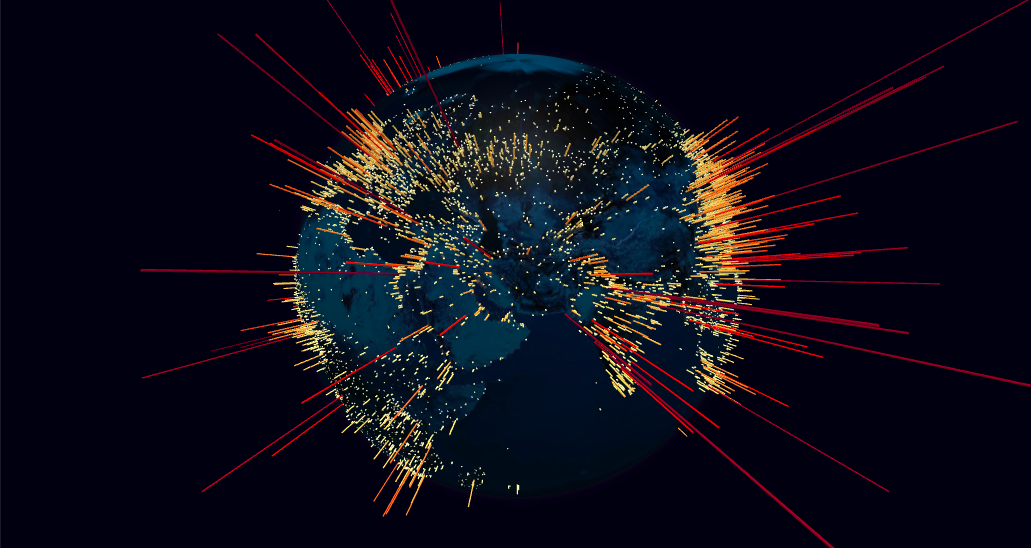
Largely inspired by WebGL Globe, this is a ThreeJS WebGL class to represent data visualization layers on a globe, using a spherical projection.
See also the standalone version.
- Basic (source)
- Arc Links (source)
- Country Polygons (source)
- Path lines (source)
- Heatmap (source)
- Hexagonal Binning (source)
- Hexed Country Polygons (source)
- Tiles (source)
- Ripple Rings (source)
- Clouds (source)
- Solar Terminator (source)
- Labels (source)
- HTML Markers (source)
- Satellites (source)
- Custom Globe Material (source)
- Custom Layer (source)
import ThreeGlobe from 'three-globe';or using a script tag
<script src="//unpkg.com/three-globe"></script>then
const myGlobe = new ThreeGlobe()
.globeImageUrl(myImageUrl)
.pointsData(myData);
const myScene = new THREE.Scene();
myScene.add(myGlobe);- Initialisation
- Globe Layer
- Points Layer
- Arcs Layer
- Polygons Layer
- Paths Layer
- Heatmaps Layer
- Hex Bin Layer
- Hexed Polygons Layer
- Tiles Layer
- Rings Layer
- Labels Layer
- HTML Elements Layer
- 3D Objects Layer
- Custom Layer
- Utility
- Render Options
new ThreeGlobe({ configOptions })| Config options | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| waitForGlobeReady: boolean | Whether to wait until the globe wrapping image has been fully loaded before rendering the globe or any of the data layers. | true |
| animateIn: boolean | Whether to animate the globe initialization, by scaling and rotating the globe into its inital position. | true |
| Method | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| globeImageUrl([url]) | Getter/setter for the URL of the image used in the material that wraps the globe. If no image is provided, the globe is represented as a black sphere. | null |
| bumpImageUrl([url]) | Getter/setter for the URL of the image used to create a bump map in the material, to represent the globe's terrain. | null |
| showGlobe([boolean]) | Getter/setter for whether to show the globe surface itself. | true |
| showGraticules([boolean]) | Getter/setter for whether to show a graticule grid demarking latitude and longitude lines at every 10 degrees. | false |
| showAtmosphere([boolean]) | Getter/setter for whether to show a bright halo surrounding the globe, representing the atmosphere. | true |
| atmosphereColor([str]) | Getter/setter for the color of the atmosphere. | lightskyblue |
| atmosphereAltitude([str]) | Getter/setter for the max altitude of the atmosphere, in terms of globe radius units. | 0.15 |
| globeMaterial([material]) | Getter/setter of the ThreeJS material used to wrap the globe. Can be used for more advanced styling of the globe, like in this example. | MeshPhongMaterial |
| onGlobeReady(fn) | Callback function to invoke immediately after the globe has been initialized and visible on the scene. | - |
| Method | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| pointsData([array]) | Getter/setter for the list of points to represent in the points map layer. Each point is displayed as a cylindrical 3D object rising perpendicularly from the surface of the globe. | [] |
| pointLat([num, str or fn]) | Point object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the cylinder's center latitude coordinate. | lat |
| pointLng([num, str or fn]) | Point object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the cylinder's center longitude coordinate. | lng |
| pointColor([str or fn]) | Point object accessor function or attribute for the cylinder color. | () => '#ffffaa' |
| pointAltitude([num, str or fn]) | Point object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the cylinder's altitude in terms of globe radius units (0 = 0 altitude (flat circle), 1 = globe radius). |
0.1 |
| pointRadius([num, str or fn]) | Point object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the cylinder's radius, in angular degrees. | 0.25 |
| pointResolution([num]) | Getter/setter for the radial geometric resolution of each cylinder, expressed in how many slice segments to divide the circumference. Higher values yield smoother cylinders. | 12 |
| pointsMerge([boolean]) | Getter/setter for whether to merge all the point meshes into a single ThreeJS object, for improved rendering performance. Visually both options are equivalent, setting this option only affects the internal organization of the ThreeJS objects. | false |
| pointsTransitionDuration([num]) | Getter/setter for duration (ms) of the transition to animate point changes involving geometry modifications. A value of 0 will move the objects immediately to their final position. New objects are animated by scaling them from the ground up. Only works if pointsMerge is disabled. |
1000 |
| Method | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| arcsData([array]) | Getter/setter for the list of links to represent in the arcs map layer. Each link is displayed as an arc line that rises from the surface of the globe, connecting the start and end coordinates. | [] |
| arcStartLat([num, str or fn]) | Arc object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the line's start latitude coordinate. | startLat |
| arcStartLng([num, str or fn]) | Arc object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the line's start longitude coordinate. | startLng |
| arcEndLat([num, str or fn]) | Arc object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the line's end latitude coordinate. | endLat |
| arcEndLng([num, str or fn]) | Arc object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the line's end longitude coordinate. | endLng |
| arcColor([str, [str, ...] or fn]) | Arc object accessor function or attribute for the line's color. Also supports color gradients by passing an array of colors, or a color interpolator function. | () => '#ffffaa' |
| arcAltitude([num, str or fn]) | Arc object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the arc's maximum altitude (ocurring at the half-way distance between the two points) in terms of globe radius units (0 = 0 altitude (ground line), 1 = globe radius). If a value of null or undefined is used, the altitude is automatically set proportionally to the distance between the two points, according to the scale set in arcAltitudeAutoScale. |
null |
| arcAltitudeAutoScale([num, str or fn]) | Arc object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the scale of the arc's automatic altitude, in terms of units of the great-arc distance between the two points. A value of 1 indicates the arc should be as high as its length on the ground. Only applicable if arcAltitude is not set. |
0.5 |
| arcStroke([num, str or fn]) | Arc object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the line's diameter, in angular degrees. A value of null or undefined will render a ThreeJS Line whose width is constant (1px) regardless of the camera distance. Otherwise, a TubeGeometry is used. |
null |
| arcCurveResolution([num]) | Getter/setter for the arc's curve resolution, expressed in how many straight line segments to divide the curve by. Higher values yield smoother curves. | 64 |
| arcCircularResolution([num]) | Getter/setter for the radial geometric resolution of each line, expressed in how many slice segments to divide the tube's circumference. Only applicable when using Tube geometries (defined arcStroke). |
6 |
| arcDashLength([num, str or fn]) | Arc object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the length of the dashed segments in the arc, in terms of relative length of the whole line (1 = full line length). |
1 |
| arcDashGap([num, str or fn]) | Arc object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the length of the gap between dash segments, in terms of relative line length. | 0 |
| arcDashInitialGap([num, str or fn]) | Arc object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the length of the initial gap before the first dash segment, in terms of relative line length. | 0 |
| arcDashAnimateTime([num, str or fn]) | Arc object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the time duration (in ms) to animate the motion of dash positions from the start to the end point for a full line length. A value of 0 disables the animation. |
0 |
| arcsTransitionDuration([num]) | Getter/setter for duration (ms) of the transition to animate arc changes involving geometry modifications. A value of 0 will move the arcs immediately to their final position. New arcs are animated by rising them from the ground up. |
1000 |
| Method | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| polygonsData([array]) | Getter/setter for the list of polygon shapes to represent in the polygons map layer. Each polygon is displayed as a shaped cone that extrudes from the surface of the globe. | [] |
| polygonGeoJsonGeometry([str or fn]) | Polygon object accessor function or attribute for the GeoJson geometry specification of the polygon's shape. The returned value should have a minimum of two fields: type and coordinates. Only GeoJson geometries of type Polygon or MultiPolygon are supported, other types will be skipped. |
geometry |
| polygonCapColor([str or fn]) | Polygon object accessor function or attribute for the color of the top surface. | () => '#ffffaa' |
| polygonCapMaterial([material, str or fn]) | Polygon object accessor function, attribute or material object for the ThreeJS material to use in the top surface. This property takes precedence over polygonCapColor, which will be ignored if both are defined. |
- |
| polygonSideColor([str or fn]) | Polygon object accessor function or attribute for the color of the cone sides. | () => '#ffffaa' |
| polygonSideMaterial([material, str or fn]) | Polygon object accessor function, attribute or material object for the ThreeJS material to use in the cone sides. This property takes precedence over polygonSideColor, which will be ignored if both are defined. |
- |
| polygonStrokeColor([str or fn]) | Polygon object accessor function or attribute for the color to stroke the polygon perimeter. A falsy value will disable the stroking. | - |
| polygonAltitude([num, str or fn]) | Polygon object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the polygon cone's altitude in terms of globe radius units (0 = 0 altitude (flat polygon), 1 = globe radius). |
0.01 |
| polygonCapCurvatureResolution([num, str or fn]) | Polygon object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the resolution (in angular degrees) of the cap surface curvature. The finer the resolution, the more the polygon is fragmented into smaller faces to approximate the spheric surface, at the cost of performance. | 5 |
| polygonsTransitionDuration([num]) | Getter/setter for duration (ms) of the transition to animate polygon altitude changes. A value of 0 will size the cone immediately to their final altitude. New polygons are animated by rising them from the ground up. |
1000 |
| Method | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| pathsData([array]) | Getter/setter for the list of lines to represent in the paths map layer. Each path is displayed as a line that connects all the coordinate pairs in the path array. | [] |
| pathPoints([array, str or fn]) | Path object accessor function, attribute or an array for the set of points that define the path line. By default, each path point is assumed to be a 2-position array ([<lat>, <lon>]). This default behavior can be modified using the pathPointLat and pathPointLng methods. |
pnts => pnts |
| pathPointLat([num, str or fn]) | Path point object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the latitude coordinate. | arr => arr[0] |
| pathPointLng([num, str or fn]) | Path point object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the longitude coordinate. | arr => arr[1] |
| pathPointAlt([num, str or fn]) | Path point object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the point altitude, in terms of globe radius units (0 = 0 altitude (ground), 1 = globe radius). |
0.001 |
| pathResolution([num]) | Getter/setter for the path's angular resolution, in lat/lng degrees. If the ground distance (excluding altitude) between two adjacent path points is larger than this value, the line segment will be interpolated in order to approximate the curvature of the sphere surface. Lower values yield more perfectly curved lines, at the cost of performance. | 2 |
| pathColor([str, [str, ...] or fn]) | Path object accessor function or attribute for the line's color. Also supports color gradients by passing an array of colors, or a color interpolator function. Transparent colors are not supported in Fat Lines with set width. | () => '#ffffaa' |
| pathStroke([num, str or fn]) | Path object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the line's diameter, in angular degrees. A value of null or undefined will render a ThreeJS Line whose width is constant (1px) regardless of the camera distance. Otherwise, a FatLine is used. |
null |
| pathDashLength([num, str or fn]) | Path object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the length of the dashed segments in the path line, in terms of relative length of the whole line (1 = full line length). |
1 |
| pathDashGap([num, str or fn]) | Path object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the length of the gap between dash segments, in terms of relative line length. | 0 |
| pathDashInitialGap([num, str or fn]) | Path object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the length of the initial gap before the first dash segment, in terms of relative line length. | 0 |
| pathDashAnimateTime([num, str or fn]) | Path object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the time duration (in ms) to animate the motion of dash positions from the start to the end point for a full line length. A value of 0 disables the animation. |
0 |
| pathTransitionDuration([num]) | Getter/setter for duration (ms) of the transition to animate path changes. A value of 0 will move the paths immediately to their final position. New paths are animated from start to end. |
1000 |
| Method | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| heatmapsData([array]) | Getter/setter for the list of heatmap datasets to represent in the heatmaps map layer. Each set of points is represented as an individual global heatmap with varying color and/or altitude, according to the point density. It uses a Gaussian KDE to perform the density estimation, based on the great-arc distance between points. | [] |
| heatmapPoints([array, str or fn]) | Heatmap object accessor function, attribute or an array for the set of points that define the heatmap. By default, each point is assumed to be a 2-position array ([<lat>, <lon>]). This default behavior can be modified using the heatmapPointLat and heatmapPointLng methods. |
pnts => pnts |
| heatmapPointLat([num, str or fn]) | Heatmap point object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the latitude coordinate. | arr => arr[0] |
| heatmapPointLng([num, str or fn]) | Heatmap point object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the longitude coordinate. | arr => arr[1] |
| heatmapPointWeight([num, str or fn]) | Heatmap point object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the weight of the point. The weight of a point determines its influence on the density of the surrounding area. | 1 |
| heatmapBandwidth([num, str or fn]) | Heatmap object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the heatmap bandwidth, in angular degrees. The bandwidth is an internal parameter of the Gaussian kernel function and defines how localized is the influence of a point on distant locations. A narrow bandwidth leads to a more spiky representation, while a broad one has smoother curves. | 4 |
| heatmapColorFn([str or fn]) | Heatmap object accessor function or attribute for the color interpolator function to represent density in the heatmap. This function should receive a number between 0 and 1 (or potentially higher if saturation > 1), and return a color string. |
Turbo colormap interpolator with fading opacity |
| heatmapColorSaturation([num, str or fn]) | Heatmap object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the color scale saturation. The saturation is a multiplier of the normalized density value ([0,1]) before passing it to the color interpolation function. It can be used to dampen outlier peaks in density and bring the data floor into view. |
1.5 |
| heatmapBaseAltitude([num, str or fn]) | Heatmap object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the heatmap base floor altitude in terms of globe radius units (0 = 0 altitude, 1 = globe radius). |
0.01 |
| heatmapTopAltitude([num, str or fn]) | Heatmap object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the heatmap top peak altitude in terms of globe radius units (0 = 0 altitude, 1 = globe radius). An equal value to the base altitude will yield a surface flat heatmap. If a top altitude is set, the variations in density will be used to define the altitude curves between base and top. |
- |
| heatmapsTransitionDuration([num]) | Getter/setter for duration (ms) of the transition to animate heatmap changes. A value of 0 will set the heatmap colors/altitudes immediately in their final position. New heatmaps are animated by rising them from the ground up and gently fading in through the color scale. |
0 |
| Method | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| hexBinPointsData([array]) | Getter/setter for the list of points to aggregate using the hex bin map layer. Each point is added to an hexagonal prism 3D object that represents all the points within a tesselated portion of the space. | [] |
| hexBinPointLat([num, str or fn]) | Point object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the latitude coordinate. | lat |
| hexBinPointLng([num, str or fn]) | Point object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the longitude coordinate. | lng |
| hexBinPointWeight([num, str or fn]) | Point object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the weight of the point. Weights for points in the same bin are summed and determine the hexagon default altitude. | 1 |
| hexBinResolution([num]) | The geographic binning resolution as defined by H3. Determines the area of the hexagons that tesselate the globe's surface. Accepts values between 0 and 15. Level 0 partitions the earth in 122 (mostly) hexagonal cells. Each subsequent level sub-divides the previous in roughly 7 hexagons. |
4 |
| hexMargin([num or fn]) | The radial margin of each hexagon. Margins above 0 will create gaps between adjacent hexagons and serve only a visual purpose, as the data points within the margin still contribute to the hexagon's data. The margin is specified in terms of fraction of the hexagon's surface diameter. Values below 0 or above 1 are disadvised. This property also supports using an accessor method based on the hexagon's aggregated data, following the syntax: hexMargin(({ points, sumWeight, center: { lat, lng }}) => ...). This method should return a numeric constant. |
0.2 |
| hexAltitude([num or fn]) | The altitude of each hexagon, in terms of globe radius units (0 = 0 altitude (flat hexagon), 1 = globe radius). This property also supports using an accessor method based on the hexagon's aggregated data, following the syntax: hexAltitude(({ points, sumWeight, center: { lat, lng }}) => ...). This method should return a numeric constant. |
({ sumWeight }) => sumWeight * 0.01 |
| hexTopCurvatureResolution([num]) | The resolution (in angular degrees) of the top surface curvature. The finer the resolution, the more the top area is fragmented into smaller faces to approximate the spheric surface, at the cost of performance. | 5 |
| hexTopColor([fn]) | Accessor method for each hexagon's top color. The method should follow the signature: hexTopColor(({ points, sumWeight, center: { lat, lng }}) => ...) and return a color string. |
() => '#ffffaa' |
| hexSideColor([fn]) | Accessor method for each hexagon's side color. The method should follow the signature: hexSideColor(({ points, sumWeight, center: { lat, lng }}) => ...) and return a color string. |
() => '#ffffaa' |
| hexBinMerge([boolean]) | Getter/setter for whether to merge all the hexagon meshes into a single ThreeJS object, for improved rendering performance. Visually both options are equivalent, setting this option only affects the internal organization of the ThreeJS objects. | false |
| hexTransitionDuration([num]) | Getter/setter for duration (ms) of the transition to animate hexagon changes related to geometry modifications (altitude, radius). A value of 0 will move the hexagons immediately to their final position. New hexagons are animated by scaling them from the ground up. Only works if hexBinMerge is disabled. |
1000 |
| Method | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| hexPolygonsData([array]) | Getter/setter for the list of polygon shapes to represent in the hexed polygons map layer. Each polygon is displayed as a tesselated group of hexagons that approximate the polygons shape according to the resolution specified in hexPolygonResolution. |
[] |
| hexPolygonGeoJsonGeometry([str or fn]) | Hexed polygon object accessor function or attribute for the GeoJson geometry specification of the polygon's shape. The returned value should have a minimum of two fields: type and coordinates. Only GeoJson geometries of type Polygon or MultiPolygon are supported, other types will be skipped. |
geometry |
| hexPolygonColor([str or fn]) | Hexed polygon object accessor function or attribute for the color of each hexagon in the polygon. | () => '#ffffaa' |
| hexPolygonAltitude([num, str or fn]) | Hexed polygon object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the polygon's hexagons altitude in terms of globe radius units (0 = 0 altitude, 1 = globe radius). |
0.001 |
| hexPolygonResolution([num, str or fn]) | Hexed polygon object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the geographic binning resolution as defined by H3. Determines the area of the hexagons that tesselate the globe's surface. Accepts values between 0 and 15. Level 0 partitions the earth in 122 (mostly) hexagonal cells. Each subsequent level sub-divides the previous in roughly 7 hexagons. |
3 |
| hexPolygonMargin([num, str or fn]) | Hexed polygon object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the radial margin of each hexagon. Margins above 0 will create gaps between adjacent hexagons within a polygon. The margin is specified in terms of fraction of the hexagon's surface diameter. Values below 0 or above 1 are disadvised. |
0.2 |
| hexPolygonUseDots([boolean, str or fn]) | Hexed polygon object accessor function, attribute or a boolean constant for whether to represent each polygon point as a circular dot instead of an hexagon. | false |
| hexPolygonCurvatureResolution([num, str or fn]) | Hexed polygon object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the resolution (in angular degrees) of each hexed polygon surface curvature. The finer the resolution, the more the polygon hexes are fragmented into smaller faces to approximate the spheric surface, at the cost of performance. | 5 |
| hexPolygonDotResolution([num, str or fn]) | Hexed polygon object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the resolution of each circular dot, expressed in how many slice segments to divide the circumference. Higher values yield smoother circles, at the cost of performance. This is only applicable in dot representation mode. | 12 |
| hexPolygonsTransitionDuration([num]) | Getter/setter for duration (ms) of the transition to animate hexed polygons altitude and margin changes. A value of 0 will move the hexagons immediately to their final state. New hexed polygons are animated by sizing each hexagon from 0 radius. |
0 |
| Method | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| tilesData([array]) | Getter/setter for the list of tiles to represent in the tiles map layer. Each tile is displayed as a spherical surface segment. The segments can be placed side-by-side for a tiled surface and each can be styled separately. | [] |
| tileLat([num, str or fn]) | Tile object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the segment's centroid latitude coordinate. | lat |
| tileLng([num, str or fn]) | Tile object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the segment's centroid longitude coordinate. | lng |
| tileAltitude([num, str or fn]) | Tile object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the segment's altitude in terms of globe radius units. | 0.01 |
| tileWidth([num, str or fn]) | Tile object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the segment's longitudinal width, in angular degrees. | 1 |
| tileHeight([num, str or fn]) | Tile object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the segment's latitudinal height, in angular degrees. | 1 |
| tileUseGlobeProjection([boolean, str or fn]) | Tile object accessor function, attribute or a boolean constant for whether to use the globe's projection to shape the segment to its relative tiled position (true), or break free from this projection and shape the segment as if it would be laying directly on the equatorial perimeter (false). |
true |
| tileMaterial([material, str or fn]) | Tile object accessor function, attribute or material object for the ThreeJS material used to style the segment's surface. | () => new MeshLambertMaterial({ color: '#ffbb88' }) |
| tileCurvatureResolution([num, str or fn]) | Tile object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the resolution (in angular degrees) of the surface curvature. The finer the resolution, the more the tile geometry is fragmented into smaller faces to approximate the spheric surface, at the cost of performance. | 5 |
| tilesTransitionDuration([num]) | Getter/setter for duration (ms) of the transition to animate tile changes involving geometry modifications. A value of 0 will move the tiles immediately to their final position. New tiles are animated by scaling them from the centroid outwards. |
1000 |
| Method | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| ringsData([array]) | Getter/setter for the list of self-propagating ripple rings to represent in the rings map layer. Each data point is displayed as an animated set of concentric circles that propagate outwards from (or inwards to) a central point through the spherical surface. | [] |
| ringLat([num, str or fn]) | Ring object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for each circle's center latitude coordinate. | lat |
| ringLng([num, str or fn]) | Ring object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for each circle's center longitude coordinate. | lng |
| ringAltitude([num, str or fn]) | Ring object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the circle's altitude in terms of globe radius units. | 0.0015 |
| ringColor([str, [str, ...] or fn]) | Ring object accessor function or attribute for the stroke color of each ring. Also supports radial color gradients by passing an array of colors, or a color interpolator function. | () => '#ffffaa' |
| ringResolution([num]) | Getter/setter for the geometric resolution of each circle, expressed in how many slice segments to divide the circumference. Higher values yield smoother circles. | 64 |
| ringMaxRadius([num, str or fn]) | Ring object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the maximum outer radius of the circles, at which the rings stop propagating and are removed. Defined in angular degrees. | 2 |
| ringPropagationSpeed([num, str or fn]) | Ring object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the propagation velocity of the rings, defined in degrees/second. Setting a negative value will invert the direction and cause the rings to propagate inwards from the maxRadius. |
1 |
| ringRepeatPeriod([num, str or fn]) | Ring object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the interval of time (in ms) to wait between consecutive auto-generated concentric circles. A value less or equal than 0 will disable the repetition and emit a single ring. |
700 |
| Method | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| labelsData([array]) | Getter/setter for the list of label objects to represent in the labels map layer. | [] |
| labelLat([num, str or fn]) | Label object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the latitude coordinate. | lat |
| labelLng([num, str or fn]) | Label object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the longitude coordinate. | lng |
| labelText([str or fn]) | Label object accessor function or attribute for the label text. | text |
| labelColor([str or fn]) | Label object accessor function or attribute for the label color. | () => 'lightgrey' |
| labelAltitude([num, str or fn]) | Label object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the label altitude in terms of globe radius units. | 0 |
| labelSize([num, str or fn]) | Label object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the label text height, in angular degrees. | 0.5 |
| labelTypeFace([typeface ]) | Getter/setter for the text font typeface JSON object. Supports any typeface font generated by Facetype.js. | helvetiker regular |
| labelRotation([num, str or fn]) | Label object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the label rotation in degrees. The rotation is performed clockwise along the axis of its latitude parallel plane. | 0 |
| labelResolution([num]) | Getter/setter for the text geometric resolution of each label, expressed in how many segments to use in the text curves. Higher values yield smoother labels. | 3 |
| labelIncludeDot([boolean, str or fn]) | Label object accessor function, attribute or a boolean constant for whether to include a dot marker next to the text indicating the exact lat, lng coordinates of the label. If enabled the text will be rendered offset from the dot. |
true |
| labelDotRadius([num, str or fn]) | Label object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the radius of the dot marker, in angular degrees. | 0.1 |
| labelDotOrientation([str or fn]) | Label object accessor function or attribute for the orientation of the label if the dot marker is present. Possible values are right, top and bottom. |
() => 'bottom' |
| labelsTransitionDuration([num]) | Getter/setter for duration (ms) of the transition to animate label changes involving position modifications (lat, lng, altitude, rotation). A value of 0 will move the labels immediately to their final position. New labels are animated by scaling their size. |
1000 |
| Method | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| htmlElementsData([array]) | Getter/setter for the list of objects to represent in the HTML elements map layer. Each HTML element is rendered using ThreeJS CSS2DRenderer. | [] |
| htmlLat([num, str or fn]) | HTML element accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the latitude coordinate of the element's central position. | lat |
| htmlLng([num, str or fn]) | HTML element accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the longitude coordinate of the element's central position. | lng |
| htmlAltitude([num, str or fn]) | HTML element accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the altitude coordinate of the element's position, in terms of globe radius units. | 0 |
| htmlElement([str or fn]) | Accessor function or attribute to retrieve the DOM element to use. Should return an instance of HTMLElement. | null |
| htmlTransitionDuration([num]) | Getter/setter for duration (ms) of the transition to animate HTML elements position changes. A value of 0 will move the elements immediately to their final position. |
1000 |
| Method | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| objectsData([array]) | Getter/setter for the list of custom 3D objects to represent in the objects layer. Each object is rendered according to the objectThreeObject method. |
[] |
| objectLat([num, str or fn]) | Object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the latitude coordinate of the object's position. | lat |
| objectLng([num, str or fn]) | Object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the longitude coordinate of the object's position. | lng |
| objectAltitude([num, str or fn]) | Object accessor function, attribute or a numeric constant for the altitude coordinate of the object's position, in terms of globe radius units. | 0.01 |
| objectRotation([{[x], [y], [z]}, str or fn]) | Object accessor function, attribute or a {x, y, z} object for the object's rotation (in degrees). Each dimension is optional, allowing for rotation only in some axes. Rotation is applied in the order X->Y->Z. |
- |
| objectFacesSurface([boolean, str or fn]) | Object accessor function, attribute or a boolean constant for whether the object should be rotated to face (away from) the globe surface (true), or be left in its original universe orientation (false). |
true |
| objectThreeObject([Object3d, str or fn]) | Object accessor function or attribute for defining a custom 3d object to render as part of the objects map layer. Should return an instance of ThreeJS Object3d. | A yellow sphere |
| Method | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| customLayerData([array]) | Getter/setter for the list of items to represent in the custom map layer. Each item is rendered according to the customThreeObject method. |
[] |
| customThreeObject([Object3d, str or fn]) | Object accessor function or attribute for generating a custom 3d object to render as part of the custom map layer. Should return an instance of ThreeJS Object3d. | null |
| customThreeObjectUpdate([str or fn]) | Object accessor function or attribute for updating an existing custom 3d object with new data. This can be used for performance improvement on data updates as the objects don't need to be removed and recreated at each update. The callback method's signature includes the object to be update and its new data: customThreeObjectUpdate((obj, objData) => { ... }). |
null |
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| getGlobeRadius() | Returns the cartesian distance of a globe radius in absolute spatial units. |
| getCoords(lat, lng [,altitude]) | Utility method to translate spherical coordinates. Given a pair of latitude/longitude coordinates and optionally altitude (in terms of globe radius units), returns the equivalent {x, y, z} cartesian spatial coordinates. |
| toGeoCoords({ x, y, z }) | Utility method to translate cartesian coordinates to the geographic domain. Given a set of 3D cartesian coordinates {x, y, z}, returns the equivalent {lat, lng, altitude} spherical coordinates. Altitude is defined in terms of globe radius units. |
| Method | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| rendererSize(Vector2) | It's recommended to inject the current renderer size to ensure the object proportions remain constant. This is specially necessary when using path FatLines. | Fallback to the full browser window size (THREE.Vector2(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight)) |
| pauseAnimation() | Pauses the animation on all globe layers. | |
| resumeAnimation() | Resumes the animation on all globe layers. |