front = q.front();
q.pop();
int u = front.v;
for(int i = 0; i < Adj[u].size(); i++){
Node next = Adj[u][i];
next.layer = front.layer+1;
if(vis[next.v] == false){
q.push(next);
vis[next.v] = true;
}
}
}
}
//Dijkstra 算法
//邻接矩阵版
const int MAXV = 1000;
const int INF = 1000000000;
int n,G[MAXV][MAXV];
bool vis[MAXV] = {false};
int d[MAXV];
void Dijkstra(int s){
fill(d,d+MAXV,INF);
d[s] = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
int u = -1,MIN = INF;
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
if(vis[j] == false && d[j] < MIN){
MIN = d[j];
u = j;
}
}
if(u == -1) return;
vis[u] = true;
for(int v = 0; v < n; v++){
if(vis[v] == false && G[u][v] != INF && d[u] + G[u][v] < d[v]){
d[v] = d[u] + G[u][v];
}
}
}
}
//邻接表版
const int MAXV = 1000;
const int INF = 1000000000;
struct Node{
int v;
int dis;
};
vector<Node> Adj[MAXV];
int n,d[MAXV];
bool vis[MAXV] = {false};
void Dijkstra(int s){
fill(d,d+MAXV,INF);
d[s] = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
int u = -1, MIN = INF;
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
if(vis[j] == false && d[j] < MIN){
MIN = d[j];
u = j;
}
}
if(u == -1) return;
vis[u] = true;
for(int j = 0; j < Adj[u].size(); j++){
int v = Adj[u][j].v;
if(vis[v] == false && d[u] + Adj[u][j].dis < d[v]){
d[v] = d[u] +Adj[u][j].dis;
}
}
}
}
//初始化图
fill(G[0],G[0]+MAXV*MAXV,INF);
const int MAXV = 1000;
const int INF = 10000000;
int n,G[MAXV][MAXV],cost[MAXV][MAXV];
int d[MAXV],minCost = INF;
bool vis[MAXV] = {false};
vector<int> pre[MAXV];
vector<int> tempPath,path;
void Dijkstra(int s){
fill(d,d+MAXV,INF);
d[s] = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
int u = -1, MIN = INF;
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
if(vis[j] == false && d[j] < MIN){
MIN = d[j];
u = j;
}
}
if(u == -1) return;
vis[u] = true;
for(int v = 0; v < n; v++){
if(vis[v] == false && G[u][v] != INF){
if(d[u] + G[u][v] < d[v]){
d[v] = d[u] + G[u][v];
pre[v].clear();
pre[v].push_back(u);
}else if(d[u] + G[u][v] == d[v]){
pre[v].push_back(u);
}
}
}
}
}
void DFS(int v){
if(v == st){
tempPath.push_back(v);
int tempCost = 0;//记录当前路径的花费之和
for(int i = tempPath.size()-1; i > 0; i--){
int id = tempPath[i];
int inNext = tempPath[i-1];
tempCost += cost[id][idNext];
}
//如果是计算结点的物质之和
int tempWeight = 0;
for(int i = tempPath.size()- 1; i >= 0; i--){
tempWeight += w[tempPath[i]];
}
//有最优则更新
if(tempCost < minCost){
minCost = tempCost;
path = tempPath;
}
tempPath.pop_back();
return;
}
tempPath.push_back(v);
for(int i = 0; i< pre[v].size(); i++){
DFS(pre[v][i]);
}
tempPath.pop_back();
}
//获取的path 路径要倒着输出
for(int i =0; i< path.size(); i++){
printf("%d ",path[i]);
}
//prim算法求最小生成树
const int MAXV = 1000;
const int INF = 100000000;
int n,G[MAXV][MAXV];
int d[MAXV];//这里的d[]表示点到集合S的距离
bool vis[MAXV] = {false};
int prim(int s){
fill(d,d+MAXV,INF);
d[s] = 0;
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 0 ; i < n; i++){
int u = -1, MIN = INF;
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
if(vis[j] == false && d[j] < MIN){
MIN = d[j];
u = j;
}
}
if(u == -1) return;
vis[u] = false;
ans += d[u];
for(int v = 0; v < n; v++){
if(vis[v] == false && G[u][v] != INF && G[u][v] < d[v]){
d[v] = G[u][v];
}
}
}
return ans;
}- 简单动态规划
//动态规划是一种用来解决一类最优化问题的算法**。
//动态规划会把子问题的结果记录下来,这样就避免了重复计算,节省了时间。
//1.最大连续子序列和
//如 -2 11 -4 13 -5 -2 的最大连续子序列和为 11 -4 13 --> 20
//用dp[i]表示以A[i]结尾的连续序列,那么只有两种情况,这个最大连续子序列和以A[i]开始以A[i]结尾,或者说是从前面某处A[p]开始一直到A[i]结束。于是状态转移方程为 dp[i] = max(A[i],d[i-1]+A[i]);
//具体代码如下:
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 10010;
int A[maxn],dp[maxn];
int main(){
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
scanf("%d",&A[i]);
}
dp[0] = A[0];
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){
dp[i] = max(A[i],dp[i-1]+A[i]);
}
int k = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(dp[i] > dp[k]){
k = i;
}
}
printf("%d\n",dp[k]);
return 0;
}
//2.最长不降子序列
//如 1 2 3 -1 -2 7 9 的最长不降子序列为 1 2 3 7 9 长度为 5
//dp[i] 表示以A[i] 结尾的最长不降子序列长度
//状态方程为 dp[i] = max{1,dp[j]+1} (A[i] >= A[j] i > j);
//代码如下:
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
const int maxn = 10010;
int A[maxn],dp[maxn];
int main(){
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
scanf("%d",&A[i]);
}
int ans = -1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
dp[i] = 1;
for(int j = 1; j < i; j++){
if(A[i] >= A[j] && dp[j] + 1 > dp[i]){
dp[i] = dp[j] + 1;
}
}
ans = max(ans,dp[i]);
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
return 0;
}- 平衡二叉树
//结点的表示,需要添加一个高度变量
struct node{
int v,height;
node* lchild,*rchild;
};
//新建结点
node* newNode(int v){
node *Node = new node;
Node->height = 1;
Node->lchild = Node->rchild = null;
Node->v = v;
return Node;
}
//获取以root为根的子树的当前高度
int getHeight(node* root){
if(root == NULL) return 0;
return root->height;
}
//获取平衡因子
int getBalanceFactor(node* root){
return root->lchild->height - root->rchild->height;
}
//更新结点root的height
void updateHeight(node *root){
root->height = max(getHeight(root->lchild),getHeiht(root->rchild)) + 1;
//AVL树的查找
void search(node* root,int x){
if(root == NULL){
return ;
}
if(x == root->data){
printf("%d\n",root->data);
}else if(x > root->data){
search(root->rchild,x);
}else if(x < root->data){
search(root->lchild,x);
}
}
}
//左旋 需要改变根节点的指向 需用&root
void LeftRotation(node* &root){
node* temp = root->rchild;
root->rchild = temp->lchild;
temp->lchild = root;
updateHeight(root);
updateHeight(temp);
root = temp;
}
//右旋 需要改变根节点的指向 需用&root
void RightRotation(node* &root){
node* temp = root->lchild;
root->lchild = temp->rchild;
temp->rchild = root;
updateHeight(root);
updataHeight(temp);
root = temp;
}
//AVL树的插入操作
void insert(node* &root,int v){
if(root == NULL){
root = newNode(v);
return;
}
if(v < root->data){
insert(root->lchild,v);
updateHeight(root);
if(getBalanceFactor(root) == 2){
if(getBalanceFactor(root->lchild) == 1){
RightRotation(root); //LL
}else if(getBalanceFactor(root->lchild) == -1){
LeftRotation(root->lchild);//LR
RightRotation(root);
}
}
}else {
insert(root->rchild,v);
updateHeight(root);
if(getBalanceFactor(root) == -2){
if(getBalanceFactor(root->rchild) == -1){
LeftRotation(root);//RR
}else if(getBalanceFactor(root->rchild) == 1){
RightRotation(root->rchild);
LeftRotation(root);//RL
}
}
}
}
}
//AVL树的建立
node* create(int data[],int n){
node* root = NULL;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
insert(root,data[i]);
}
return root;
}| 树形 | 判定条件 | 调整方法 |
|---|---|---|
| LL | BF(root) = 2,BF(root->lchild) = 1 | 对root进行右旋操作 |
| LR | BF(root) = 2,BF(root->lchild) = -1 | 对root->lchild先进行左旋,再对root进行右旋 |
| RR | BF(root) = -2,BF(root->rchild) = -1 | 对root进行左旋 |
| RL | BF(root) = -2,BF(root->rchild) 1 | 先对root->rchild进行右旋,再对root进行左旋 |
- 完全二叉树的判定
int isCompleteTree(node* root){
queue<node*> q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()){
node* p = q.front();
q.pop();
if(p != NULL){
q.push(root->lchild);
q.push(root->rchild);
}else{
while(!q.empty()){
p = q.front();
if(p != NULL){
return 0;
}
}
}
}
return 1;
}- 关于n!的一个问题
//求n!中有多少个p的质因子
//计算方法:n!中有(n/p + n/p^2 + n/p^3 + ···)个质因子,也就是级数求和
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
int cal(int n,int p){
int ans = 0;
while(n){
ans += n/p;
n /= p;
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
int n,p;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&p);
printf("%d\n",cal(n,p));
return 0;
}- 质因子分解
//对于一个正整数n来说,如果它存在[2,n]范围内的质因子,要么这些质因子全部小于等于sqrt(n),要么只存在一个大于sqrt(n) 的质因子,而其余质因子全部小于等于sqrt(n).
//具体代码如下:
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 10010;
int pNum,prime[maxn];
struct factor{
int x; //质因子
int cnt;//个数
}fac[10];
bool isPrime(int n){
if(n <= 1) return false;
int sqr = (int)sqrt(1.0 * n);
for(int i = 2; i <= sqr; i++){
if(n % i == 0) return false;
}
return true;
}
void findPrime(){
for(int i = 1; i < maxn; i++){
if(isPrime(i) == true){
prime[pNum++] = i;
}
}
}
int main()
{
findPrime();
int n,num = 0;
scanf("%d",&n);
if(n == 1) printf("1=1");
else{
printf("%d=",n);
int sqr = (int)sqrt(1.0 * n);
for(int i = 0; i < pNum && prime[i] <= sqr; i++){
if(n % prime[i] == 0){
fac[num].x = prime[i];
fac[num].cnt = 0;
while(n % prime[i] == 0){
fac[num].cnt++;
n /= prime[i];
}
num++;
}
}
if(n != 1){
fac[num].x = n;
fac[num].cnt = 1;
num++;
}
for(int i = 0; i< num; i++){
if(i > 0) printf("*");
printf("%d",fac[i].x);
if(fac[i].cnt > 1){
printf("^%d",fac[i].cnt);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
//求数n的后p位
int ans = n%pow(10,p);- 优先队列
//priority_queue 默认是大顶堆
//使用时要加
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
//访问只能 访问堆顶元素
priority_queue<int> q;
q.top();
q.empty();//检测是否为空
q.size();//返回优先队列的大小
//设置优先级
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,less<int>> q;//表示大顶堆
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>> q;//表示小顶堆
//Huffman树的构造
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string.h>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1010;
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int> > q;
int main()
{
int n,temp;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
scanf("%d",&temp);
q.push(temp);
}
int ans = 0;
while(q.size() != 1){
int f1,f2,f3;
f1 = q.top();
q.pop();
f2 = q.top();
q.pop();
f3 = f1 + f2;
q.push(f3);
ans += f3;
}
printf("%d\n",ans);
return 0;
}- 根据二叉树的层序遍历序列和中序遍历序列来构建二叉树
在先序+中序中,先序的第一个结点是根结点,然后用中序区分出左右子树。到这里为止,层序+中序也是一样的,层序的第一个结点是根结点,然后用中序区分出左右子树。不同在于后面的步骤。由于先序中是按照“根结点-左子树所有结点-右子树所有结点”的顺序的,因此可直接对左子树跟右子树进行递归,但是层序不行,层序的左右子树结点在层序序列中可能是分散的。因此必须想办法把左子树所有结点跟右子树所有结点都找出来。于是可以开两个vector,一个存左子树所有结点的层序,一个存右子树所有结点的层序。然后遍历当前层序序列的所有结点,根据中序序列判断其属于左子树还是右子树,如果是左子树就push_back到左子树的vector,否则就push_back到右子树的vector.这样就可以继续递归了,递归参数中用vector表示层序,而中序可以仍然用数组下标。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 50;
struct node {
int data;
node* lchild;
node* rchild;
};
int in[maxn]; //中序
node* create(vector<int> layer,int inL,int inR){
if(layer.size() == 0){
return;
}
node* root = new node;
root->data = layer[0];
int k;
for(k = inL; k <= inR; k++){
if(in[k] == layer[0]){
break;
}
}
for(int i = 1; i < layer.size(); i++){
bool isLeft = false;
for(int j = inL; j < k; j++){
if(layer[i] == in[j]){
isLeft = true;
break;
}
}
if(isLeft){
layerLeft.push_back(layer[i]);
}else{
layerRight.push_back(layer[i]);
}
}
root->lchild = create(layerLeft,inL,k-1);
root->rchild = create(layerRight,k+1,inR);
return root;
}- 拓扑排序
//判定一个图是否是有向无环图
const int maxn = 1010;
vector<int> G[maxn],topOrder;//邻接表,拓扑序列
int inDegree[maxn] = {0}; //每个顶点的入度
int n,m;//顶点数和边数
int topologicalSort(){
int num = 0;
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>> q;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if(inDegree[i] == 0){
q.push(i);
}
}
while(!q.empty()){
int u = q.top();
topOrder.push_back(u);
q.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < G[u].size(); i++){
int v = G[u][i];
inDegree[v]--;
if(inDegree[v] == 0){
q.push(v);
}
}
G[u].clear();
num++;
}
return num;
}
//具体图的输入
//1.邻接表
vector<int> Adj[maxn];
int u,v;
scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
//有向图
Adj[u].push_back(v);
//无向图
Adj[u].push_back(v);
Adj[v].push_back(u);
inDegree[v]++;
//2.邻接矩阵
int G[maxn][maxn];
int u,v;
scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
//有向图
G[u][v] = 0;
//无向图
G[v][u] = 0;